-
-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 9.2k
add solution 0952 #132
New issue
Have a question about this project? Sign up for a free GitHub account to open an issue and contact its maintainers and the community.
By clicking “Sign up for GitHub”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy statement. We’ll occasionally send you account related emails.
Already on GitHub? Sign in to your account
add solution 0952 #132
Changes from 1 commit
0cdcf0f
37e669f
eb0794d
d8117b5
7cb9d46
725b587
9896e55
46c9982
File filter
Filter by extension
Conversations
Jump to
Diff view
Diff view
- Loading branch information
There are no files selected for viewing
| Original file line number | Diff line number | Diff line change |
|---|---|---|
| @@ -0,0 +1,224 @@ | ||
| # 952.按公因数计算最大组件大小 | ||
|
|
||
| ## 题目描述 | ||
|
|
||
| 给定一个由不同正整数的组成的非空数组 `A`,考虑下面的图: | ||
|
|
||
| - 有 `A.length` 个节点,按从 `A[0]` 到 `A[A.length - 1]` 标记; | ||
| - 只有当 `A[i]` 和 `A[j]` 共用一个大于 1 的公因数时,`A[i]` 和 `A[j]` 之间才有一条边。 | ||
|
|
||
| 返回图中最大连通组件的大小。 | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| **示例 2:** | ||
|
|
||
| 输入:[4,6,15,35] | ||
| 输出:4 | ||
|
|
||
| 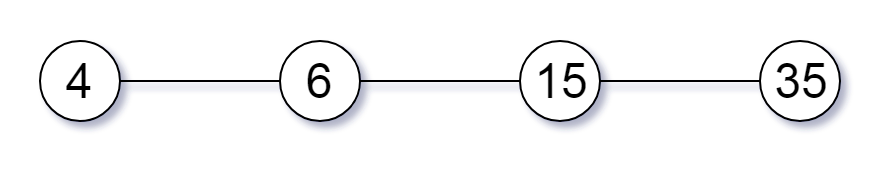 | ||
|
|
||
| **提示:** | ||
|
|
||
| 1. `1 <= A.length <= 20000` | ||
| 2. `1 <= A[i] <= 100000` | ||
|
|
||
| ## 解法 | ||
|
|
||
| ### Naive 版本 | ||
|
|
||
| 这道题涉及到画连线,应当涉及到 union-find。初步解法是: | ||
|
|
||
| * 使用数组,初始化各节点的 root 为自身,并且维护各节点 root 所连通的图的节点数量(size)为 1 | ||
| * 遍历数组中的每一个数,如果和其他数有大于 1 的公因数,则用 union 方法将他们连在一起 | ||
| * 在 union 的过程中,由于 union 的对象为各节点的根,因此需要使用 find 方法,并且缩短所涉及的节点和其根(root)的搜索距离,即将该节点与 root 直接连在一起。同时更新 size 数组的对应值 | ||
| * 在遍历结束后,遍历 size 数组,找到 size 最大的。 | ||
|
|
||
| ```java | ||
| class Solution { | ||
| public int largestComponentSize(int[] A) { | ||
| int n = A.length; | ||
| int[] root = new int[n]; | ||
| int[] size = new int[n]; | ||
| // 初始化 root 和 size array | ||
| for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { | ||
| root[i] = i; | ||
| size[i] = 1; | ||
| } | ||
| for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { | ||
| for (int j = i + 1; j < n; j++) { | ||
| if (!isCoprime(A[i], A[j])) { | ||
| union(size, root, i, j); | ||
| } | ||
| } | ||
| } | ||
| int max = 0; | ||
| for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { | ||
| max = Math.max(size[i], max); | ||
| } | ||
| return max; | ||
| } | ||
|
|
||
| public void union(int[] size, int[] root, int i, int j) { | ||
| int rootI = find(root, i); | ||
| int rootJ = find(root, j); | ||
| if (rootI == rootJ) { | ||
| // 它们已经属于同一个 root | ||
| return; | ||
| } | ||
| // 决定两个节点如何连接和 size 的更新 | ||
| if (size[rootI] > size[rootJ]) { | ||
| root[rootJ] = rootI; | ||
| size[rootI] += size[rootJ]; | ||
| } else { | ||
| root[rootI] = rootJ; | ||
| size[rootJ] += size[rootI]; | ||
| } | ||
| } | ||
|
|
||
| public int find(int[] root, int i) { | ||
| // 当某节点的根不是他自己时,则需要继续找到其 root | ||
| List<Integer> records = new LinkedList<>(); | ||
| while (root[i] != i) { | ||
| records.add(i); | ||
| i = root[i]; | ||
| } | ||
| // 将这些节点均指向其 root | ||
| for (Integer record: records) { | ||
| root[record] = i; | ||
| } | ||
|
|
||
| return i; | ||
| } | ||
|
|
||
| public boolean isCoprime(int x, int y) { | ||
| // 检查 x,y 是否互质 | ||
| if (x == 1 || y == 1) { | ||
| return true; | ||
| } | ||
| while (true) { | ||
| int temp = x % y; | ||
| if (temp == 0) { | ||
| if (y == 1) { | ||
| return true; | ||
| } | ||
| return false; | ||
| } | ||
| x = y; | ||
| y = temp; | ||
| } | ||
| } | ||
| } | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| 但是这个代码其实会超时,因为中间的遍历逻辑会耗费很长的时间,时间复杂度为 O(n^2)。因此我们需要更快一点的解法。 | ||
|
||
|
|
||
| ### 优化版本 | ||
|
|
||
| 由于连通节点的条件是两个节点有公因数,那么他们可以通过这个公因数连在一起,而这个公因数又可以被分解为质因数,这样,我们只需要知道一个节点的质因数有哪些,并且将这些质因数和该节点相连。则对于每一个节点,我们都连接的是其质因数,或者说是质因数所对应的节点,但是本质上我们把这些有相同质因数的节点都连在了一起。具体步骤为: | ||
|
|
||
| * 维护 prime set,找到 100000 以内所有质数(找质数的方法应该都会吧) | ||
| * 维护三个数组,分别为: | ||
| * 各节点所连接的 root 编号,初始化为节点本身的编号 | ||
| * 各节点为 root 时,连通图的 size,初始化为 1 | ||
| * 各质数所连接到的节点对应的 root 的编号,初始化为 -1(因为开始时这些质数都没有和节点连在一起) | ||
| * 遍历节点,其中遍历所有质数,如果节点可以整除质数,则将该质数所连通的节点(如果有的话)和当前节点连在一起;并且更新该质数连通 到 新的连通图的 root 的编号。同时更新 root 对应的 size | ||
| * 遍历 size 数组,找到值最大的集合 | ||
|
|
||
| 而题中给定了节点大小小于 100000,因此我们只需要找到 100000 里面的所有质数,并遍历节点将其连接到可以整除该节点的质数上,就等于是完成了有公因数之间的节点的连通。而根据我们上面的推算,遍历每个节点的所有质数时间复杂度是确定的为 O(np),p 为 100000 以内质数数量,即为 O(n),而 union-find 方法的每一个步骤 amortized 复杂度为 O(log*n),一个远小于 log n 的值。因此,我们通过优化了寻找连通边的方法,来达到优化算法的目的。 | ||
|
|
||
| ```java | ||
| class Solution { | ||
| public int largestComponentSize(int[] A) { | ||
| int n = A.length, num = 100000 + 1, max = 0; | ||
| Set<Integer> primes = findPrime(num); | ||
| int[] root = new int[n]; | ||
| int[] size = new int[n]; | ||
| int[] primeToNode = new int[num]; | ||
| // 一开始 prime 没有和数组 A 中的 node 连在一起 | ||
| Arrays.fill(primeToNode, -1); | ||
| // 初始化 root 和 size array | ||
| for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { | ||
| root[i] = i; | ||
| size[i] = 1; | ||
| } | ||
| for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { | ||
| int curr = A[i]; | ||
| // find all of its prime factors | ||
| for (Integer prime: primes) { | ||
| if (primes.contains(curr)) { | ||
| prime = curr; | ||
| } | ||
| if (curr % prime == 0) { | ||
| // 我们为 curr 找到一个质因数,则需要将该节点加入该 prime 已经连接到的根节点上 | ||
| if (primeToNode[prime] != -1) { | ||
| // 该 prime 已经与数组 A 中 node 相连 | ||
| union(size, root, primeToNode[prime], i); | ||
| } | ||
| primeToNode[prime] = find(root, i); | ||
| while (curr % prime == 0) { | ||
| // 将质因数 prime 全部剔除 | ||
| curr = curr / prime; | ||
| } | ||
| } | ||
| if (curr == 1) { | ||
| break; | ||
| } | ||
| } | ||
| } | ||
| for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { | ||
| max = Math.max(size[i], max); | ||
| } | ||
| return max; | ||
| } | ||
|
|
||
| public Set<Integer> findPrime(int num) { | ||
| boolean[] isPrime = new boolean[num]; | ||
| Arrays.fill(isPrime, true); | ||
| Set<Integer> primes = new HashSet<>(); | ||
| for (int i = 2; i < isPrime.length; i++) { | ||
| if (isPrime[i]) { | ||
| primes.add(i); | ||
| for (int j = 0; i * j < isPrime.length; j++) { | ||
| isPrime[i * j] = false; | ||
| } | ||
| } | ||
| } | ||
| return primes; | ||
| } | ||
|
|
||
| public void union(int[] size, int[] root, int i, int j) { | ||
| int rootI = find(root, i); | ||
| int rootJ = find(root, j); | ||
| if (rootI == rootJ) { | ||
| // 它们已经属于同一个 root | ||
| return; | ||
| } | ||
| if (size[rootI] > size[rootJ]) { | ||
| root[rootJ] = rootI; | ||
| size[rootI] += size[rootJ]; | ||
| } else { | ||
| root[rootI] = rootJ; | ||
| size[rootJ] += size[rootI]; | ||
| } | ||
| } | ||
|
|
||
| public int find(int[] root, int i) { | ||
| // 当某节点的根不是他自己时,则需要继续找到其 root | ||
| List<Integer> records = new LinkedList<>(); | ||
| while (root[i] != i) { | ||
| records.add(i); | ||
| i = root[i]; | ||
| } | ||
| // 将这些节点均指向其 root | ||
| for (Integer record: records) { | ||
| root[record] = i; | ||
| } | ||
|
|
||
| return i; | ||
| } | ||
| } | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Original file line number | Diff line number | Diff line change |
|---|---|---|
| @@ -0,0 +1,90 @@ | ||
| class Solution { | ||
| public int largestComponentSize(int[] A) { | ||
| int n = A.length, num = 100000 + 1, max = 0; | ||
| Set<Integer> primes = findPrime(num); | ||
| int[] root = new int[n]; | ||
| int[] size = new int[n]; | ||
| int[] primeToNode = new int[num]; | ||
| // 一开始 prime 没有和数组 A 中的 node 连在一起 | ||
| Arrays.fill(primeToNode, -1); | ||
| // 初始化 root 和 size array | ||
| for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { | ||
| root[i] = i; | ||
| size[i] = 1; | ||
| } | ||
| for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { | ||
| int curr = A[i]; | ||
| // find all of its prime factors | ||
| for (Integer prime: primes) { | ||
| if (primes.contains(curr)) { | ||
| prime = curr; | ||
| } | ||
| if (curr % prime == 0) { | ||
| // 我们为 curr 找到一个质因数,则需要将该节点加入该 prime 已经连接到的根节点上 | ||
| if (primeToNode[prime] != -1) { | ||
| // 该 prime 已经与数组 A 中 node 相连 | ||
| union(size, root, primeToNode[prime], i); | ||
| } | ||
| primeToNode[prime] = find(root, i); | ||
| while (curr % prime == 0) { | ||
| // 将质因数 prime 全部剔除 | ||
| curr = curr / prime; | ||
| } | ||
| } | ||
| if (curr == 1) { | ||
| break; | ||
| } | ||
| } | ||
| } | ||
| for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { | ||
| max = Math.max(size[i], max); | ||
| } | ||
| return max; | ||
| } | ||
|
|
||
| public Set<Integer> findPrime(int num) { | ||
| boolean[] isPrime = new boolean[num]; | ||
| Arrays.fill(isPrime, true); | ||
| Set<Integer> primes = new HashSet<>(); | ||
| for (int i = 2; i < isPrime.length; i++) { | ||
| if (isPrime[i]) { | ||
| primes.add(i); | ||
| for (int j = 0; i * j < isPrime.length; j++) { | ||
| isPrime[i * j] = false; | ||
| } | ||
| } | ||
| } | ||
| return primes; | ||
| } | ||
|
|
||
| public void union(int[] size, int[] root, int i, int j) { | ||
| int rootI = find(root, i); | ||
| int rootJ = find(root, j); | ||
| if (rootI == rootJ) { | ||
| // 它们已经属于同一个 root | ||
| return; | ||
| } | ||
| if (size[rootI] > size[rootJ]) { | ||
| root[rootJ] = rootI; | ||
| size[rootI] += size[rootJ]; | ||
| } else { | ||
| root[rootI] = rootJ; | ||
| size[rootJ] += size[rootI]; | ||
| } | ||
| } | ||
|
|
||
| public int find(int[] root, int i) { | ||
| // 当某节点的根不是他自己时,则需要继续找到其 root | ||
| List<Integer> records = new LinkedList<>(); | ||
| while (root[i] != i) { | ||
| records.add(i); | ||
| i = root[i]; | ||
| } | ||
| // 将这些节点均指向其 root | ||
| for (Integer record: records) { | ||
| root[record] = i; | ||
| } | ||
|
|
||
| return i; | ||
| } | ||
| } |