-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 1
Add redis api #5
New issue
Have a question about this project? Sign up for a free GitHub account to open an issue and contact its maintainers and the community.
By clicking “Sign up for GitHub”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy statement. We’ll occasionally send you account related emails.
Already on GitHub? Sign in to your account
Merged
Changes from all commits
Commits
File filter
Filter by extension
Conversations
Failed to load comments.
Loading
Jump to
Jump to file
Failed to load files.
Loading
Diff view
Diff view
There are no files selected for viewing
123 changes: 123 additions & 0 deletions
redis_api/README.md
This file contains hidden or bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| Original file line number | Diff line number | Diff line change |
|---|---|---|
| @@ -0,0 +1,123 @@ | ||
| # Create Scalable Async API using REDIS | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| - This repo contains a simplified version of this [blog](https://medium.com/analytics-vidhya/deploy-machine-learning-models-with-keras-fastapi-redis-and-docker-4940df614ece) post and [code repo](https://github.com/shanesoh/deploy-ml-fastapi-redis-docker) | ||
|
|
||
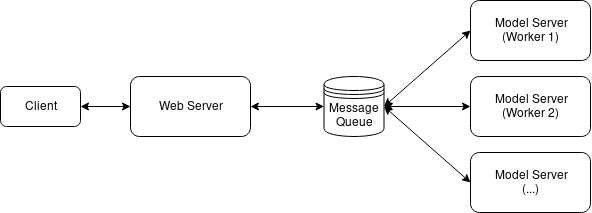
| ## Architecture | ||
|
|
||
|  | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| This repo has three main file: | ||
|
|
||
| - `model_server.py` - contains the dummy classifier | ||
| - In actual application replace the dummy model with the original one. | ||
| - `web_server.py` - contains the `/predict` api using FastAPI | ||
| - `locustfile.py` - script for load testing | ||
|
|
||
| ---- | ||
|
|
||
| ## :star: Package dependencies: | ||
|
|
||
| - `redis` | ||
| - `locust` | ||
| - `fastapi` | ||
| - `uvicorn` | ||
| - ... | ||
|
|
||
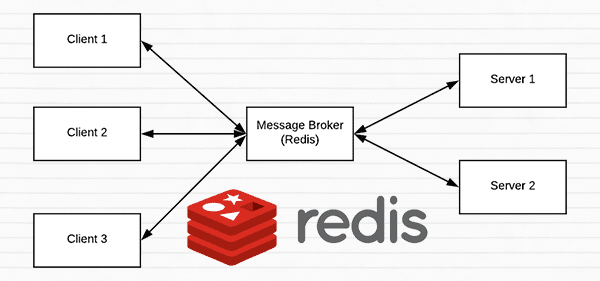
| ## :star: How to setup Redis: | ||
|
|
||
|  | ||
|
|
||
| - Follow [this](https://www.pyimagesearch.com/2018/01/29/scalable-keras-deep-learning-rest-api/) article | ||
|
|
||
| **Installation:** | ||
|
|
||
| ```py | ||
| $ wget http://download.redis.io/redis-stable.tar.gz | ||
| $ tar xvzf redis-stable.tar.gz | ||
| $ cd redis-stable | ||
| $ make | ||
| $ sudo make install | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| **To start the Redis server, use the following command:** | ||
|
|
||
| ```py | ||
| $ cd redis-stable | ||
| $ src/redis-server | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| ## :star: Start model_server.py | ||
|
|
||
| ```py | ||
| python model_server.py | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| ## :star: Start web_server.py | ||
|
|
||
| ```py | ||
| uvicorn web_server:app --reload --port 8032 --host 0.0.0.0 | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| <center> | ||
| <img src="assets/web_server.png" width="600" alt="image"> | ||
| </center> | ||
|
|
||
| ---- | ||
|
|
||
| ## :star: Load testing | ||
|
|
||
| ```py | ||
| locust -f locustfile.py | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| <center> | ||
| <img src="assets/locust_1.png" width="600" alt="image"> | ||
| </center> | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| <center> | ||
| <img src="assets/locust_2.png" width="600" alt="image"> | ||
| </center> | ||
|
|
||
| **Reference:** | ||
|
|
||
| - [Serve a machine learning model using Sklearn, FastAPI and Docker](https://medium.com/analytics-vidhya/serve-a-machine-learning-model-using-sklearn-fastapi-and-docker-85aabf96729b) | ||
| - [Deploy Machine Learning Models with Keras, FastAPI, Redis and Docker](https://medium.com/analytics-vidhya/deploy-machine-learning-models-with-keras-fastapi-redis-and-docker-4940df614ece) | ||
| - [A scalable Keras + deep learning REST API](https://www.pyimagesearch.com/2018/01/29/scalable-keras-deep-learning-rest-api/) | ||
|
|
||
| ---- | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| # :dart: Multiple model syndrome | ||
|
|
||
| Quoting from [this](https://www.pyimagesearch.com/2018/01/29/scalable-keras-deep-learning-rest-api/) blog: | ||
|
|
||
| Depending on how you deploy your REST API, there is a subtle problem with keeping the `classify_process()` function in the same file as the rest of our web API code i.e `/predict`. | ||
|
|
||
| Most web servers, including Apache and nginx, allow for multiple client threads. | ||
|
|
||
| If you keep `classify_process()` in the same file as your `/predict` | ||
| view, then you may load multiple models if your server software deems it necessary to create a new thread to serve the incoming client requests — for every new thread, a new view will be created, and therefore a new model will be loaded. | ||
|
|
||
| The solution is to move `classify_process()` | ||
| to an entirely separate process and then start it along with your `FastAPI` web server and `Redis` server. | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| - This repository implements the above strategy. | ||
|
|
||
| ---- | ||
|
|
||
| ## ToDO: | ||
|
|
||
| - [ ] implement `docker` version | ||
| - [x] Set up `locust` for load testing | ||
|
|
||
| ---- | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
Binary file added
redis_api/assets/locust_1.png
Binary file added
redis_api/assets/locust_2.png
Binary file added
redis_api/assets/web_server.png
35 changes: 35 additions & 0 deletions
redis_api/locustfile.py
This file contains hidden or bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| Original file line number | Diff line number | Diff line change |
|---|---|---|
| @@ -0,0 +1,35 @@ | ||
| from locust import HttpUser, task, between | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| # class UserBehavior(TaskSet): | ||
| # @task | ||
| # def predict(self): | ||
| # self.client.post('/predict', files={'input_text': "i love you"}) | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| # class WebsiteUser(HttpUser): | ||
| # task_set = UserBehavior | ||
| # min_wait = 500 | ||
| # max_wait = 5000 | ||
|
|
||
| class WebsiteUser(HttpUser): | ||
| wait_time = between(500, 5000) | ||
|
|
||
| def on_start(self): | ||
| """ on_start is called when a Locust start before any task is scheduled """ | ||
| pass | ||
|
|
||
| def on_stop(self): | ||
| """ on_stop is called when the TaskSet is stopping """ | ||
| pass | ||
|
|
||
| @task(1) | ||
| def predict(self): | ||
| self.client.post("/predict", json={"input": [{"input_text": "love you"}]}) | ||
|
|
||
| @task(2) | ||
| def hello_world(self): | ||
| self.client.get("http://0.0.0.0:8032") | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
60 changes: 60 additions & 0 deletions
redis_api/model_server.py
This file contains hidden or bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| Original file line number | Diff line number | Diff line change |
|---|---|---|
| @@ -0,0 +1,60 @@ | ||
| import redis | ||
| import os | ||
| import time | ||
| import json | ||
| import numpy as np | ||
|
|
||
| # Connect to Redis server | ||
| REDIS_HOST="localhost" #os.environ.get("REDIS_HOST") | ||
| db = redis.StrictRedis(host=REDIS_HOST) | ||
|
|
||
| IMAGE_QUEUE="image_queue"# os.environ.get("IMAGE_QUEUE") | ||
|
|
||
| SERVER_SLEEP = 0.25 # Time in ms between each poll by model server against Redis # os.environ.get("SERVER_SLEEP") | ||
| BATCH_SIZE = 32 | ||
|
|
||
| def get_prediction(batch:list): | ||
| n = len(batch) | ||
| return list(np.random.rand(n)) | ||
|
|
||
| def classify_process(): | ||
| # Continually poll for new images to classify | ||
| while True: | ||
| # Pop off multiple images from Redis queue atomically | ||
| with db.pipeline() as pipe: | ||
| pipe.lrange(IMAGE_QUEUE, 0, BATCH_SIZE - 1) | ||
| pipe.ltrim(IMAGE_QUEUE, BATCH_SIZE, -1) | ||
| queue, _ = pipe.execute() | ||
|
|
||
| imageIDs = [] | ||
| batch = [] | ||
| for q in queue: | ||
| # Deserialize the object and obtain the input image | ||
| q = json.loads(q.decode("utf-8")) | ||
|
|
||
| # Update the list with inputs | ||
| batch.append(q["input_text"]) | ||
|
|
||
| # Update the list of image IDs | ||
| imageIDs.append(q["id"]) | ||
|
|
||
| # Check to see if we need to process the batch | ||
| if len(imageIDs) > 0: | ||
| # Classify the batch | ||
| print(">> Batch size: {}".format(len(batch))) | ||
| print(f"\t input: {batch}") | ||
| preds = get_prediction(batch) # return list | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| # Loop over the image IDs and their corresponding set of results from our model | ||
| for (imageID, resultSet) in zip(imageIDs, preds): | ||
| # Initialize the list of output predictions | ||
|
|
||
| # Store the output predictions in the database, using image ID as the key so we can fetch the results | ||
| db.set(imageID, json.dumps(resultSet)) | ||
|
|
||
| # Sleep for a small amount | ||
| time.sleep(float(SERVER_SLEEP)) | ||
|
|
||
| if __name__ == "__main__": | ||
| classify_process() |
79 changes: 79 additions & 0 deletions
redis_api/web_server.py
This file contains hidden or bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| Original file line number | Diff line number | Diff line change |
|---|---|---|
| @@ -0,0 +1,79 @@ | ||
| import json | ||
| import os | ||
| import time | ||
| import uuid | ||
|
|
||
| import redis | ||
|
|
||
| from fastapi import FastAPI, File, HTTPException, Body | ||
| from starlette.requests import Request | ||
| from pydantic import BaseModel | ||
| from typing import List, Dict | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| # Connect to Redis server | ||
| REDIS_HOST="localhost" #os.environ.get("REDIS_HOST") | ||
| db = redis.StrictRedis(host=REDIS_HOST) | ||
|
|
||
| app = FastAPI() | ||
|
|
||
| CLIENT_SLEEP=0.25 # Time in ms between each poll by web server against Redis | ||
| CLIENT_MAX_TRIES=100 | ||
|
|
||
| IMAGE_QUEUE="image_queue"# os.environ.get("IMAGE_QUEUE") | ||
|
|
||
| class PredictionInput(BaseModel): | ||
| input: List | ||
|
|
||
| @app.get("/") | ||
| def index(): | ||
| return "Hello World!" | ||
|
|
||
| @app.post("/predict") | ||
| def predict(request: Request, body: PredictionInput = Body( | ||
| ..., | ||
| example={ | ||
| "input": [{"input_text":"winter is coming"}] | ||
| }, | ||
| )): | ||
| data = {"success": False} | ||
|
|
||
| if request.method == "POST": | ||
|
|
||
| content = body.input | ||
| print(content) | ||
|
|
||
| # Generate an ID for the classification then add the classification ID + image to the queue | ||
| k = str(uuid.uuid4()) | ||
| d = {"id": k, "input_text": content[0]['input_text']} | ||
| db.rpush(IMAGE_QUEUE, json.dumps(d)) | ||
|
|
||
| # Keep looping for CLIENT_MAX_TRIES times | ||
| num_tries = 0 | ||
|
|
||
| while num_tries < CLIENT_MAX_TRIES: | ||
| num_tries += 1 | ||
|
|
||
| # Attempt to grab the output predictions | ||
| output = db.get(k) | ||
|
|
||
| # Check to see if our model has classified the input image | ||
| if output is not None: | ||
| # Add the output predictions to our data dictionary so we can return it to the client | ||
| output = output.decode("utf-8") | ||
| data["predictions"] = json.loads(output) | ||
|
|
||
| # Delete the result from the database and break from the polling loop | ||
| db.delete(k) | ||
| break | ||
|
|
||
| # Sleep for a small amount to give the model a chance to classify the input image | ||
| time.sleep(CLIENT_SLEEP) | ||
|
|
||
| # Indicate that the request was a success | ||
| data["success"] = True | ||
|
|
||
| else: | ||
| raise HTTPException(status_code=400, detail="Request failed after {} tries".format(CLIENT_MAX_TRIES)) | ||
|
|
||
| return data |
Add this suggestion to a batch that can be applied as a single commit.
This suggestion is invalid because no changes were made to the code.
Suggestions cannot be applied while the pull request is closed.
Suggestions cannot be applied while viewing a subset of changes.
Only one suggestion per line can be applied in a batch.
Add this suggestion to a batch that can be applied as a single commit.
Applying suggestions on deleted lines is not supported.
You must change the existing code in this line in order to create a valid suggestion.
Outdated suggestions cannot be applied.
This suggestion has been applied or marked resolved.
Suggestions cannot be applied from pending reviews.
Suggestions cannot be applied on multi-line comments.
Suggestions cannot be applied while the pull request is queued to merge.
Suggestion cannot be applied right now. Please check back later.