-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 93
Added tasks 623, 628, 629, 630, 632 #244
New issue
Have a question about this project? Sign up for a free GitHub account to open an issue and contact its maintainers and the community.
By clicking “Sign up for GitHub”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy statement. We’ll occasionally send you account related emails.
Already on GitHub? Sign in to your account
Merged
Merged
Changes from all commits
Commits
Show all changes
3 commits
Select commit
Hold shift + click to select a range
File filter
Filter by extension
Conversations
Failed to load comments.
Loading
Jump to
Jump to file
Failed to load files.
Loading
Diff view
Diff view
There are no files selected for viewing
35 changes: 35 additions & 0 deletions
src/main/java/g0601_0700/s0623_add_one_row_to_tree/Solution.java
This file contains hidden or bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| Original file line number | Diff line number | Diff line change |
|---|---|---|
| @@ -0,0 +1,35 @@ | ||
| package g0601_0700.s0623_add_one_row_to_tree; | ||
|
|
||
| // #Medium #Depth_First_Search #Breadth_First_Search #Tree #Binary_Tree | ||
|
|
||
| import com_github_leetcode.TreeNode; | ||
|
There was a problem hiding this comment. Choose a reason for hiding this commentThe reason will be displayed to describe this comment to others. Learn more. Please add tags |
||
|
|
||
| public class Solution { | ||
| public TreeNode addOneRow(TreeNode root, int val, int depth) { | ||
| if (depth == 1) { | ||
| TreeNode newRoot = new TreeNode(val); | ||
| newRoot.left = root; | ||
| return newRoot; | ||
| } | ||
| dfs(root, depth - 2, val); | ||
| return root; | ||
| } | ||
|
|
||
| private void dfs(TreeNode node, int depth, int val) { | ||
| if (depth == 0) { | ||
| TreeNode left = new TreeNode(val); | ||
| TreeNode right = new TreeNode(val); | ||
| left.left = node.left; | ||
| right.right = node.right; | ||
| node.left = left; | ||
| node.right = right; | ||
| } else { | ||
| if (node.left != null) { | ||
| dfs(node.left, depth - 1, val); | ||
| } | ||
| if (node.right != null) { | ||
| dfs(node.right, depth - 1, val); | ||
| } | ||
| } | ||
| } | ||
| } | ||
38 changes: 38 additions & 0 deletions
src/main/java/g0601_0700/s0623_add_one_row_to_tree/readme.md
This file contains hidden or bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| Original file line number | Diff line number | Diff line change |
|---|---|---|
| @@ -0,0 +1,38 @@ | ||
| 623\. Add One Row to Tree | ||
|
|
||
| Medium | ||
|
|
||
| Given the `root` of a binary tree and two integers `val` and `depth`, add a row of nodes with value `val` at the given depth `depth`. | ||
|
|
||
| Note that the `root` node is at depth `1`. | ||
|
|
||
| The adding rule is: | ||
|
|
||
| * Given the integer `depth`, for each not null tree node `cur` at the depth `depth - 1`, create two tree nodes with value `val` as `cur`'s left subtree root and right subtree root. | ||
| * `cur`'s original left subtree should be the left subtree of the new left subtree root. | ||
| * `cur`'s original right subtree should be the right subtree of the new right subtree root. | ||
| * If `depth == 1` that means there is no depth `depth - 1` at all, then create a tree node with value `val` as the new root of the whole original tree, and the original tree is the new root's left subtree. | ||
|
|
||
| **Example 1:** | ||
|
|
||
| 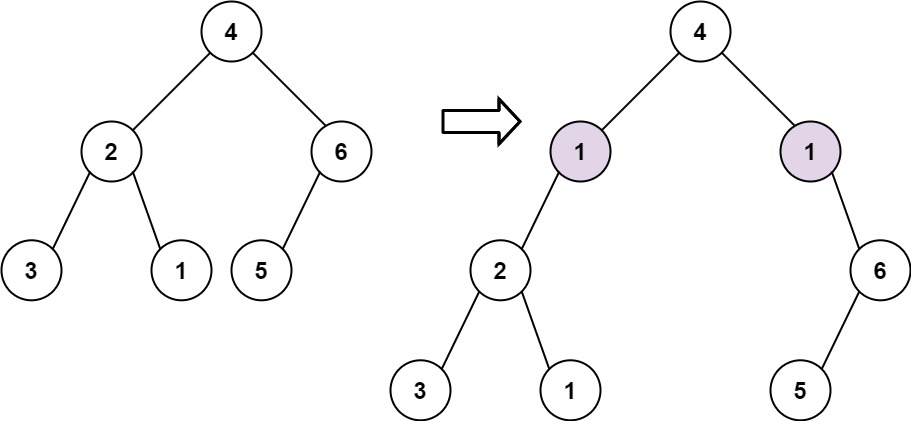 | ||
|
|
||
| **Input:** root = [4,2,6,3,1,5], val = 1, depth = 2 | ||
|
|
||
| **Output:** [4,1,1,2,null,null,6,3,1,5] | ||
|
|
||
| **Example 2:** | ||
|
|
||
| 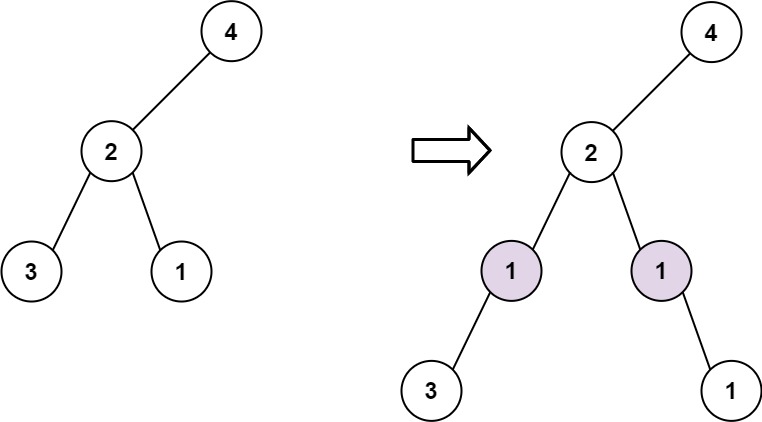 | ||
|
|
||
| **Input:** root = [4,2,null,3,1], val = 1, depth = 3 | ||
|
|
||
| **Output:** [4,2,null,1,1,3,null,null,1] | ||
|
|
||
| **Constraints:** | ||
|
|
||
| * The number of nodes in the tree is in the range <code>[1, 10<sup>4</sup>]</code>. | ||
| * The depth of the tree is in the range <code>[1, 10<sup>4</sup>]</code>. | ||
| * `-100 <= Node.val <= 100` | ||
| * <code>-10<sup>5</sup> <= val <= 10<sup>5</sup></code> | ||
| * `1 <= depth <= the depth of tree + 1` |
32 changes: 32 additions & 0 deletions
src/main/java/g0601_0700/s0628_maximum_product_of_three_numbers/Solution.java
This file contains hidden or bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| Original file line number | Diff line number | Diff line change |
|---|---|---|
| @@ -0,0 +1,32 @@ | ||
| package g0601_0700.s0628_maximum_product_of_three_numbers; | ||
|
|
||
| // #Easy #Array #Math #Sorting | ||
|
|
||
| public class Solution { | ||
|
There was a problem hiding this comment. Choose a reason for hiding this commentThe reason will be displayed to describe this comment to others. Learn more. Please add tags |
||
| public int maximumProduct(int[] a) { | ||
| int min1 = Integer.MAX_VALUE; | ||
| int min2 = Integer.MAX_VALUE; | ||
| int max1 = Integer.MIN_VALUE; | ||
| int max2 = Integer.MIN_VALUE; | ||
| int max3 = Integer.MIN_VALUE; | ||
| for (int i : a) { | ||
| if (i > max1) { | ||
| max3 = max2; | ||
| max2 = max1; | ||
| max1 = i; | ||
| } else if (i > max2) { | ||
| max3 = max2; | ||
| max2 = i; | ||
| } else if (i > max3) { | ||
| max3 = i; | ||
| } | ||
| if (i < min1) { | ||
| min2 = min1; | ||
| min1 = i; | ||
| } else if (i < min2) { | ||
| min2 = i; | ||
| } | ||
| } | ||
| return Math.max(min1 * min2 * max1, max1 * max2 * max3); | ||
| } | ||
| } | ||
28 changes: 28 additions & 0 deletions
src/main/java/g0601_0700/s0628_maximum_product_of_three_numbers/readme.md
This file contains hidden or bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| Original file line number | Diff line number | Diff line change |
|---|---|---|
| @@ -0,0 +1,28 @@ | ||
| 628\. Maximum Product of Three Numbers | ||
|
|
||
| Easy | ||
|
|
||
| Given an integer array `nums`, _find three numbers whose product is maximum and return the maximum product_. | ||
|
|
||
| **Example 1:** | ||
|
|
||
| **Input:** nums = [1,2,3] | ||
|
|
||
| **Output:** 6 | ||
|
|
||
| **Example 2:** | ||
|
|
||
| **Input:** nums = [1,2,3,4] | ||
|
|
||
| **Output:** 24 | ||
|
|
||
| **Example 3:** | ||
|
|
||
| **Input:** nums = [-1,-2,-3] | ||
|
|
||
| **Output:** -6 | ||
|
|
||
| **Constraints:** | ||
|
|
||
| * <code>3 <= nums.length <= 10<sup>4</sup></code> | ||
| * `-1000 <= nums[i] <= 1000` |
29 changes: 29 additions & 0 deletions
src/main/java/g0601_0700/s0629_k_inverse_pairs_array/Solution.java
This file contains hidden or bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| Original file line number | Diff line number | Diff line change |
|---|---|---|
| @@ -0,0 +1,29 @@ | ||
| package g0601_0700.s0629_k_inverse_pairs_array; | ||
|
|
||
| // #Hard #Dynamic_Programming | ||
|
|
||
| public class Solution { | ||
| public int kinversepairs(int n, int k) { | ||
| k = Math.min(k, n * (n - 1) / 2 - k); | ||
| if (k < 0) { | ||
| return 0; | ||
| } | ||
| int[] dp = new int[k + 1]; | ||
| int[] dp1 = new int[k + 1]; | ||
| dp[0] = 1; | ||
| dp1[0] = 1; | ||
| int mod = 1_000_000_007; | ||
| for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) { | ||
| int[] temp = dp; | ||
| dp = dp1; | ||
| dp1 = temp; | ||
| for (int j = 1, m = Math.min(k, i * (i - 1) / 2); j <= m; j++) { | ||
| dp[j] = (dp1[j] + dp[j - 1] - (j >= i ? dp1[j - i] : 0)) % mod; | ||
| if (dp[j] < 0) { | ||
| dp[j] += mod; | ||
| } | ||
| } | ||
| } | ||
| return dp[k]; | ||
| } | ||
| } |
28 changes: 28 additions & 0 deletions
src/main/java/g0601_0700/s0629_k_inverse_pairs_array/readme.md
This file contains hidden or bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| Original file line number | Diff line number | Diff line change |
|---|---|---|
| @@ -0,0 +1,28 @@ | ||
| 629\. K Inverse Pairs Array | ||
|
|
||
| Hard | ||
|
|
||
| For an integer array `nums`, an **inverse pair** is a pair of integers `[i, j]` where `0 <= i < j < nums.length` and `nums[i] > nums[j]`. | ||
|
|
||
| Given two integers n and k, return the number of different arrays consist of numbers from `1` to `n` such that there are exactly `k` **inverse pairs**. Since the answer can be huge, return it **modulo** <code>10<sup>9</sup> + 7</code>. | ||
|
|
||
| **Example 1:** | ||
|
|
||
| **Input:** n = 3, k = 0 | ||
|
|
||
| **Output:** 1 | ||
|
|
||
| **Explanation:** Only the array [1,2,3] which consists of numbers from 1 to 3 has exactly 0 inverse pairs. | ||
|
|
||
| **Example 2:** | ||
|
|
||
| **Input:** n = 3, k = 1 | ||
|
|
||
| **Output:** 2 | ||
|
|
||
| **Explanation:** The array [1,3,2] and [2,1,3] have exactly 1 inverse pair. | ||
|
|
||
| **Constraints:** | ||
|
|
||
| * `1 <= n <= 1000` | ||
| * `0 <= k <= 1000` |
93 changes: 93 additions & 0 deletions
src/main/java/g0601_0700/s0630_course_schedule_iii/Solution.java
This file contains hidden or bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| Original file line number | Diff line number | Diff line change |
|---|---|---|
| @@ -0,0 +1,93 @@ | ||
| package g0601_0700.s0630_course_schedule_iii; | ||
|
|
||
| // #Hard #Array #Greedy #Heap_Priority_Queue | ||
|
|
||
| import java.util.Arrays; | ||
|
|
||
| public class Solution { | ||
| public int scheduleCourse(int[][] courses) { | ||
| Arrays.sort(courses, (a, b) -> a[1] - b[1]); | ||
| int course = 0; | ||
| int time = 0; | ||
| MaxHeap heap = new MaxHeap(courses.length); | ||
| for (int[] cours : courses) { | ||
| if (cours[1] - time >= cours[0]) { | ||
| time += cours[0]; | ||
| course++; | ||
| heap.add(cours[0]); | ||
| } else if (cours[0] < heap.getHeap()[0]) { | ||
| int t = heap.pop(); | ||
| heap.add(cours[0]); | ||
| time = time - t + cours[0]; | ||
| } | ||
| } | ||
| return course; | ||
| } | ||
|
|
||
| static class MaxHeap { | ||
| private final int[] heap; | ||
| private int pin; | ||
|
|
||
| public MaxHeap(int mexLen) { | ||
| this.heap = new int[mexLen]; | ||
| this.pin = 0; | ||
| } | ||
|
|
||
| public int[] getHeap() { | ||
| return heap; | ||
| } | ||
|
|
||
| public int getPin() { | ||
| return pin; | ||
| } | ||
|
|
||
| public void setPin(int pin) { | ||
| this.pin = pin; | ||
| } | ||
|
|
||
| public void add(int e) { | ||
| heap[pin] = e; | ||
| int temp = pin; | ||
| pin++; | ||
| while (temp > 0 && heap[(temp - 1) / 2] < e) { | ||
| heap[temp] = heap[(temp - 1) / 2]; | ||
| temp = (temp - 1) / 2; | ||
| heap[temp] = e; | ||
| } | ||
| } | ||
|
|
||
| public int pop() { | ||
| int res = heap[0]; | ||
| pin--; | ||
| heap[0] = heap[pin]; | ||
| int h0 = heap[0]; | ||
| int temp = 0; | ||
| while (temp * 2 + 1 < pin) { | ||
| if (temp * 2 + 2 == pin) { | ||
| if (heap[temp * 2 + 1] > h0) { | ||
| heap[temp] = heap[temp * 2 + 1]; | ||
| temp = temp * 2 + 1; | ||
| heap[temp] = h0; | ||
| } else { | ||
| break; | ||
| } | ||
| } else { | ||
| if (h0 < heap[temp * 2 + 1] || h0 < heap[temp * 2 + 2]) { | ||
| if (heap[temp * 2 + 1] > heap[temp * 2 + 2]) { | ||
| heap[temp] = heap[temp * 2 + 1]; | ||
| temp = temp * 2 + 1; | ||
| heap[temp] = h0; | ||
| } else { | ||
| heap[temp] = heap[temp * 2 + 2]; | ||
| temp = temp * 2 + 2; | ||
| heap[temp] = h0; | ||
| } | ||
| } else { | ||
| break; | ||
| } | ||
| } | ||
| } | ||
| return res; | ||
| } | ||
| } | ||
| } |
32 changes: 32 additions & 0 deletions
src/main/java/g0601_0700/s0630_course_schedule_iii/readme.md
This file contains hidden or bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| Original file line number | Diff line number | Diff line change |
|---|---|---|
| @@ -0,0 +1,32 @@ | ||
| 630\. Course Schedule III | ||
|
|
||
| Hard | ||
|
|
||
| There are `n` different online courses numbered from `1` to `n`. You are given an array `courses` where <code>courses[i] = [duration<sub>i</sub>, lastDay<sub>i</sub>]</code> indicate that the <code>i<sup>th</sup></code> course should be taken **continuously** for <code>duration<sub>i</sub></code> days and must be finished before or on <code>lastDay<sub>i</sub></code>. | ||
|
|
||
| You will start on the <code>1<sup>st</sup></code> day and you cannot take two or more courses simultaneously. | ||
|
|
||
| Return _the maximum number of courses that you can take_. | ||
|
|
||
| **Example 1:** | ||
|
|
||
| **Input:** courses = [[100,200],[200,1300],[1000,1250],[2000,3200]] | ||
|
|
||
| **Output:** 3 Explanation: There are totally 4 courses, but you can take 3 courses at most: First, take the 1<sup>st</sup> course, it costs 100 days so you will finish it on the 100<sup>th</sup> day, and ready to take the next course on the 101<sup>st</sup> day. Second, take the 3<sup>rd</sup> course, it costs 1000 days so you will finish it on the 1100<sup>th</sup> day, and ready to take the next course on the 1101<sup>st</sup> day. Third, take the 2<sup>nd</sup> course, it costs 200 days so you will finish it on the 1300<sup>th</sup> day. The 4<sup>th</sup> course cannot be taken now, since you will finish it on the 3300<sup>th</sup> day, which exceeds the closed date. | ||
|
|
||
| **Example 2:** | ||
|
|
||
| **Input:** courses = [[1,2]] | ||
|
|
||
| **Output:** 1 | ||
|
|
||
| **Example 3:** | ||
|
|
||
| **Input:** courses = [[3,2],[4,3]] | ||
|
|
||
| **Output:** 0 | ||
|
|
||
| **Constraints:** | ||
|
|
||
| * <code>1 <= courses.length <= 10<sup>4</sup></code> | ||
| * <code>1 <= duration<sub>i</sub>, lastDay<sub>i</sub> <= 10<sup>4</sup></code> |
60 changes: 60 additions & 0 deletions
src/main/java/g0601_0700/s0632_smallest_range_covering_elements_from_k_lists/Solution.java
This file contains hidden or bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| Original file line number | Diff line number | Diff line change |
|---|---|---|
| @@ -0,0 +1,60 @@ | ||
| package g0601_0700.s0632_smallest_range_covering_elements_from_k_lists; | ||
|
|
||
| // #Hard #Array #Hash_Table #Sorting #Greedy #Heap_Priority_Queue #Sliding_Window | ||
|
|
||
| import java.util.List; | ||
| import java.util.Objects; | ||
| import java.util.PriorityQueue; | ||
|
|
||
| public class Solution { | ||
| static class Triplet implements Comparable<Triplet> { | ||
| int value; | ||
| int row; | ||
| int idx; | ||
|
|
||
| Triplet(int value, int row, int idx) { | ||
| this.value = value; | ||
| this.row = row; | ||
| this.idx = idx; | ||
| } | ||
|
|
||
| public int compareTo(Triplet obj) { | ||
| return this.value - obj.value; | ||
| } | ||
| } | ||
|
|
||
| public int[] smallestRange(List<List<Integer>> nums) { | ||
| PriorityQueue<Triplet> pq = new PriorityQueue<>(); | ||
| int maxInPq = Integer.MIN_VALUE; | ||
| for (int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++) { | ||
| pq.add(new Triplet(nums.get(i).get(0), i, 0)); | ||
| if (maxInPq < nums.get(i).get(0)) { | ||
| maxInPq = nums.get(i).get(0); | ||
| } | ||
| } | ||
| int rangeSize = maxInPq - Objects.requireNonNull(pq.peek()).value + 1; | ||
| int rangeLeft = Objects.requireNonNull(pq.peek()).value; | ||
| int rangeRight = maxInPq; | ||
| while (true) { | ||
| Triplet nextNumber = pq.remove(); | ||
| if (nextNumber.idx + 1 < nums.get(nextNumber.row).size()) { | ||
| int val = nums.get(nextNumber.row).get(nextNumber.idx + 1); | ||
| if (val > maxInPq) { | ||
| maxInPq = val; | ||
| } | ||
| pq.add(new Triplet(val, nextNumber.row, nextNumber.idx + 1)); | ||
| if (maxInPq - Objects.requireNonNull(pq.peek()).value + 1 < rangeSize) { | ||
| rangeSize = maxInPq - pq.peek().value + 1; | ||
| rangeLeft = maxInPq; | ||
| rangeRight = pq.peek().value; | ||
| } | ||
| } else { | ||
| break; | ||
| } | ||
| } | ||
| int[] answer = new int[2]; | ||
| answer[0] = rangeLeft; | ||
| answer[1] = rangeRight; | ||
| return answer; | ||
| } | ||
| } |
Oops, something went wrong.
Add this suggestion to a batch that can be applied as a single commit.
This suggestion is invalid because no changes were made to the code.
Suggestions cannot be applied while the pull request is closed.
Suggestions cannot be applied while viewing a subset of changes.
Only one suggestion per line can be applied in a batch.
Add this suggestion to a batch that can be applied as a single commit.
Applying suggestions on deleted lines is not supported.
You must change the existing code in this line in order to create a valid suggestion.
Outdated suggestions cannot be applied.
This suggestion has been applied or marked resolved.
Suggestions cannot be applied from pending reviews.
Suggestions cannot be applied on multi-line comments.
Suggestions cannot be applied while the pull request is queued to merge.
Suggestion cannot be applied right now. Please check back later.