forked from youngyangyang04/leetcode-master
-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 0
[pull] master from youngyangyang04:master #49
New issue
Have a question about this project? Sign up for a free GitHub account to open an issue and contact its maintainers and the community.
By clicking “Sign up for GitHub”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy statement. We’ll occasionally send you account related emails.
Already on GitHub? Sign in to your account
Merged
Merged
Changes from 1 commit
Commits
Show all changes
4 commits
Select commit
Hold shift + click to select a range
File filter
Filter by extension
Conversations
Failed to load comments.
Loading
Jump to
Jump to file
Failed to load files.
Loading
Diff view
Diff view
There are no files selected for viewing
This file contains hidden or bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
199 changes: 199 additions & 0 deletions
problems/0417.太平洋大西洋水流问题.md
This file contains hidden or bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| Original file line number | Diff line number | Diff line change |
|---|---|---|
| @@ -0,0 +1,199 @@ | ||
| # 417. 太平洋大西洋水流问题 | ||
|
|
||
| [题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/pacific-atlantic-water-flow/) | ||
|
|
||
| 不少同学可能被这道题的题目描述迷惑了,其实就是找到哪些点 可以同时到达太平洋和大西洋。 流动的方式只能从高往低流。 | ||
|
|
||
| 那么一个比较直白的想法,其实就是 遍历每个点,然后看这个点 能不能同时到达太平洋和大西洋。 | ||
|
|
||
| 至于遍历方式,可以用dfs,也可以用bfs,以下用dfs来举例。 | ||
|
|
||
| 那么这种思路的实现代码如下: | ||
|
|
||
| ```CPP | ||
| class Solution { | ||
| private: | ||
| int dir[4][2] = {-1, 0, 0, -1, 1, 0, 0, 1}; | ||
| void dfs(vector<vector<int>>& heights, vector<vector<bool>>& visited, int x, int y) { | ||
| if (visited[x][y]) return; | ||
|
|
||
| visited[x][y] = true; | ||
|
|
||
| for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) { | ||
| int nextx = x + dir[i][0]; | ||
| int nexty = y + dir[i][1]; | ||
| if (nextx < 0 || nextx >= heights.size() || nexty < 0 || nexty >= heights[0].size()) continue; | ||
| if (heights[x][y] < heights[nextx][nexty]) continue; // 高度不合适 | ||
|
|
||
| dfs (heights, visited, nextx, nexty); | ||
| } | ||
| return; | ||
| } | ||
| bool isResult(vector<vector<int>>& heights, int x, int y) { | ||
| vector<vector<bool>> visited = vector<vector<bool>>(heights.size(), vector<bool>(heights[0].size(), false)); | ||
|
|
||
| // 深搜,将x,y出发 能到的节点都标记上。 | ||
| dfs(heights, visited, x, y); | ||
| bool isPacific = false; | ||
| bool isAtlantic = false; | ||
|
|
||
| // 以下就是判断x,y出发,是否到达太平洋和大西洋 | ||
| for (int j = 0; j < heights[0].size(); j++) { | ||
| if (visited[0][j]) { | ||
| isPacific = true; | ||
| break; | ||
| } | ||
| } | ||
| for (int i = 0; i < heights.size(); i++) { | ||
| if (visited[i][0]) { | ||
| isPacific = true; | ||
| break; | ||
| } | ||
| } | ||
| for (int j = 0; j < heights[0].size(); j++) { | ||
| if (visited[heights.size() - 1][j]) { | ||
| isAtlantic = true; | ||
| break; | ||
| } | ||
| } | ||
| for (int i = 0; i < heights.size(); i++) { | ||
| if (visited[i][heights[0].size() - 1]) { | ||
| isAtlantic = true; | ||
| break; | ||
| } | ||
| } | ||
| if (isAtlantic && isPacific) return true; | ||
| return false; | ||
| } | ||
| public: | ||
|
|
||
| vector<vector<int>> pacificAtlantic(vector<vector<int>>& heights) { | ||
| vector<vector<int>> result; | ||
| // 遍历每一个点,看是否能同时到达太平洋和大西洋 | ||
| for (int i = 0; i < heights.size(); i++) { | ||
| for (int j = 0; j < heights[0].size(); j++) { | ||
| if (isResult(heights, i, j)) result.push_back({i, j}); | ||
| } | ||
| } | ||
| return result; | ||
| } | ||
| }; | ||
|
|
||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| 这种思路很直白,但很明显,以上代码超时了。 来看看时间复杂度。 | ||
|
|
||
| 遍历每一个节点,是 m * n,遍历每一个节点的时候,都要做深搜,深搜的时间复杂度是: m * n | ||
|
|
||
| 那么整体时间复杂度 就是 O(m^2 * n^2) ,这是一个四次方的时间复杂度。 | ||
|
|
||
| ## 优化 | ||
|
|
||
| 那么我们可以 反过来想,从太平洋边上的节点 逆流而上,将遍历过的节点都标记上。 从大西洋的边上节点 逆流而长,讲遍历过的节点也标记上。 | ||
|
|
||
| 从太平洋边上节点出发,如图: | ||
|
|
||
| 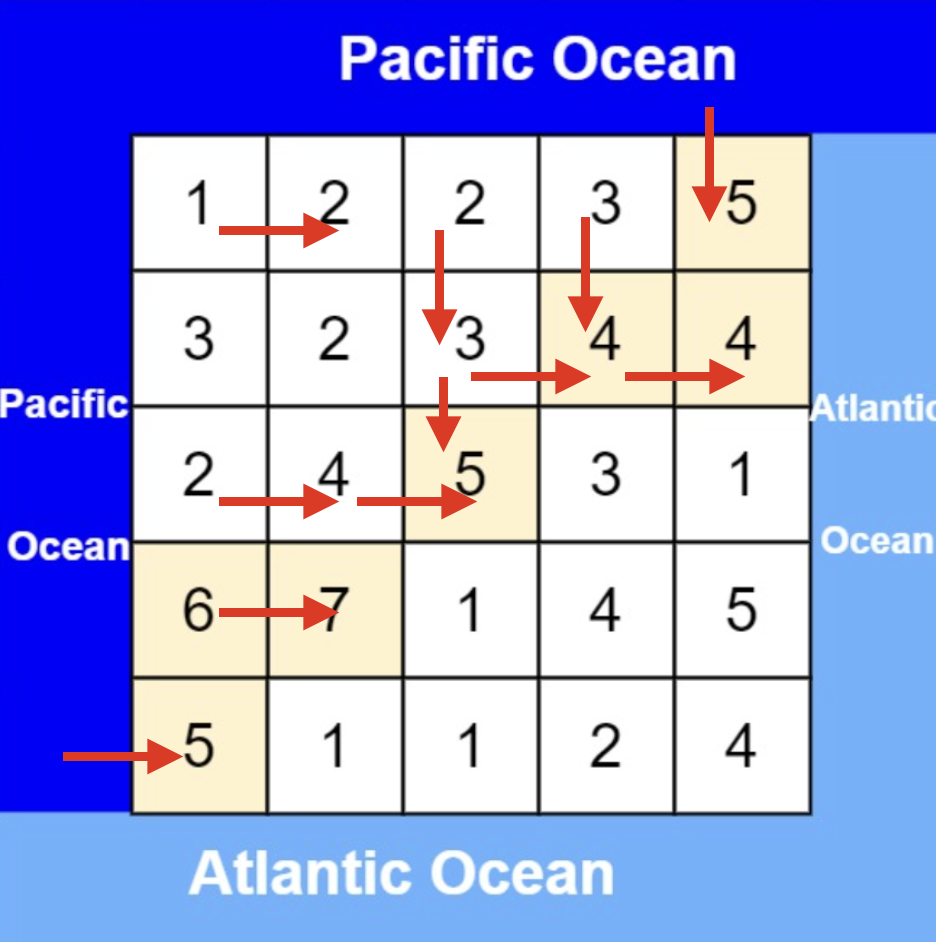 | ||
|
|
||
| 从大西洋边上节点出发,如图: | ||
|
|
||
| 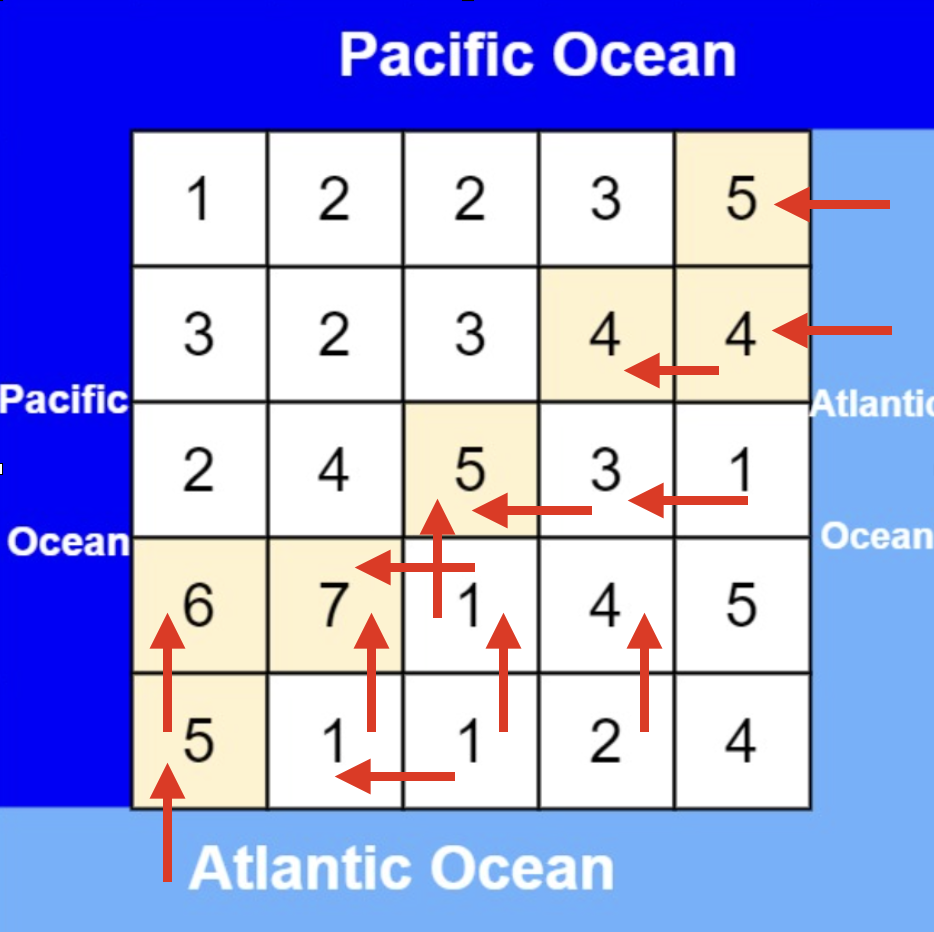 | ||
|
|
||
| 按照这样的逻辑,就可以写出如下遍历代码:(详细注释) | ||
|
|
||
| (如果对dfs基础内容就不懂,建议看 [「代码随想录」DFS算法精讲!](https://leetcode.cn/problems/all-paths-from-source-to-target/solution/by-carlsun-2-66pf/),还可以顺便解决 797. 所有可能的路径) | ||
|
|
||
| ```CPP | ||
| class Solution { | ||
| private: | ||
| int dir[4][2] = {-1, 0, 0, -1, 1, 0, 0, 1}; // 保存四个方向 | ||
|
|
||
| // 从低向高遍历,注意这里visited是引用,即可以改变传入的pacific和atlantic的值 | ||
| void dfs(vector<vector<int>>& heights, vector<vector<bool>>& visited, int x, int y) { | ||
| if (visited[x][y]) return; | ||
| visited[x][y] = true; | ||
| for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) { // 向四个方向遍历 | ||
| int nextx = x + dir[i][0]; | ||
| int nexty = y + dir[i][1]; | ||
| // 超过边界 | ||
| if (nextx < 0 || nextx >= heights.size() || nexty < 0 || nexty >= heights[0].size()) continue; | ||
| // 高度不合适,注意这里是从低向高判断 | ||
| if (heights[x][y] > heights[nextx][nexty]) continue; | ||
|
|
||
| dfs (heights, visited, nextx, nexty); | ||
| } | ||
| return; | ||
|
|
||
| } | ||
|
|
||
| public: | ||
|
|
||
| vector<vector<int>> pacificAtlantic(vector<vector<int>>& heights) { | ||
| vector<vector<int>> result; | ||
| int n = heights.size(); | ||
| int m = heights[0].size(); // 这里不用担心空指针,题目要求说了长宽都大于1 | ||
|
|
||
| // 记录从太平洋边出发,可以遍历的节点 | ||
| vector<vector<bool>> pacific = vector<vector<bool>>(n, vector<bool>(m, false)); | ||
|
|
||
| // 记录从大西洋出发,可以遍历的节点 | ||
| vector<vector<bool>> atlantic = vector<vector<bool>>(n, vector<bool>(m, false)); | ||
|
|
||
| // 从最上最下行的节点出发,向高处遍历 | ||
| for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { | ||
| dfs (heights, pacific, i, 0); // 遍历最上行,接触太平洋 | ||
| dfs (heights, atlantic, i, m - 1); // 遍历最下行,接触大西洋 | ||
| } | ||
|
|
||
| // 从最左最右列的节点出发,向高处遍历 | ||
| for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) { | ||
| dfs (heights, pacific, 0, j); // 遍历最左列,接触太平洋 | ||
| dfs (heights, atlantic, n - 1, j); // 遍历最右列,接触大西洋 | ||
| } | ||
| for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { | ||
| for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) { | ||
| // 如果这个节点,从太平洋和大西洋出发都遍历过,就是结果 | ||
| if (pacific[i][j] && atlantic[i][j]) result.push_back({i, j}); | ||
| } | ||
| } | ||
| return result; | ||
| } | ||
| }; | ||
|
|
||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| 时间复杂度分析, 关于dfs函数搜索的过程 时间复杂度是 O(n * m),这个大家比较容易想。 | ||
|
|
||
| 关键看主函数,那么每次dfs的时候,上面还是有for循环的。 | ||
|
|
||
| 第一个for循环,时间复杂度是:n * (n * m) 。 | ||
|
|
||
| 第二个for循环,时间复杂度是:m * (n * m)。 | ||
|
|
||
| 所以本题看起来 时间复杂度好像是 : n * (n * m) + m * (n * m) = (m * n) * (m + n) 。 | ||
|
|
||
| 其实这是一个误区,大家再自己看 dfs函数的实现,其实 有visited函数记录 走过的节点,而走过的节点是不会再走第二次的。 | ||
|
|
||
| 所以 调用dfs函数,**只要参数传入的是 数组pacific,那么地图中 每一个节点其实就遍历一次,无论你调用多少次**。 | ||
|
|
||
| 同理,调用 dfs函数,只要 参数传入的是 数组atlantic,地图中每个节点也只会遍历一次。 | ||
|
|
||
| 所以,以下这段代码的时间复杂度是 2 * n * m。 地图用每个节点就遍历了两次,参数传入pacific的时候遍历一次,参数传入atlantic的时候遍历一次。 | ||
| ```CPP | ||
| // 从最上最下行的节点出发,向高处遍历 | ||
| for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { | ||
| dfs (heights, pacific, i, 0); // 遍历最上行,接触太平洋 | ||
| dfs (heights, atlantic, i, m - 1); // 遍历最下行,接触大西洋 | ||
| } | ||
|
|
||
| // 从最左最右列的节点出发,向高处遍历 | ||
| for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) { | ||
| dfs (heights, pacific, 0, j); // 遍历最左列,接触太平洋 | ||
| dfs (heights, atlantic, n - 1, j); // 遍历最右列,接触大西洋 | ||
| } | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| 那么本题整体的时间复杂度其实是: 2 * n * m + n * m ,所以最终时间复杂度为 O(n * m) 。 | ||
|
|
||
| 空间复杂度为:O(n * m) 这个就不难理解了。开了几个 n * m 的数组。 | ||
|
|
This file contains hidden or bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
Add this suggestion to a batch that can be applied as a single commit.
This suggestion is invalid because no changes were made to the code.
Suggestions cannot be applied while the pull request is closed.
Suggestions cannot be applied while viewing a subset of changes.
Only one suggestion per line can be applied in a batch.
Add this suggestion to a batch that can be applied as a single commit.
Applying suggestions on deleted lines is not supported.
You must change the existing code in this line in order to create a valid suggestion.
Outdated suggestions cannot be applied.
This suggestion has been applied or marked resolved.
Suggestions cannot be applied from pending reviews.
Suggestions cannot be applied on multi-line comments.
Suggestions cannot be applied while the pull request is queued to merge.
Suggestion cannot be applied right now. Please check back later.