-104 <= ax1, ay1, ax2, ay2, bx1, by1, bx2, by2 <= 104
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/java/g0201_0300/s0224_basic_calculator/Solution.java b/src/main/java/g0201_0300/s0224_basic_calculator/Solution.java
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..08cc07d89
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/java/g0201_0300/s0224_basic_calculator/Solution.java
@@ -0,0 +1,46 @@
+package g0201_0300.s0224_basic_calculator;
+
+public class Solution {
+ int i = 0;
+
+ public int calculate(String s) {
+ char[] ca = s.toCharArray();
+
+ return helper(ca);
+ }
+
+ public int helper(char[] ca) {
+
+ int num = 0;
+ int prenum = 0;
+ boolean isPlus = true;
+ for (; i < ca.length; i++) { + char c = ca[i]; + if (c != ' ') { + if (c>= '0' && c <= '9') { + if (num == 0) { + num = (c - '0'); + } else { + num = num * 10 + c - '0'; + } + } else if (c == '+') { + prenum += num * (isPlus ? 1 : -1); + isPlus = true; + num = 0; + } else if (c == '-') { + prenum += num * (isPlus ? 1 : -1); + num = 0; + isPlus = false; + } else if (c == '(') { + i++; + prenum += helper(ca) * (isPlus ? 1 : -1); + isPlus = true; + num = 0; + } else if (c == ')') { + return prenum + num * (isPlus ? 1 : -1); + } + } + } + return prenum + num * (isPlus ? 1 : -1); + } +} diff --git a/src/main/java/g0201_0300/s0224_basic_calculator/readme.md b/src/main/java/g0201_0300/s0224_basic_calculator/readme.md new file mode 100644 index 000000000..cc42fe44b --- /dev/null +++ b/src/main/java/g0201_0300/s0224_basic_calculator/readme.md @@ -0,0 +1,35 @@ +224\. Basic Calculator + +Hard + +Given a string `s` representing a valid expression, implement a basic calculator to evaluate it, and return _the result of the evaluation_. + +**Note:** You are **not** allowed to use any built-in function which evaluates strings as mathematical expressions, such as `eval()`. + +**Example 1:** + +**Input:** s = "1 + 1" + +**Output:** 2 + +**Example 2:** + +**Input:** s = " 2-1 + 2 " + +**Output:** 3 + +**Example 3:** + +**Input:** s = "(1+(4+5+2)-3)+(6+8)" + +**Output:** 23 + +**Constraints:** + +* 1 <= s.length <= 3 * 105
+* `s` consists of digits, `'+'`, `'-'`, `'('`, `')'`, and `' '`.
+* `s` represents a valid expression.
+* `'+'` is **not** used as a unary operation (i.e., `"+1"` and `"+(2 + 3)"` is invalid).
+* `'-'` could be used as a unary operation (i.e., `"-1"` and `"-(2 + 3)"` is valid).
+* There will be no two consecutive operators in the input.
+* Every number and running calculation will fit in a signed 32-bit integer.
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/java/g0201_0300/s0225_implement_stack_using_queues/MyStack.java b/src/main/java/g0201_0300/s0225_implement_stack_using_queues/MyStack.java
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..3fd24fcd0
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/java/g0201_0300/s0225_implement_stack_using_queues/MyStack.java
@@ -0,0 +1,48 @@
+package g0201_0300.s0225_implement_stack_using_queues;
+
+import java.util.LinkedList;
+import java.util.Queue;
+
+public class MyStack {
+ Queue[-231, 231 - 1].
+
+**Note:** You are not allowed to use any built-in function which evaluates strings as mathematical expressions, such as `eval()`.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** s = "3+2\*2"
+
+**Output:** 7
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** s = " 3/2 "
+
+**Output:** 1
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** s = " 3+5 / 2 "
+
+**Output:** 5
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 1 <= s.length <= 3 * 105
+* `s` consists of integers and operators `('+', '-', '*', '/')` separated by some number of spaces.
+* `s` represents **a valid expression**.
+* All the integers in the expression are non-negative integers in the range [0, 231 - 1].
+* The answer is **guaranteed** to fit in a **32-bit integer**.
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/java/g0201_0300/s0228_summary_ranges/Solution.java b/src/main/java/g0201_0300/s0228_summary_ranges/Solution.java
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..fac9db87d
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/java/g0201_0300/s0228_summary_ranges/Solution.java
@@ -0,0 +1,54 @@
+package g0201_0300.s0228_summary_ranges;
+
+import java.util.ArrayList;
+import java.util.List;
+
+public class Solution {
+ public List-231 <= nums[i] <= 231 - 1
+* All the values of `nums` are **unique**.
+* `nums` is sorted in ascending order.
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/java/g0201_0300/s0229_majority_element_ii/Solution.java b/src/main/java/g0201_0300/s0229_majority_element_ii/Solution.java
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..f0d9e50f3
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/java/g0201_0300/s0229_majority_element_ii/Solution.java
@@ -0,0 +1,52 @@
+package g0201_0300.s0229_majority_element_ii;
+
+import java.util.ArrayList;
+import java.util.List;
+
+public class Solution {
+ public List1 <= nums.length <= 5 * 104
+* -109 <= nums[i] <= 109
+
+**Follow up:** Could you solve the problem in linear time and in `O(1)` space?
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/java/g0201_0300/s0230_kth_smallest_element_in_a_bst/Solution.java b/src/main/java/g0201_0300/s0230_kth_smallest_element_in_a_bst/Solution.java
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..d9ceb1120
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/java/g0201_0300/s0230_kth_smallest_element_in_a_bst/Solution.java
@@ -0,0 +1,37 @@
+package g0201_0300.s0230_kth_smallest_element_in_a_bst;
+
+import com_github_leetcode.TreeNode;
+
+public class Solution {
+ private int k;
+ int count = 0;
+ private int val;
+
+ public int kthSmallest(TreeNode root, int k) {
+ this.k = k;
+ count(root);
+ return val;
+ }
+
+ private void count(TreeNode node) {
+ if (node.left == null && node.right == null) {
+ count++;
+ if (count == k) {
+ this.val = node.val;
+ }
+ return;
+ }
+
+ if (node.left != null) {
+ count(node.left);
+ }
+ count++;
+ if (count == k) {
+ this.val = node.val;
+ return;
+ }
+ if (node.right != null) {
+ count(node.right);
+ }
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/main/java/g0201_0300/s0230_kth_smallest_element_in_a_bst/readme.md b/src/main/java/g0201_0300/s0230_kth_smallest_element_in_a_bst/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..3532ff8fa
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/java/g0201_0300/s0230_kth_smallest_element_in_a_bst/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,29 @@
+230\. Kth Smallest Element in a BST
+
+Medium
+
+Given the `root` of a binary search tree, and an integer `k`, return _the_ kth _smallest value (**1-indexed**) of all the values of the nodes in the tree_.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
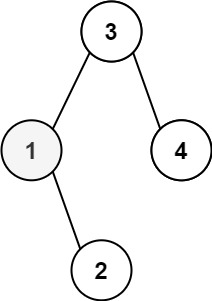
+
+
+**Input:** root = \[3,1,4,null,2\], k = 1
+
+**Output:** 1
+
+**Example 2:**
+
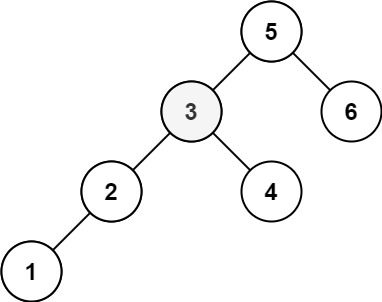
+
+
+**Input:** root = \[5,3,6,2,4,null,null,1\], k = 3
+
+**Output:** 3
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* The number of nodes in the tree is `n`.
+* 1 <= k <= n <= 104
+* 0 <= Node.val <= 104
+
+**Follow up:** If the BST is modified often (i.e., we can do insert and delete operations) and you need to find the kth smallest frequently, how would you optimize?
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/java/g0201_0300/s0231_power_of_two/Solution.java b/src/main/java/g0201_0300/s0231_power_of_two/Solution.java
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..db44acb4b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/java/g0201_0300/s0231_power_of_two/Solution.java
@@ -0,0 +1,18 @@
+package g0201_0300.s0231_power_of_two;
+
+public class Solution {
+ public boolean isPowerOfTwo(int n) {
+ if (n <= 0) { + return false; + } + while (true) { + if (n == 1) { + return true; + } + if (n % 2 == 1) { + return false; + } + n /= 2; + } + } +} diff --git a/src/main/java/g0201_0300/s0231_power_of_two/readme.md b/src/main/java/g0201_0300/s0231_power_of_two/readme.md new file mode 100644 index 000000000..d0e0841df --- /dev/null +++ b/src/main/java/g0201_0300/s0231_power_of_two/readme.md @@ -0,0 +1,47 @@ +231\. Power of Two + +Easy + +Given an integer `n`, return _`true` if it is a power of two. Otherwise, return `false`_. + +An integer `n` is a power of two, if there exists an integer `x` such that n == 2x.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** n = 1
+
+**Output:** true
+
+**Explanation:** 20 = 1
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** n = 16
+
+**Output:** true
+
+**Explanation:** 24 = 16
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** n = 3
+
+**Output:** false
+
+**Example 4:**
+
+**Input:** n = 4
+
+**Output:** true
+
+**Example 5:**
+
+**Input:** n = 5
+
+**Output:** false
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* -231 <= n <= 231 - 1
+
+**Follow up:** Could you solve it without loops/recursion?
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/java/g0201_0300/s0232_implement_queue_using_stacks/MyQueue.java b/src/main/java/g0201_0300/s0232_implement_queue_using_stacks/MyQueue.java
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..999d50294
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/java/g0201_0300/s0232_implement_queue_using_stacks/MyQueue.java
@@ -0,0 +1,43 @@
+package g0201_0300.s0232_implement_queue_using_stacks;
+
+import java.util.ArrayDeque;
+import java.util.Deque;
+
+public class MyQueue {
+ Deque