|
| 1 | +699\. Falling Squares |
| 2 | + |
| 3 | +Hard |
| 4 | + |
| 5 | +There are several squares being dropped onto the X-axis of a 2D plane. |
| 6 | + |
| 7 | +You are given a 2D integer array `positions` where <code>positions[i] = [left<sub>i</sub>, sideLength<sub>i</sub>]</code> represents the <code>i<sup>th</sup></code> square with a side length of <code>sideLength<sub>i</sub></code> that is dropped with its left edge aligned with X-coordinate <code>left<sub>i</sub></code>. |
| 8 | + |
| 9 | +Each square is dropped one at a time from a height above any landed squares. It then falls downward (negative Y direction) until it either lands **on the top side of another square** or **on the X-axis**. A square brushing the left/right side of another square does not count as landing on it. Once it lands, it freezes in place and cannot be moved. |
| 10 | + |
| 11 | +After each square is dropped, you must record the **height of the current tallest stack of squares**. |
| 12 | + |
| 13 | +Return _an integer array_ `ans` _where_ `ans[i]` _represents the height described above after dropping the_ <code>i<sup>th</sup></code> _square_. |
| 14 | + |
| 15 | +**Example 1:** |
| 16 | + |
| 17 | +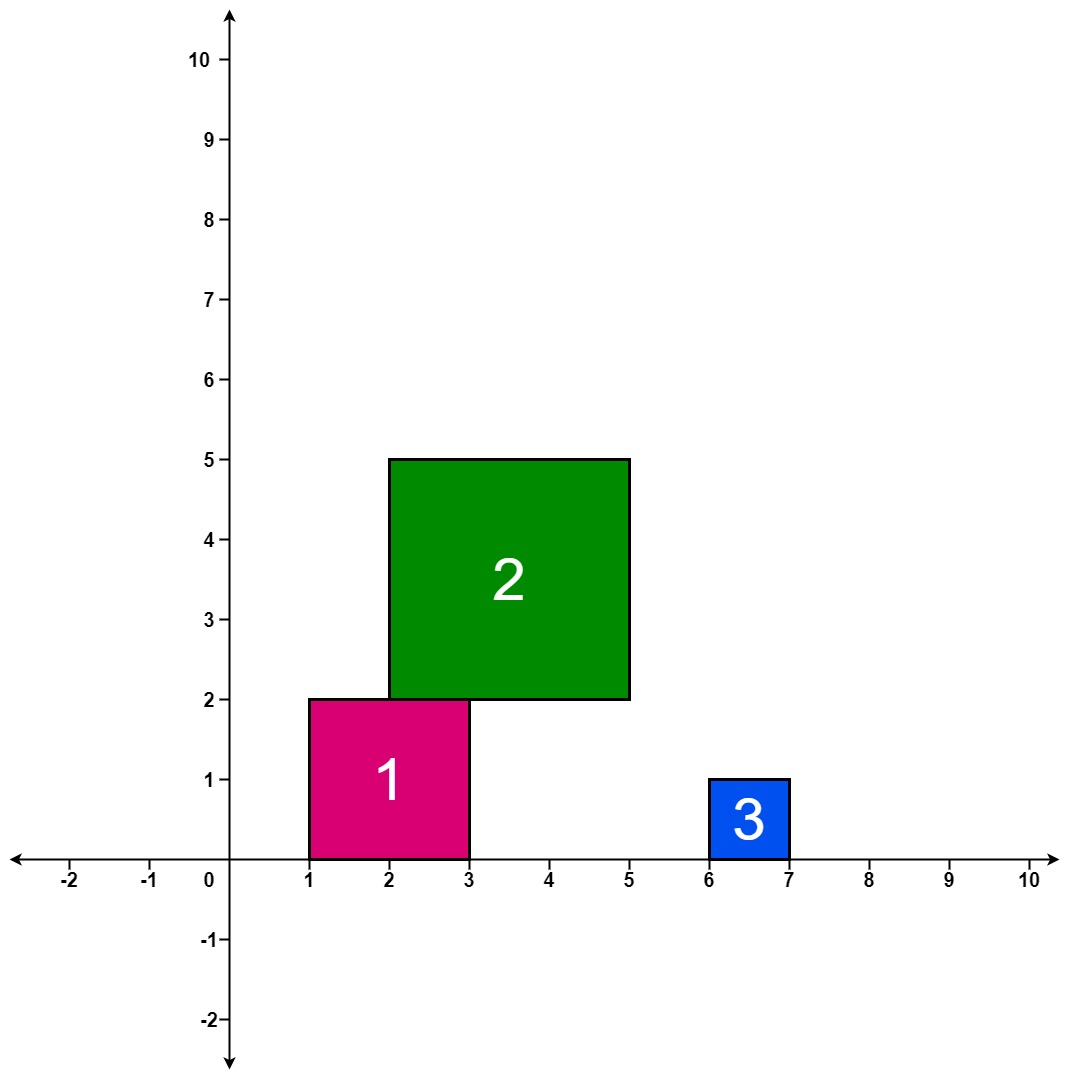 |
| 18 | + |
| 19 | +**Input:** positions = [[1,2],[2,3],[6,1]] |
| 20 | + |
| 21 | +**Output:** [2,5,5] |
| 22 | + |
| 23 | +**Explanation:** |
| 24 | + |
| 25 | +After the first drop, the tallest stack is square 1 with a height of 2. |
| 26 | + |
| 27 | +After the second drop, the tallest stack is squares 1 and 2 with a height of 5. |
| 28 | + |
| 29 | +After the third drop, the tallest stack is still squares 1 and 2 with a height of 5. |
| 30 | + |
| 31 | +Thus, we return an answer of [2, 5, 5]. |
| 32 | + |
| 33 | +**Example 2:** |
| 34 | + |
| 35 | +**Input:** positions = [[100,100],[200,100]] |
| 36 | + |
| 37 | +**Output:** [100,100] |
| 38 | + |
| 39 | +**Explanation:** |
| 40 | + |
| 41 | +After the first drop, the tallest stack is square 1 with a height of 100. |
| 42 | + |
| 43 | +After the second drop, the tallest stack is either square 1 or square 2, both with heights of 100. |
| 44 | + |
| 45 | +Thus, we return an answer of [100, 100]. |
| 46 | + |
| 47 | +Note that square 2 only brushes the right side of square 1, which does not count as landing on it. |
| 48 | + |
| 49 | +**Constraints:** |
| 50 | + |
| 51 | +* `1 <= positions.length <= 1000` |
| 52 | +* <code>1 <= left<sub>i</sub> <= 10<sup>8</sup></code> |
| 53 | +* <code>1 <= sideLength<sub>i</sub> <= 10<sup>6</sup></code> |
0 commit comments