diff --git a/.gitignore b/.gitignore
old mode 100755
new mode 100644
diff --git a/1.Java Based.md b/1.Java Based.md
old mode 100755
new mode 100644
index b1d7ce6..c224e3c
--- a/1.Java Based.md
+++ b/1.Java Based.md
@@ -27,36 +27,29 @@ JDK8后,接口中可以包含default方法,抽象类中不可以
### 面向对象开发的六个基本原则,在项目中用过哪些原则
- 六个基本原则
-
- - 单一原则
-
- 一个类只做它该做的事情(高内聚)。在面向对象中,如果只让一个类完成它该做的事,而不涉及与它无关的领域就是践行了高内聚的原则,这个类就只有单一原则
-
- - 开闭原则
-
- 软件实体应当对扩展开发,对修改关闭,要做到开闭有两个要点:
-
- 1. 抽象是关键,一个系统中如果没有抽象类或接口系统就没有扩展点
- 2. 封装可变性,将系统中的各种可变因素封装到一个继承结构中,如果多个可变因素混杂在一起,系统将变的复杂而繁乱
-
- - 里氏替换原则
-
- 任何时候都可以用子类型替换掉父类型,子类一定是增加父类的能力而不是减少父类的能力
-
- - 依赖倒置原则
-
- 面向接口编程。高层模块不应该依赖底层模块,两者都应该依赖其抽象,尽可能使用抽象类型而不用具体类型,因为抽象类型可以被它的任何一个子类型所替代。
-
- - 接口隔离原则
-
- 类间的依赖关系应该建立在最小的接口上,不能大而全,接口表示能力,一个接口只应该描述一种能力,接口也应该高度内聚
-
- - 迪米特法则
-
- 由叫最少知识原则,一个对象应该对其他对象有尽可能少的了解
+
+ - 单一原则
+ 一个类只做它该做的事情(高内聚)。在面向对象中,如果只让一个类完成它该做的事,而不涉及与它无关的领域就是践行了高内聚的原则,这个类就只有单一原则
+
+ - 开闭原则
+ 软件实体应当对扩展开发,对修改关闭,要做到开闭有两个要点:
+
+ 1. 抽象是关键,一个系统中如果没有抽象类或接口系统就没有扩展点
+ 2. 封装可变性,将系统中的各种可变因素封装到一个继承结构中,如果多个可变因素混杂在一起,系统将变的复杂而繁乱
+
+ - 里氏替换原则
+ 任何时候都可以用子类型替换掉父类型,子类一定是增加父类的能力而不是减少父类的能力
+
+ - 依赖倒置原则
+ 面向接口编程。高层模块不应该依赖底层模块,两者都应该依赖其抽象,尽可能使用抽象类型而不用具体类型,因为抽象类型可以被它的任何一个子类型所替代。
+
+ - 接口隔离原则
+ 类间的依赖关系应该建立在最小的接口上,不能大而全,接口表示能力,一个接口只应该描述一种能力,接口也应该高度内聚
+
+ - 迪米特法则
+ 又叫最少知识原则,一个对象应该对其他对象有尽可能少的了解
- 根据自己的项目来说
-
详细的可以看这里:https://www.cnblogs.com/qifengshi/p/5709594.html
> 关于网络方面的问题,面试官应该只会问一题,不会多问
@@ -73,37 +66,47 @@ JDK8后,接口中可以包含default方法,抽象类中不可以
### TCP 三次握手,四次挥手
-可见该文:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_38950316/article/details/81087809
+* **SYN(Synchronize)**:同步标志位,用于发起连接、请求同步序列号。
+* **ACK(Acknowledgment)**:确认标志位,用于确认收到对方数据,`ACK=1`表示确认有效。
+* **序列号(Seq)**:随机生成的初始值(ISN,Initial Sequence Number),后续数据按 "Seq + 数据长度" 递增,确保数据有序。
+* **确认号(Ack)**:表示 "期望收到对方的下一个序列号",值为 "对方已发 Seq + 已接收数据长度"。
+- 三次握手详细流程(以 "客户端→服务器" 建立连接为例)
+
+| 步骤 | 发起方 | 标志位 | 关键字段 | 目的 |
+| --- | --- | ---------------- | ------------------------------ | --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
+| 1 | 客户端 | SYN=1 | Seq = x(随机初始值) | 向服务器 "请求建立连接",并告知服务器:"我后续发送数据的序列号从 x 开始"。 |
+| 2 | 服务器 | SYN=1
ACK=1 | Seq = y(服务器随机值)
Ack = x+1 | 1. 用`ACK=1`和`Ack=x+1`确认 "已收到客户端的连接请求";
2. 用`SYN=1`和`Seq=y`向客户端发起 "反向连接请求",告知客户端:"我后续发送数据的序列号从 y 开始"。 |
+| 3 | 客户端 | ACK=1 | Seq = x+1
Ack = y+1 | 用`ACK=1`和`Ack=y+1`确认 "已收到服务器的反向连接请求",至此双方确认 "收发能力正常",连接建立。 |
+
+- 四次挥手详细流程(以 "客户端→服务器" 主动断开连接为例)
+
+| 步骤 | 发起方 | 标志位 | 关键字段 | 目的 |
+| --- | --- | ---------------- | ------------------------------------------ | -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
+| 1 | 客户端 | FIN=1
ACK=1 | Seq = u(客户端当前 Seq)
Ack = v(服务器当前 Ack) | 客户端告知服务器:"我没有数据要发了,请求关闭我的发送通道(单向)",但仍能接收服务器的数据。 |
+| 2 | 服务器 | ACK=1 | Seq = v
Ack = u+1 | 服务器确认 "已收到客户端关闭发送通道的请求",此时客户端→服务器的发送通道关闭,但服务器→客户端的发送通道仍可传输数据(服务器可能还有未发完的数据)。 |
+| 3 | 服务器 | FIN=1
ACK=1 | Seq = w(服务器剩余数据后的 Seq)
Ack = u+1 | 服务器发送完所有剩余数据后,告知客户端:"我也没有数据要发了,请求关闭我的发送通道(单向)"。 |
+| 4 | 客户端 | ACK=1 | Seq = u+1
Ack = w+1 | 客户端确认 "已收到服务器关闭发送通道的请求",此时服务器→客户端的发送通道关闭。客户端会等待**2MSL(Maximum Segment Lifetime,报文最大生存时间)** 后释放连接(确保服务器能收到该确认,避免服务器重发 FIN)。 |
### TCP 和 UDP区别
- 区别:
-
UDP是无连接的,即发送数据之前不需要建立连接
-
UDP使用尽最大努力交付,即不保证可靠交付,同时也不使用拥塞控制
-
UDP是面向报文的,没有拥塞控制,适合多媒体通信要求
-
UDP支持一对一,一对多,多对一和多对多的交互通信
-
UDP首部开销小,只有8个字节
-
TCP是面向连接的运输层协议
-
TCP只能一对一连接
-
TCP提供可靠的交付服务,提供全双工通信
-
TCP 面向字节流,头部最低20个字节
### 从输入网址到获取页面的过程
- 查询DNS, 获取域名对应的IP地址
- - 浏览器搜索自身的DNS缓存
- - 搜索操作系统的DNS缓存
- - 读取本地的HOST文件
- - 发起一个DNS系统调用(宽带运营服务器查看本身缓存,运营服务器发起一个迭代DNS解析请求)
+ - 浏览器搜索自身的DNS缓存
+ - 搜索操作系统的DNS缓存
+ - 读取本地的HOST文件
+ - 发起一个DNS系统调用(宽带运营服务器查看本身缓存,运营服务器发起一个迭代DNS解析请求)
- 浏览器获得域名对应的IP地址后,发起HTTP三次握手
- TCP/IP建立连接后,浏览器可以向服务器发送HTTP请求了
- 服务器接收到请求后,根据路径参数,经过后端处理将页面返回给浏览器
@@ -117,28 +120,24 @@ Session:
Cookie:
-数据已文件形式存在用户浏览器端,用户可以通过浏览器禁用Cookie,用户可以对Cookie进行查看,修改,和删除
+数据以文件形式存在用户浏览器端,用户可以通过浏览器禁用Cookie,用户可以对Cookie进行查看,修改,和删除
### 列出自己常用的JDK包
常用的包:
-java.lang 包装类,线程等都在该包
+java.lang 包装类,线程等都在该包
-java.match 有BigDecimal 精确数字类型
+java.math 有BigDecimal 精确数字类型
java.util 并发,集合等都在该包内
### equals与==的区别
1. equals 比较两个实体值是否相同,可以被覆盖,但需要遵循几个约定:
-
自反性:对于任何非null的引用值x, x.equals(x)必须返回true
-
对称性:对于任何非null的引用值x和y,当y.equals(x)返回true时,x.equlas(y)必须返回true
-
传递性:对于任何非null的引用值x、y、z,如果x.equals(y)返回true,并且y.equals(x)也返回true,那么x.equals(z)也必须返回true
-
一致性:对于任何非null的引用值x和y,只要比较对象中的所有信息没有被修改,多次调用equals一致返回true,或者false
2. == 比较两个实体的引用地址是否相等,不能覆盖,如果引用地址相等,那认为两个实体为同一个实体
@@ -217,9 +216,92 @@ wait(long timeout)导致当前的线程等待,直到其他线程调用此对
### 创建线程的方式
-1. 继承Thread类创建线程,并重写run方法,调用实例对象的start()方法启动线程
-2. 实现Runnable接口,并实现run方法,将实现Runnable的类传入Thread构造函数中,并调用Thread实例对象的start方法启动线程
-3. 实现Callable接口,并实现call方法,创建Callable实现类的实例,使用FutureTask包装Callable对象,使用FutureTask对象传入Thread中,调用start方法启动线程,使用FutureTask对象的get方法获取线程的返回值
+- 继承Thread类创建线程,并重写run方法,调用实例对象的start()方法启动线程
+
+```java
+public class ThreadDemo extends Thread {
+ @Override
+ public void run() {
+ // 线程执行逻辑
+ for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { + System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ": " + i); + } + } + + public static void main(String[] args) { + ThreadDemo thread = new ThreadDemo(); + thread.setName("子线程1"); + thread.start(); // 启动线程,JVM会调用run() + + // 主线程逻辑 + for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { + System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ": " + i); + } + } +} +``` + +- 实现Runnable接口,并实现run方法,将实现Runnable的类传入Thread构造函数中,并调用Thread实例对象的start方法启动线程 + +```java +public class RunnableDemo implements Runnable { + @Override + public void run() { + // 线程执行逻辑 + for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { + System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ": " + i); + } + } + + public static void main(String[] args) { + // 创建任务对象 + RunnableDemo task = new RunnableDemo(); + + // 创建线程并关联任务 + Thread thread = new Thread(task, "子线程1"); + thread.start(); + + // 主线程逻辑 + for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { + System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ": " + i); + } + } +} +``` + +- 实现Callable接口,并实现call方法,创建Callable实现类的实例,使用FutureTask包装Callable对象,使用FutureTask对象传入Thread中,调用start方法启动线程,使用FutureTask对象的get方法获取线程的返回值 + +```java +import java.util.concurrent.Callable; +import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException; +import java.util.concurrent.FutureTask; + +public class CallableDemo implements Callable {
+ @Override
+ public Integer call() throws Exception {
+ // 线程执行逻辑,返回计算结果
+ int sum = 0;
+ for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) { + sum += i; + } + return sum; + } + + public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException { + // 创建任务对象 + CallableDemo task = new CallableDemo(); + + // 包装任务,用于获取结果 + FutureTask futureTask = new FutureTask(task);
+
+ // 启动线程
+ new Thread(futureTask, "计算线程").start();
+
+ // 获取结果(会阻塞,直到子线程执行完毕)
+ System.out.println("1-10的和为:" + futureTask.get());
+ }
+}
+```
### ArrayList 与 LinkedList 区别
@@ -230,67 +312,50 @@ LinkedList是一种链式存储的线性表,本质是一个双向链表,实
### 自定义注解
1. 声明注解的保留期限类型
-
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)表示该注解可以在运行期保留
-
保留期限类型:java.lang.annotation.Retention
-
SOURCE: 注解信息仅保留在目标类源代码文件中,对应的字节码文件不会保留
-
CLASS: 注解信息存在于源代码、字节码文件中,但运行期JVM不能获得该注解信息
-
RUNTIME: 注解信息存在于源代码、字节码文件、运行期JVM中,能够通过反射机制获取注解类信息
2. 声明注解可以使用的目标类型
-
@Target(ElementType.METHOD) 表示这个注解只能在方法上使用
-
目标类型:java.lang.annotation.ElementType
-
TYPE: 类、接口、注解类、Enum
-
FIELD: 类成员变量或常量
-
METHOD: 方法
-
PARAMETER: 参数
-
CONSTRUCTOR: 构造器
-
LOCAL_VARIABLE: 局部变量
-
ANNOTATION_TYPE: 注解
-
PACKAGE: 包
3. 使用@interface 修饰类
4. 声明注解成员
-
成员无入参、不能抛出异常;
-
可以通过default成员指定默认值
-
成员类型只能使用基本数据类型、String、Class、enums、注解类型,及上述类型的数组类型。如ForumService value()是非法的
-
如果注解只有一个成员,则成员名必须取名为value(),再使用时可以忽略成员名和赋值号,如果注解类拥有多个成员时,
-
对value成员赋值,可以省略value和赋值号,如果是多个成员赋值,必须使用赋值号
### ArrayList扩容机制是怎么样的? 详细说一下。
在往ArrayList add元素的时候,如果ArrayList 已有元素数量+1 大于 ArrayList 存储元素的总长度,就会触发扩容。
-首先ArrayList会计算新数组的长度,长度为老数组的0.5倍,如果新数组长度还是小于插入元素需要的最小长度,那么新数组长度赋值为最小长度,如果超过ArrayList允许的最大长度Integer.MAX_VALUE(2ドル^{31} - 1$),那么新数组长度为Integer.MAX_VALUE,否则为Integer.MAX_VALUE - 8(为什么要-8?[Why the maximum array size of ArrayList is Integer.MAX_VALUE - 8?](https://stackoverflow.com/questions/35756277/why-the-maximum-array-size-of-arraylist-is-integer-max-value-8))
+首先ArrayList会计算新数组的长度,长度为老数组的1.5倍,如果新数组长度还是小于插入元素需要的最小长度,那么新数组长度赋值为最小长度,如果超过ArrayList允许的最大长度Integer.MAX_VALUE(2ドル^{31} - 1$),那么新数组长度为Integer.MAX_VALUE,否则为Integer.MAX_VALUE - 8(为什么要-8?[Why the maximum array size of ArrayList is Integer.MAX_VALUE - 8?](https://stackoverflow.com/questions/35756277/why-the-maximum-array-size-of-arraylist-is-integer-max-value-8))
最后将原数组元素拷贝到新数组进行扩容
+> 为什么要预留8个字节
+>
+> 数组除了存储元素的数组体外,还需要额外的元数据来记录数组的长度、类型信息等,本质是 **为数组元数据预留内存空间**,避免因数组容量达到理论最大值时,元数据无内存可用而导致的分配失败
+
### HashMap 1.7 和 1.8 的区别
- 1.7,在发生hash冲突的时候,数据结构只有链表;
- 1.8,数据结构有链表和红黑树,使用红黑树是为了能够提高查询效率。在链表长度达到7时(bingCount>= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1),并且hash tab[]数组长度大于等于64时,将链表转换成红黑树,如果数组长度小于64,只是对数组进行扩容
-
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_21251983/article/details/90056067
### HashMap中的key可以是任何对象或数据类型吗
@@ -326,16 +391,16 @@ cap -1 ,-1是为了在计算的时候能得到大于等于输入参数的值
```java
final Node[] resize() {
- //原table数组赋值
+ //原table数组赋值
Node[] oldTab = table;
- //如果原数组为null,那么原数组长度为0
+ //如果原数组为null,那么原数组长度为0
int oldCap = (oldTab == null) ? 0 : oldTab.length;
- //赋值阈值
+ //赋值阈值
int oldThr = threshold;
- //newCap 新数组长度
- //newThr 下次扩容的阈值
+ //newCap 新数组长度
+ //newThr 下次扩容的阈值
int newCap, newThr = 0;
- // 1. 如果原数组长度大于0
+ // 1. 如果原数组长度大于0
if (oldCap> 0) {
//如果大于最大长度1 << 30 = 1073741824,那么阈值赋值为Integer.MAX_VALUE后直接返回 if (oldCap>= MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) {
@@ -347,7 +412,7 @@ final Node[] resize() {
oldCap>= DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY)
newThr = oldThr << 1; // double threshold } - // 3. 如果原数组长度等于0,但原阈值大于0,那么新的数组长度赋值为原阈值大小 + // 3. 如果原数组长度等于0,但原阈值大于0,那么新的数组长度赋值为原阈值大小 else if (oldThr> 0) // initial capacity was placed in threshold
newCap = oldThr;
else { // zero initial threshold signifies using defaults
@@ -355,7 +420,7 @@ final Node[] resize() {
newCap = DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY;
newThr = (int)(DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR * DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY);
}
- // 5.如果新的阈值等于0
+ // 5.如果新的阈值等于0
if (newThr == 0) {
//计算临时阈值
float ft = (float)newCap * loadFactor;
@@ -363,13 +428,13 @@ final Node[] resize() {
newThr = (newCap < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY && ft < (float)MAXIMUM_CAPACITY ? (int)ft : Integer.MAX_VALUE); } - //计算出来的新阈值赋值给对象的阈值 + //计算出来的新阈值赋值给对象的阈值 threshold = newThr; @SuppressWarnings({"rawtypes","unchecked"}) - //用新计算的数组长度新建一个Node数组,并赋值给对象的table + //用新计算的数组长度新建一个Node数组,并赋值给对象的table Node[] newTab = (Node[])new Node[newCap];
table = newTab;
- //后面是copy数组和链表数据逻辑
+ //后面是copy数组和链表数据逻辑
if (oldTab != null) {
for (int j = 0; j < oldCap; ++j) { Node e;
@@ -467,13 +532,12 @@ if ((tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)
- HashMap并发下产生问题:由于在发生hash冲突,插入链表的时候,多线程会造成环链,再get的时候变成死循环,Map.size()不准确,数据丢失
https://www.iteye.com/blog/hwl-sz-1897468
-
+
- HashTable: 通过synchronized来修饰,效率低,多线程put的时候,只能有一个线程成功,其他线程都处于阻塞状态
- ConcurrentHashMap:
1.7 采用锁分段技术提高并发访问率
1.8 数据依旧是分段存储,但锁采用了synchronized,内部采用Node数组+链表+红黑树的结构存储,当单个链表存储数量达到红黑树阈值8时(此时链表已有元素7),并且数组长度大于64时,存储结构转换为红黑树来存储,否则只进行数组的扩容
-
https://www.cnblogs.com/banjinbaijiu/p/9147434.html
### HashMap 为什么不用平衡树,而用红黑树
@@ -485,7 +549,7 @@ if ((tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)
查找时间复杂度都维持在O(logN)
> 关于HashMap的其他文章:https://blog.csdn.net/login_sonata/article/details/76598675
->
+>
> 源码解析:https://www.jianshu.com/p/0a70ce2d3b67
### 常见异常分为哪两种(Exception,Error),区别是什么,了解受检异常和非受检异常吗
@@ -496,7 +560,7 @@ Error: 表示程序发生错误,是程序无法处理的,不可恢复的,
Exception: 表示程序可处理的异常,又分为CheckedException(受检异常)、UncheckedException(非受检异常),受检异常发生在编译期,必须要使用try...catch 或者 throws捕获或者抛出异常,否则编译不通过;非受检异常发生在运行期,具有不确定性,主要由程序的逻辑问题引起的,在程序设计的时候要认真考虑,尽量处理异常
-### 实现一个LRU
+### 实现一个LRU(最近最少使用)
可以直接使用LinkedHashMap实现
@@ -521,30 +585,25 @@ public class LRUCache extends LinkedHashMap {
}
```
-### 用过流没有,流怎么实现
-
-Stream流是Java8中引入的新特性,Stream有几个特点:
-
-不存数据,都是通过管道将源数据元素传递给操作;
-
-对Stream的任何修改都不会修改数据源,都是新产生一个流
-
-流的很多操作如filter、map都是延迟执行的,只有到终点才会将操作顺序执行
-
-对于无限流可以通过"短路"操作访问到有限元素后就返回
+### 获取一个Class对象的方式
-流的元素只访问一次,如果需要重新访问,需要重新生成一个新的流
+1. 通过类对象的getClass方法
-Stream中BaseStream规定了流的基本接口,在Stream中使用Stage来描述一个完整的操作,将具有先后顺序的各个Stage连一起,就构成了整个流水线。
+```java
+User user = new User();
+Class clazz = user.getClass();
+```
-AbstractPipeline是流水线的核心,定义了三个AbstractPipeline类型的变量:sourceStage(源阶段)、previousStage(上游pipeline,上一阶段),nexStage(下一阶段)
+2. 通过类的静态成员,每个类都有隐含的静态成员class
-ReferencePipeline 继承了AbstractPipeline
+```java
+Class clazz = User.class;
+```
-Head、StatefulOp、StatelessOp继承了ReferencePipeline,分别表示源,无状态操作,有状态操作
+3. 通过Class类的静态方法forName方法获取
-
+```java
+Class clazz = Class.forName("com.itsaysay.User");
+```
-比如Collection.stream()方法得到Head也就是stage0,紧接着调用一系列的中间操作,不断产生新的stage。这些stage对象以双向链表的形式组织在一起,构成整个流水线。
-由于每个Stage都记录了前一个Stage和本次的操作以及回调函数,依靠这种结构就建立起对数据源的所有操作。
diff --git a/10.Spring.md b/10.Spring.md
old mode 100755
new mode 100644
index 5aece9f..c3c7878
--- a/10.Spring.md
+++ b/10.Spring.md
@@ -6,17 +6,17 @@
### BeanFactory 与ApplicationContext 是干什么的,两者的区别
-BeanFactory、ApplicationContext都代表容器,BeanFactory是一个基础接口,实现了容器基础的功能,ApplicationContext是容器的高级形态,增加了许多了特性,顶级父类是BeanFactory。
+BeanFactory、ApplicationContext都代表容器,BeanFactory是一个基础接口,实现了容器基础的功能,ApplicationContext是容器的高级形态,增加了许多特性,顶级父类是BeanFactory。
跟FactoryBean的区别是:
-FactoryBean 是一个Bean,用于生产修饰其他的Bean实例,典型应用是AOP代理类,使用'&'获取FactoryBean本身
+FactoryBean 是一个Bean,用于创建或修饰其他的Bean实例,典型应用是AOP代理类,使用'&'获取FactoryBean本身,通过getObject来获取原来的Bean实例
-BeanFactory 是一个工厂,是容器的顶层接口
+BeanFactory 是一个工厂,是容器的顶层接口
### BeanPostProcessor 的实现
-Bean的后置处理器,是一个监听器,可以监听容器触发的事件。将它向IOC容器注册后,容器中管理的Bean具备了接收IOC容器事件回调的能力。BeanPostProcessor是一个接口类,有两个接口方法,postProcessBeforeInitialization提供Bean初始化前的回调入口;postProcessAfterInitialization 提供Bean初始化后的回调入口`AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory#initializeBean`
+Bean的后置处理器,是一个监听器,可以监听容器触发的事件。将它向IOC容器注册后,容器中管理的Bean具备了接收IOC容器事件回调的能力。BeanPostProcessor是一个接口类,有两个接口方法,postProcessBeforeInitialization提供Bean初始化前的回调入口;postProcessAfterInitialization 提供Bean初始化后的回调入口`AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory#initializeBean`,这个类可以对项目中的Bean进行修饰,所有Bean都会调用该实现。
### BeanDefinition 的实现
@@ -32,7 +32,7 @@ Spring通过`refresh()`方法对容器进行初始化和资源的载入
第二个过程是BeanDefinition载入,把定义好的Bean表示成IOC容器的内部数据结构BeanDefinition,通过定义BeanDefinition来管理应用的各种对象及依赖关系,其是容器实现依赖反转功能的核心数据结构
-第三个过程是BeanDefinition注册,容器解析得到BeanDefinition后,需要在容器中注册,这由IOC实现BeanDefinitionRegistry接口来实现,注册过程是IOC容器内部维护了一个ConcurrentHasmap来保存得到的BeanDefinition。如果某些Bean设置了lazyinit属性,Bean的依赖注入会在这个过程预先完成,而不需要等到第一次使用Bean的时候才触发。
+第三个过程是BeanDefinition注册,容器解析得到BeanDefinition后,需要在容器中注册,这由IOC实现BeanDefinitionRegistry接口来实现,注册过程是IOC容器内部维护了一个ConcurrentHasmap来保存得到的BeanDefinition。如果某些Bean设置了lazyinit=false属性,Bean的依赖注入会在这个过程预先完成,而不需要等到第一次使用Bean的时候才触发。
### Spring DI(依赖注入)的实现
@@ -51,7 +51,7 @@ getBean()方法定义在BeanFactory接口中,具体实现在子类AbstractBean
5. 通过populateBean注入Bean属性,并调用init-method初始化方法
6. 注册实例化的Bean
-### Spring如何解决循环依赖问题
+### Spring如何解决循环依赖问题(三级缓存)
比如A依赖B, B依赖A.
@@ -131,7 +131,7 @@ AOP面向切面编程,可以通过预编译和运行时动态代理,实现
### Spring MVC运行流程
-image-20190910155238902
+image-20190910155238902
1. 客户端请求到DispatcherServlet
2. DispatcherServlet根据请求地址查询映射处理器HandleMapping,获取Handler
@@ -193,6 +193,64 @@ TransactionTemplate 事务模版是对原始事务管理方式的封装,原始
事务模版主要通过execute(TransactionCallback action)来执行事务,TransactionCallback 有两种方式一种是有返回值TransactionCallback,一种是没有返回值TransactionCallbackWithoutResult。
+手动处理事务的方法:
+
+1. 使用TransactionTemplate
+
+```java
+@Autowired
+private TransactionTemplate transactionTemplate;
+
+public void manualTransaction() {
+ transactionTemplate.execute(status -> {
+ try {
+ // 业务逻辑代码
+ // ...
+
+ // 手动提交
+ // 不需要显式调用,execute方法成功完成后会自动提交
+ return result; // 返回执行结果
+ } catch (Exception e) {
+ // 手动回滚
+ status.setRollbackOnly();
+ throw e; // 或者处理异常
+ }
+ });
+}
+```
+
+
+
+2. 使用PlatformTransactionManager
+
+```java
+@Autowired
+private PlatformTransactionManager transactionManager;
+
+public void manualTransactionWithManager() {
+ // 定义事务属性
+ DefaultTransactionDefinition def = new DefaultTransactionDefinition();
+ def.setPropagationBehavior(TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_REQUIRED);
+
+ // 开启事务
+ TransactionStatus status = transactionManager.getTransaction(def);
+
+ try {
+ // 业务逻辑代码
+ // ...
+
+ // 手动提交
+ transactionManager.commit(status);
+ } catch (Exception e) {
+ // 手动回滚
+ transactionManager.rollback(status);
+ throw e; // 或者处理异常
+ }
+}
+```
+
+
+
### Spring 事务底层原理
1. 事务的准备
@@ -255,13 +313,13 @@ TTI:空闲期,即一个数据多久没被访问就从缓存中移除的时
### Spring Cache 注解
-| 注解 | 用法 |
-| ------------ | -------------------------------------------------- |
-| @Cacheable | 先查询缓存,如果没有执行方法并缓存结果,用于取数据 |
-| @CachePut | 先执行方法,然后将返回值放入缓存,用于更新数据 |
-| @CacheEvict | 删除缓存,用于删除数据 |
-| @Caching | 基于前3者的注解数组,多用于一个类有多种实现的情况 |
-| @CacheConfig | 全局缓存注解,用于类上 |
+| 注解 | 用法 |
+| ------------ | ------------------------------------------------------ |
+| @Cacheable | 先查询缓存,如果没有缓存执行方法并缓存结果,用于取数据 |
+| @CachePut | 先执行方法,然后将返回值放入缓存,用于更新数据 |
+| @CacheEvict | 删除缓存,用于删除数据 |
+| @Caching | 基于前3者的注解数组,多用于一个类有多种实现的情况 |
+| @CacheConfig | 全局缓存注解,用于类上 |
缓存管理器
@@ -270,6 +328,32 @@ TTI:空闲期,即一个数据多久没被访问就从缓存中移除的时
3. ConcurrentMapCacheManager 不用配置缓存列表,自动生成缓存ConcurrentMapCache
4. CompositeCacheManager 可以将不同的缓存管理器组合在一起,不同的缓存使用不同的缓存管理器,并且可以通过fallbackToNoOpCache属性回到NoOpCacheManager
+手动处理Spring Cache缓存:
+
+```java
+@Autowired
+private CacheManager cacheManager;
+
+public void manualCacheOperations() {
+ // 获取指定缓存
+ Cache cache = cacheManager.getCache("cacheName");
+
+ // 存入缓存
+ cache.put("key", "value");
+
+ // 获取缓存值
+ ValueWrapper wrapper = cache.get("key");
+ if (wrapper != null) {
+ Object value = wrapper.get();
+ // 使用缓存值
+ }
+
+ // 删除缓存
+ cache.evict("key"); // 删除指定key
+ cache.clear(); // 清空整个缓存
+}
+```
+
### Spring BeanUtils bean拷贝工具用过吗?它是浅拷贝还是深拷贝?怎么实现的?有没有什么坑?其他还有什么bean 拷贝的方法,是浅拷贝还是深拷贝?如何实现深拷贝?
diff --git a/11.Spring Boot.md b/11.Spring Boot.md
old mode 100755
new mode 100644
index f50a1eb..02af055
--- a/11.Spring Boot.md
+++ b/11.Spring Boot.md
@@ -19,42 +19,39 @@ Spring Boot是 Spring 的子项目,正如其名字,提供 Spring 的引导(
- 判断webApplication是什么类型的
- 设置ApplicationContextInitializer,ApplicationListener,通过加载META-INF/spring.factories中配置的类
- 找到main方法找到启动主类
-
4. run方法中,做的工作
- StopWatch主要是监控启动过程,统计启动时间,检测应用是否已经启动或者停止。
-
- 加载SpringApplicationRunListener(也是通过META-INF/spring.factories),默认加载的是EventPublishingRunListener
-
- - 调用RunListener.starting()方法。
-
- - 根据args创建应用参数解析器ApplicationArguments;
-
+ - 调用RunListener.starting()方法。
+ - 根据args创建应用参数解析器ApplicationArguments;
- 准备环境变量:获取环境变量environment,将应用参数放入到环境变量持有对象中,监听器监听环境变量对象的变化(listener.environmentPrepared)
-
- 打印Banner信息(SpringBootBanner)
-
- 创建SpringBoot的应用上下文(AnnotationConfigEmbeddedWebApplicationContext)
-
- prepareContext上下文之前的准备
-
- refreshContext刷新上下文
-
- afterRefresh(ApplicationRunner,CommandLineRunner接口实现类的启动)
-
- 返回上下文对象
-
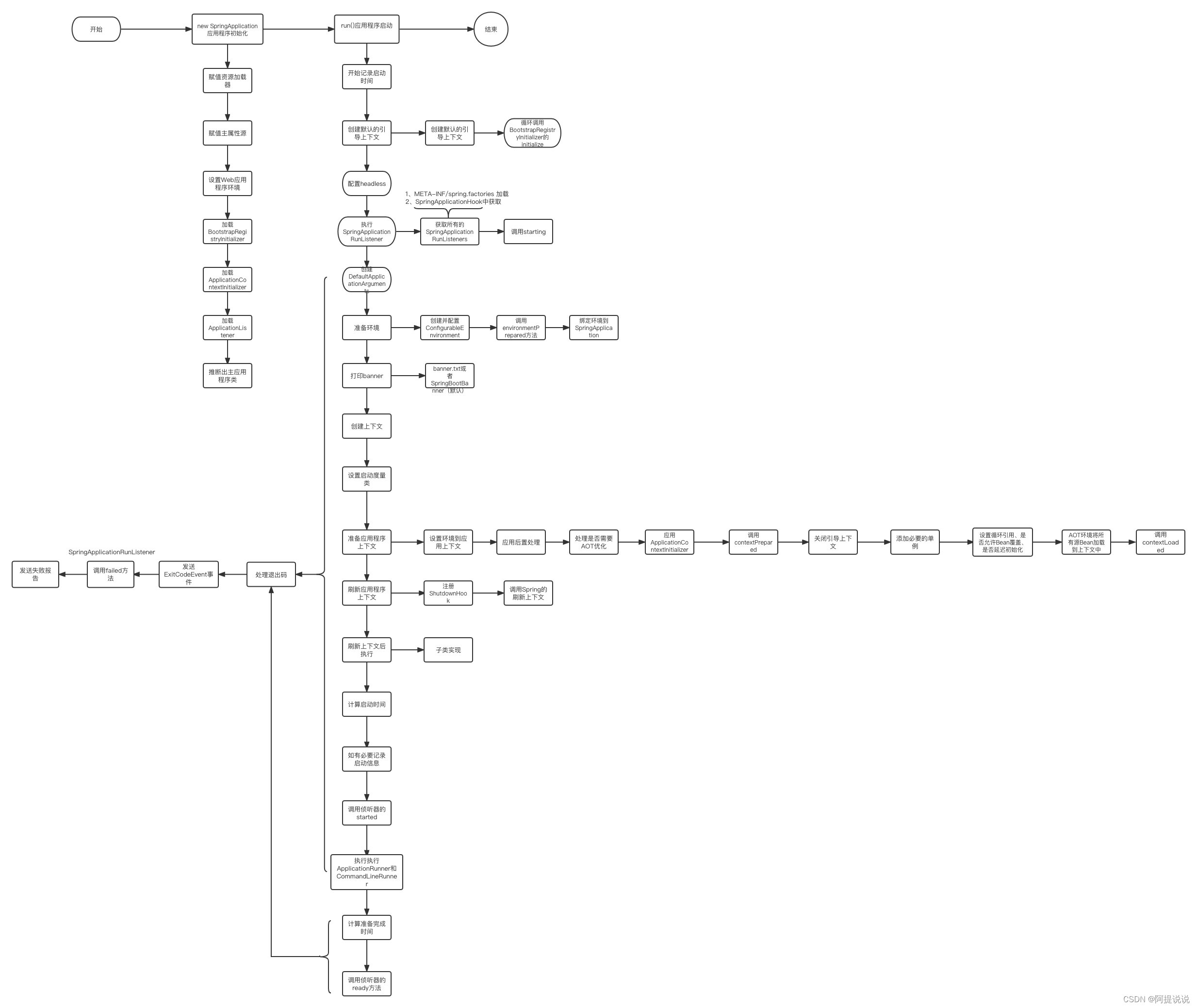
+基于SB3.x的启动流程图:
+
+
### Spring Boot启动的时候会加载哪些包?
在web项目中,会在Maven中配置 spring-boot-starter-web 包,该包中包含了spring-core、spring-content、servlet、tomcat、jackson、HikariCP、junit、jdbc、slf4j 等
+### Spring Boot 的监听器
+Spring Boot 的监听器指的是SpringApplicationRunListener和ApplicationListener
-### 如何重新加载 Spring Boot 上的更改,而无需重新启动服务器?
+SpringApplicationRunListener 是Spring Boot 定义的监听器,用于监听 `SpringApplication` 的启动过程,并在**启动的不同阶段执行自定义逻辑**(只在启动阶段)。它允许开发者在应用启动的各个生命周期节点插入自己的代码,例如初始化资源、记录日志、监控启动过程等,通过`META-INF/spring.factories` 文件配置注册。
+
+ApplicationListener是Spring 定义的监听器,能够监听 Spring 容器内发布的 `ApplicationEvent` 事件,覆盖应用的全生命周期,通过作为 Spring Bean 注册(如 `@Component`)、META-INF/spring.factories(org.springframework.context.ApplicationListener)、SpringApplication的addListener和配置文件context.istener.classes
-一共有三种方式,可以实现效果:
+
+
+### 如何重新加载 Spring Boot 上的更改,而无需重新启动服务器?
- 【推荐】`spring-boot-devtools` 插件。注意,这个工具需要配置 IDEA 的自动编译。
@@ -64,6 +61,8 @@ Spring Boot是 Spring 的子项目,正如其名字,提供 Spring 的引导(
- [JRebel](https://www.jianshu.com/p/bab43eaa4e14) 插件,需要付费。
+- 使用插件化开发,插件化代码使用手动注册Bean的方式
+
关于如何使用 `spring-boot-devtools` 和 Spring Loaded 插件,可以看看 [《Spring Boot 学习笔记:Spring Boot Developer Tools 与热部署》](https://segmentfault.com/a/1190000014488100) 。
@@ -71,8 +70,8 @@ Spring Boot是 Spring 的子项目,正如其名字,提供 Spring 的引导(
### 什么是 Spring Boot 自动配置?
1. Spring Boot 在启动时扫描项目所依赖的 jar 包,寻找包含`spring.factories` 文件的 jar 包。
-2. 根据 `spring.factories` 配置加载 AutoConfigure 类。
+2. 根据 `spring.factories` 配置加载 AutoConfigure 类。(Spring Boot 2.7 以后,从META-INF/spring/org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.AutoConfiguration.imports中加载配置的Jar包)
3. 根据 `@Conditional` 等条件注解的条件,进行自动配置并将 Bean 注入 Spring IoC 中。
-https://my.oschina.net/itsaysay/blog/3011826
+> 详细介绍:https://itsaysay.blog.csdn.net/article/details/131736129
diff --git a/12.Dubbo.md b/12.Dubbo.md
old mode 100755
new mode 100644
diff --git a/13.Spring Cloud.md b/13.Spring Cloud.md
old mode 100755
new mode 100644
index 13286a0..9ee37f4
--- a/13.Spring Cloud.md
+++ b/13.Spring Cloud.md
@@ -18,15 +18,15 @@ Spring Cloud 主要提供了如下核心的功能:
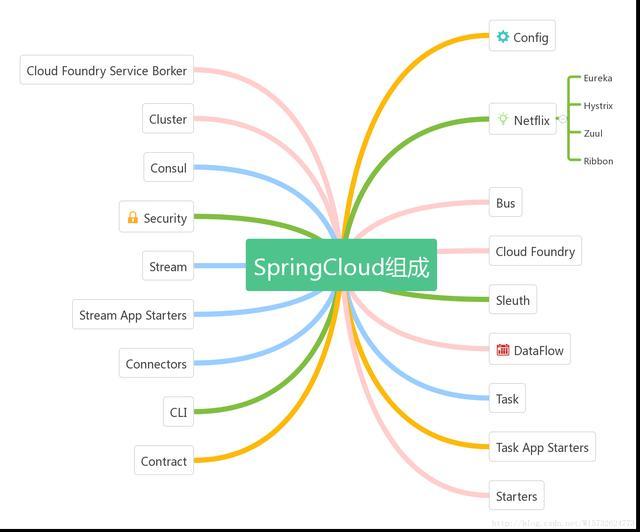
脑图如下:
-
+
由于 [Spring Cloud Netflix](https://github.com/spring-cloud/spring-cloud-netflix) 要进入维护模式,下面是一些可以替代组件
-| | Netflix | 阿里 | 其它 |
-| -------- | ------- | -------- | ------------------------------------------------------------ |
-| 注册中心 | Eureka | Nacos | Zookeeper、Consul、Etcd |
-| 熔断器 | Hystrix | Sentinel | Resilience4j |
-| 网关 | Zuul | 暂无 | Spring Cloud Gateway |
+| | Netflix | 阿里 | 其它 |
+| ---- | ------- | -------- | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
+| 注册中心 | Eureka | Nacos | Zookeeper、Consul、Etcd |
+| 熔断器 | Hystrix | Sentinel | Resilience4j |
+| 网关 | Zuul | 暂无 | Spring Cloud Gateway |
| 负载均衡 | Ribbon | Dubbo | [`spring-cloud-loadbalancer`](https://github.com/spring-cloud/spring-cloud-commons/tree/master/spring-cloud-loadbalancer) |
### Spring Cloud 和 Spring Boot 的区别和关系?
@@ -53,7 +53,7 @@ Spring Cloud 主要提供了如下核心的功能:
### SpringCloud的注册和发现流程,以Eureka为注册中心
-
+img
1. 服务启动时会生成服务的基本信息对象InstanceInfo,然后再启动时注册到服务治理中心
2. 服务注册完成后,会从服务治理中心拉取所有的服务信息,缓存在本地
@@ -100,139 +100,92 @@ Spring Cloud 主要提供了如下核心的功能:
在计算中,负载平衡可以改善跨计算机,计算机集群,网络链接,中央处理单元或磁盘驱动器等多种计算资源的工作负载分布。负载平衡旨在优化资源使用,最大化吞吐量,最小化响应时间并避免任何单一资源的过载。使用多个组件进行负载平衡而不是单个组件可能会通过冗余来提高可靠性和可用性。负载平衡通常涉及专用软件或硬件,例如多层交换机或域名系统服务器进程。
-### Ribbon 有哪些负载均衡算法?
-
-详细文章可见:[《Ribbon 负载均衡策略配置》](https://blog.csdn.net/rickiyeat/article/details/64918756)
-
-其中,默认的负载均衡算法是 Round Robin 算法,顺序向下轮询。
-
-### Ribbon 是怎么和 Eureka 整合的?
-
- Ribbon 原理图:
-
-
-
-- 首先,Ribbon 会从 Eureka Client 里获取到对应的服务列表。
-- 然后,Ribbon 使用负载均衡算法获得使用的服务。
-- 最后,Ribbon 调用对应的服务。
-
-另外,此处的 Eureka 仅仅是作为注册中心的举例,也是可以配合其它的注册中心使用,例如 Zookeeper 。可参考 [《以 Zookeeper 为注册中心搭建 Spring Cloud 环境》](https://www.jianshu.com/p/775c363d0fda) 文章。
-
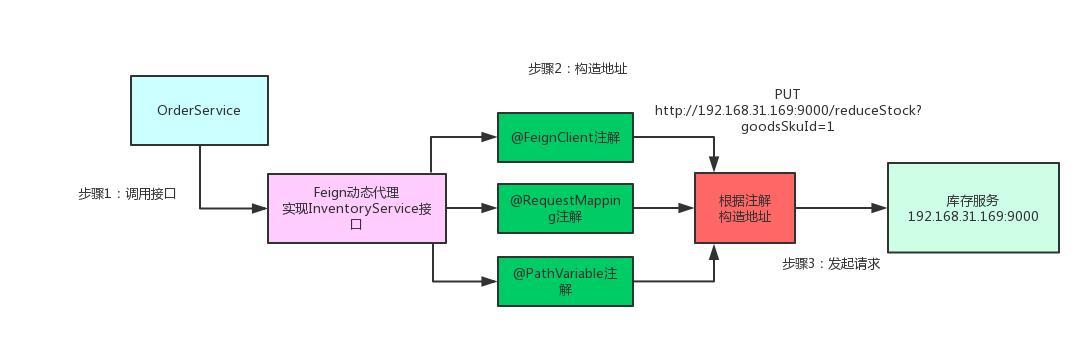
### Feign 实现原理
**Feign的一个关键机制就是使用了动态代理**。咱们一起来看看下面的图,结合图来分析:
- 首先,如果你对某个接口定义了 `@FeignClient` 注解,Feign 就会针对这个接口创建一个动态代理。
- 接着你要是调用那个接口,本质就是会调用 Feign 创建的动态代理,这是核心中的核心。
-- Feig n的动态代理会根据你在接口上的 `@RequestMapping` 等注解,来动态构造出你要请求的服务的地址。
+- Feign的动态代理会根据你在接口上的 `@RequestMapping` 等注解,来动态构造出你要请求的服务的地址。
- 最后针对这个地址,发起请求、解析响应。
-
+
### Feign 和 Ribbon 的区别?
Ribbon 和 Feign 都是使用于调用用其余服务的,不过方式不同。
- 启动类用的注解不同。
- - Ribbon 使用的是 `@RibbonClient` 。
- - Feign 使用的是 `@EnableFeignClients` 。
+ - Ribbon 使用的是 `@RibbonClient` 。
+ - Feign 使用的是 `@EnableFeignClients` 。
- 服务的指定位置不同。
- - Ribbon 是在 `@RibbonClient` 注解上设置。
- - Feign 则是在定义声明方法的接口中用 `@FeignClient` 注解上设置。
+ - Ribbon 是在 `@RibbonClient` 注解上设置。
+ - Feign 则是在定义声明方法的接口中用 `@FeignClient` 注解上设置。
- 调使用方式不同。
- - Ribbon 需要自己构建 Http 请求,模拟 Http 请求而后用 RestTemplate 发送给其余服务,步骤相当繁琐。
- - Feign 采使用接口的方式,将需要调使用的其余服务的方法定义成声明方法就可,不需要自己构建 Http 请求。不过要注意的是声明方法的注解、方法签名要和提供服务的方法完全一致。
-
-### Feign 是怎么和 Ribbon、Eureka 整合的?
-
-
-
-- 首先,用户调用 Feign 创建的动态代理。
-
-- 然后,Feign 调用 Ribbon 发起调用流程。
-
- - 首先,Ribbon 会从 Eureka Client 里获取到对应的服务列表。
-
- - 然后,Ribbon 使用负载均衡算法获得使用的服务。
-
- - 最后,Ribbon 调用 Feign ,而 Feign 调用 HTTP 库最终调用使用的服务。
-
-> 因为 Feign 和 Ribbon 都存在使用 HTTP 库调用指定的服务,那么两者在集成之后,必然是只能保留一个。比较正常的理解,也是保留 Feign 的调用,而 Ribbon 更纯粹的只负责负载均衡的功能。
-
-想要完全理解,建议胖友直接看如下两个类:
-
-- [LoadBalancerFeignClient](https://github.com/spring-cloud/spring-cloud-openfeign/blob/master/spring-cloud-openfeign-core/src/main/java/org/springframework/cloud/openfeign/ribbon/LoadBalancerFeignClient.java) ,Spring Cloud 实现 Feign Client 接口的二次封装,实现对 Ribbon 的调用。
-
-- [FeignLoadBalancer](https://github.com/spring-cloud/spring-cloud-openfeign/blob/master/spring-cloud-openfeign-core/src/main/java/org/springframework/cloud/openfeign/ribbon/FeignLoadBalancer.java) ,Ribbon 的集成。
-
-> 集成的是 AbstractLoadBalancerAwareClient 抽象类,它会自动注入项目中所使用的负载均衡组件。
-
-- LoadBalancerFeignClient =》调用=》 FeignLoadBalancer 。
-
-### Hystrix 隔离策略?
-
-Hystrix 有两种隔离策略:
-
-- 线程池隔离
-- 信号量隔离
-
-实际场景下,使用线程池隔离居多,因为支持超时功能。
-
-详细的,可以看看 [《Hystrix 的资源隔离策略》](https://blog.csdn.net/liuchuanhong1/article/details/73718794) 文章。
-
-#### 聊聊 Hystrix 缓存机制?
+ - Ribbon 需要自己构建 Http 请求,模拟 Http 请求而后用 RestTemplate 发送给其余服务,步骤相当繁琐。
+ - Feign 采使用接口的方式,将需要调使用的其余服务的方法定义成声明方法就可,不需要自己构建 Http 请求。不过要注意的是声明方法的注解、方法签名要和提供服务的方法完全一致。
-Hystrix 提供缓存功能,作用是:
-
-- 减少重复的请求数。
-- 在同一个用户请求的上下文中,相同依赖服务的返回数据始终保持一致。
-
-详细的,可以看看 [《Hystrix 缓存功能的使用》](https://blog.csdn.net/zhuchuangang/article/details/74566185) 文章。
-
-### 什么是 Hystrix 断路器?
-
-Hystrix 断路器通过 HystrixCircuitBreaker 实现。
+### 为什么要网关服务?
-HystrixCircuitBreaker 有三种状态 :
+使用网关服务,我们实现统一的功能:
-- `CLOSED` :关闭
-- `OPEN` :打开
-- `HALF_OPEN` :半开
+- 动态路由
+- 灰度发布
+- 健康检查
+- 限流
+- 熔断
+- 认证: 如数支持 HMAC, JWT, Basic, OAuth 2.0 等常用协议
+- 鉴权: 权限控制,IP 黑白名单,同样是 OpenResty 的特性
+- 可用性
+- 高性能
-其中,断路器处于 `OPEN` 状态时,链路处于**非健康**状态,命令执行时,直接调用**回退**逻辑,跳过**正常**逻辑。
+### 熔断和降级区别
-HystrixCircuitBreaker 状态变迁如下图 :
+熔断是下层服务一旦产生故障就断掉;降级需要对服务进行分级,把产生故障的服务丢掉,换一个轻量级的方案。
-
-- **红线**:初始时,断路器处于``CLOSED``状态,链路处于健康状态。当满足如下条件,断路器从``CLOSED``变成``OPEN``
- 状态:
+### Spring Cloud Gateway
- - **周期**( 可配,`HystrixCommandProperties.default_metricsRollingStatisticalWindow = 10000 ms` )内,总请求数超过一定**量**( 可配,`HystrixCommandProperties.circuitBreakerRequestVolumeThreshold = 20` ) 。
-- **错误**请求占总请求数超过一定**比例**( 可配,`HystrixCommandProperties.circuitBreakerErrorThresholdPercentage = 50%` ) 。
-
-- **绿线** :断路器处于 `OPEN` 状态,命令执行时,若当前时间超过断路器**开启**时间一定时间( `HystrixCommandProperties.circuitBreakerSleepWindowInMilliseconds = 5000 ms` ),断路器变成 `HALF_OPEN` 状态,**尝试**调用**正常**逻辑,根据执行是否成功,**打开或关闭**熔断器【**蓝线**】。
+#### 过滤器
-### 什么是 Hystrix 服务降级?
+分类:
-在 Hystrix 断路器熔断时,可以调用一个降级方法,返回相应的结果。当然,降级方法需要配置和编码,如果不需要,也可以不写,也就是不会有服务降级的功能。
+1、 GatewayFilter,网关过滤器,只应用在单个路由或者一个分组的路由上
-具体的使用方式,可以看看 [《通过 Hystrix 理解熔断和降级》](https://blog.csdn.net/jiaobuchong/article/details/78232920) 。
+- AddRequestHeader:用于在请求头中添加自定义键值对
+- AddRequestParameter:用于在请求中添加请求参数的键值对
+- AddResponseHeader:用于在响应头中添加键值对
+- Hystrix网关过滤工厂:用于将断路器引入网关路由中
+- PrefixPath:用于使用简单的Prefix参数
+- PreserveHostHeader:用于设置路由过滤器的请求属性,检查是否发送原始主机头或由HTTP客户端确定主机头
+- RequestRateLimiter:用于确定当前请求是否允许继续,如果不允许,返回提示"HTTP 429 - Too Many Requests"
+- RedirectTo:用于接收请求的状态和URL参数,该状态是一个重定向的300系列的HTTP代码,如301,URL是Location的头部值
+- RemoveNonProxyHeaders:用于从转发的请求中删除请求头
+- RemoveRequestHeader:用于删除请求头,需要请求头名
+- RemoveResponseHeader:用于响应头,需要响应头名
+- RewritePath:用于使用Java正则表达式重写请求路径
+- SaveSession:用于在转发下游调用之前强制执行保存Session操作
+- SecureHeaders:用于为响应添加安全头
+- SetPath:允许通过路径的模版段来操作请求的路径,使用了Spring框架的URI模版,支持多种匹配
+- SetResponseHeader:用于设置响应头,需要有一个Key-Value对
+- SetStatus:用于设置请求响应状态,需要一个Status参数,该参数的值必须是有效的SpringHttpStatus,
+- StripPrefix:用于剥离前缀,需要parts参数,表明在请求被发送到下游之前从请求路径中剥离的元素数量
+- Retry:用于重试
+- RequestSize:用于限制请求的大小,当请求超过限制时启用,限制请求到达下游服务,该过滤器将RequestSize作为参数
-### 为什么要网关服务?
+2、 GlobalFilter,全局过滤器,应用在所有的路由上
-使用网关服务,我们实现统一的功能:
+- Forward Routing Filter
+- LoadBalancerClientFilter
+- Netty Routing Filter
+- Netty Write Response Filter
+- RouteToRequestUrl Filter
+- Websocket Routing Filter
+- GateWay Metrics Filter 网关指标过滤器
+- Combined Global Filter and GateWayFilter 组合式全局过滤器和网关过滤器排序
+- Marking An Exchange As Routed 路由交换
-- 动态路由
-- 灰度发布
-- 健康检查
-- 限流
-- 熔断
-- 认证: 如数支持 HMAC, JWT, Basic, OAuth 2.0 等常用协议
-- 鉴权: 权限控制,IP 黑白名单,同样是 OpenResty 的特性
-- 可用性
-- 高性能
+> 详细见:[Spring Cloud Gateway 参考指南_cloud: gateway: metrics: enabled: true-CSDN博客](https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_40972073/article/details/125840118?ops_request_misc=%7B%22request%5Fid%22%3A%22171941508116800184151243%22%2C%22scm%22%3A%2220140713.130102334.pc%5Fblog.%22%7D&request_id=171941508116800184151243&biz_id=0&utm_medium=distribute.pc_search_result.none-task-blog-2~blog~first_rank_ecpm_v1~rank_v31_ecpm-1-125840118-null-null.nonecase&utm_term=gateway&spm=1018.2226.3001.4450)
-详细的,可以看看 [《为什么微服务需要 API 网关?》](http://dockone.io/article/2033) 。
diff --git a/14.Message Queue.md b/14.Message Queue.md
old mode 100755
new mode 100644
index 2201513..a7777b5
--- a/14.Message Queue.md
+++ b/14.Message Queue.md
@@ -8,6 +8,18 @@
Kafka是一款高性能的消息中间件,包括Producer,Consumer,Broker,以及Zookeeper,Zookeeper用来负责集群元数据管理,控制器的选举等操作,Producer将消息发送到Broker,由Broker负责将收到的消息存储到磁盘中,Consumer负责从Broker订阅并消费消息。Kafka中的消息是以主题为单位,主题可以分布在不同的分区,分区可以分布于不同的Broker,分区有Leader 与副本follower,follower负责从leader同步数据,leader负责读写请求
+从4.0.0开始彻底去掉了Zookeeper,转为使用 KRaft 模式
+
+| 特性 | Zookeeper 模式 | KRaft 模式 |
+| ------------------ | ---------------------------------------- | --------------------------------------------- |
+| **元数据存储** | 存储在 Zookeeper 中(内存 + 磁盘) | 存储在 Controller 节点的本地磁盘(Raft 日志) |
+| **控制器选举** | 由 Zookeeper 协调选举 | 基于 Raft 协议自主选举(Leader 节点即控制器) |
+| **元数据更新效率** | 需通过网络请求 Zookeeper,延迟较高 | 本地元数据直接更新,延迟低(毫秒级) |
+| **集群扩展性** | Zookeeper 集群扩容复杂,易成瓶颈 | 支持动态添加 Controller 节点,扩展性更好 |
+| **启动速度** | 需等待 Zookeeper 和 Kafka 双重初始化 | 仅需启动 Kafka 节点,启动更快 |
+| **数据一致性保障** | 依赖 Zookeeper 的 Paxos 协议 | 基于 Raft 协议,强一致性更易理解和维护 |
+| **安全性** | 需分别配置 Kafka 和 Zookeeper 的安全策略 | 统一的安全配置(如 SSL、SASL) |
+
#### 消息的幂等性处理思路
@@ -63,6 +75,16 @@ kafka保证消息可靠性,可以通过如下几个配置:
+#### 怎么保证消息顺序消费
+
+消息要顺序消费的场景,比如发送了一个用户新增的消息,随后用户修改了发送了一个修改的消息,最后又删除了发送了一个删除的消息,由于Kafka的多分区,多消费者,消费端势必会变成无序消费,但消费端业务需要顺序处理,如果先消费了删除消息,根本没数据,随后又消费了新增消息,最后消息没有删除,变成了脏数据。
+
+解决方法是:
+
+- 生产者发送消息的时候,根据用户id指定分区key,指定后kafka会将消息发送到指定的分区中,这样保证了分区中消息的顺序。消费端,可以使用单线程从指定分区中消费,如果要保证性能,消费端定义多个内存队列,将相同用户id的消息发送到同一个内存队列中,然后开启多线程从来消费多个内存队列,一个线程处理一个内存队列
+
+- 让消费者只消费一个指定的分区,速度会变慢
+
#### kafka的分区策略
消费者客户端参数partition.assignment.strategy 来配置消费分区策略
@@ -70,3 +92,90 @@ kafka保证消息可靠性,可以通过如下几个配置:
2. RoundRobinAssignor 轮询分配策略
3. StickyAssignor 能够使分区的分配尽可能与上一次保持一致,避免过度重分配
4. 自定义分配,实现PartitionAssignor接口
+
+
+
+#### kafka 集群如何搭建
+
+- 安装zk集群,修改各个节点的kafka配置文件server.properties(broker.id、listeners、zookeeper.connect)
+- 启动zk、启动kafka
+
+k8s 上创建:[K8s - 安装部署Kafka、Zookeeper集群教程(支持从K8s外部访问) - 蜂蜜log - 博客园 (cnblogs.com)](https://www.cnblogs.com/fengyuanfei/p/17789107.html)
+
+
+
+#### 什么是ISR
+
+- AR(Assigned Repllicas)一个partition的所有副本(即使replica,不区分leader或follower)
+- ISR(In-Sync Replicas)能够和leader保持同步的follower+leader本身组成的集合
+- OSR(Out-Sync Relipcas)不能和leader 保持同步的follower集合
+
+### RocketMQ
+
+#### RocketMQ的核心组件是什么
+
+NameServer: 轻量级服务发现中心,管理Broker的地址路由信息;无状态,支持快速扩容
+
+Broker: 消息存储和转发节点,负责接收生产者消息、持久化存储、投递给消费者;主从架构,支持同步/异步复制
+
+Producer: 消息生产者,通过NameServer找到目标Broker发送消息,支持同步、异步、单向发送模式
+
+Consumer: 消息消费者,从Broker拉取消息,支持集群消费和广播消费
+
+#### RocketMQ 的消息模型有哪些
+
+- 点对点(Queue模型):
+
+ 消息通过队列存储,同一消费者组内竞争消费(每条消息仅被一个消费者处理)
+
+- 发布/订阅(Pub-Sub):
+
+- 延迟消息
+- 顺序消息
+
+ 通过MessageQueueSelector 保证同一业务键(如订单ID)的消息发送到同一队列,消费者按队列顺序消费
+
+#### RocketMQ 如何保证消息不丢失
+
+1. 生产者端:同步发送+重试机制;事务消息
+
+2. Broker端:消息持久化,同步刷盘或异步刷盘;同步复制,保证Slave写入成功后才返回ACK
+
+3. 消费者端:手动提交消费偏移量;消费失败重试
+
+#### RocketMQ 怎么实现顺序消息
+
+生产者:通过MessageQueueSelector 将同一业务键(如订单ID)的消息发送到同一队列
+
+Broker:单个队列内的消息天然有序
+
+消费者:单线程消费队列(或锁保证并发安全),并且关闭异步提交消费偏移量
+
+#### 如何解决消息堆积问题
+
+1. 扩容消费者:增加消费者实例数(不超过队列数),提升并行消费能力
+2. 调整消费逻辑:优化消费代码(如批量处理,异步)
+3. 跳过非关键消息:在业务允许时,重置消费偏移量到最新位置
+
+#### 事务消息的实现原理
+
+RokectMQ支持在分布式场景下保障消息生产和本地事务的最终一致性。
+
+1. **第一阶段(发送半消息)**:
+ - 生产者发送"半消息"(对消费者不可见)到 Broker。
+ - Broker 返回 ACK 确认半消息持久化成功。
+2. **第二阶段(执行本地事务)**:
+ - 生产者执行本地事务(如数据库操作),生成事务状态(提交/回滚)。
+3. **Broker 回调检查**:
+ - 若生产者未响应,Broker 定期回调查询本地事务状态。
+4. **最终提交/回滚**:
+ - 根据事务状态提交(投递消息)或回滚(丢弃消息)。
+
+### RabbitMQ
+
+#### 说一下RabbitMQ
+
+RabbitMQ 是一个开源的消息代理软件,核心有Producer(生产者)、Consumer(消费者)、Queue(队列)、Exchange(交换机)、Binding(绑定)、Message(消息),交换机类型有:Fanout(广播到所有绑定的队列)、Direct(精确匹配路由键)、Topic(基于通配符的路由)、Headers(通过消息头属性匹配),另外有死信队列(DLX)可以处理失败或超时的消息,用来实现延时消息
+
+
+
diff --git a/15.Mybatis.md b/15.Mybatis.md
old mode 100755
new mode 100644
index 28cce8c..4c4d323
--- a/15.Mybatis.md
+++ b/15.Mybatis.md
@@ -62,7 +62,7 @@
-#####Mybatis 的 XML Mapper文件中,不同的 XML 映射文件,id 是否可以重复?
+### Mybatis 的 XML Mapper文件中,不同的 XML 映射文件,id 是否可以重复?
不同的 XML Mapper 文件,如果配置了 `"namespace"` ,那么 id 可以重复;如果没有配置 `"namespace"` ,那么 id 不能重复。毕竟`"namespace"` 不是必须的,只是最佳实践而已。
diff --git a/16.Zookeeper.md b/16.Zookeeper.md
old mode 100755
new mode 100644
index caef830..c16f716
--- a/16.Zookeeper.md
+++ b/16.Zookeeper.md
@@ -1,4 +1,6 @@
-# 16.Zookeeper
+# 16.注册中心
+
+## Zookeeper
### Zookeeper 是什么?
@@ -200,4 +202,51 @@ Zookeeper 的选举算法有两种:一种是基于 basic paxos 实现的,另
FastLeaderElection 算法通过异步的通信方式来收集其它节点的选票,同时在分析选票时又根据投票者的当前状态来作不同的处理,以加快 Leader 的选举进程。
- 流程
\ No newline at end of file
+ 流程
+
+## Nacos
+
+### Nacos 与 Eureka、Consul、Zookeeper 等注册中心有何区别?
+
+| 特性 | Nacos | Eureka | Consul | Zookeeper |
+| :----------- | :------------------------- | :---------- | :------------ | :--------- |
+| 一致性协议 | AP + CP 可切换 | AP | CP | CP |
+| 健康检查 | TCP/HTTP/MYSQL/Client Beat | Client Beat | TCP/HTTP/gRPC | Keep Alive |
+| 负载均衡 | 权重/metadata/Selector | Ribbon | Fabio | - |
+| 配置中心 | 支持 | 不支持 | 支持 | 支持 |
+| 雪崩保护 | 支持 | 支持 | 不支持 | 不支持 |
+| 自动注销实例 | 支持 | 支持 | 支持 | 支持 |
+| 访问协议 | HTTP/DNS | HTTP | HTTP/DNS | 客户端 |
+| 监听支持 | 支持 | 支持 | 支持 | 支持 |
+| 多数据中心 | 支持 | 支持 | 支持 | 不支持 |
+| 跨注册中心 | 支持 | 不支持 | 支持 | 不支持 |
+| 易用性 | 简单 | 简单 | 中等 | 复杂 |
+
+Nacos 的优势在于:
+
+- 同时支持服务发现和配置管理
+- 支持 AP 和 CP 两种模式切换
+- 提供更丰富的健康检查机制
+- 支持权重路由等更灵活的路由策略
+- 提供更友好的管理界面
+
+### Nacos 如何实现配置的动态更新?其原理是什么?
+
+1. **客户端长轮询机制**:
+ - 客户端发起配置查询请求时,会携带配置的 MD5 值
+ - 服务端比较客户端 MD5 和服务端 MD5:
+ - 如果相同,服务端会保持连接,直到配置发生变化或超时(默认 30s)
+ - 如果不同,立即返回最新配置
+2. **服务端配置变更处理**:
+ - 当管理员通过控制台或 API 更新配置时
+ - 服务端更新配置并计算新 MD5
+ - 服务端检查所有保持的长轮询连接
+ - 向相关客户端发送配置变更通知
+3. **客户端处理更新**:
+ - 客户端收到变更通知后,立即拉取最新配置
+ - 更新本地缓存和内存中的配置值
+ - 触发配置变更回调(如果有注册监听器)
+4. **监听器机制**:
+ - 应用可以注册配置监听器
+ - 当配置变更时,监听器会被触发
+ - 应用可以在监听器中实现自定义逻辑
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/17.Maven.md b/17.Maven.md
old mode 100755
new mode 100644
diff --git a/18.Open Question.md b/18.Open Question.md
old mode 100755
new mode 100644
index 6b4198b..75a2ece
--- a/18.Open Question.md
+++ b/18.Open Question.md
@@ -1,16 +1,12 @@
# 18.开放题
-##### 假设一个场景,要求stop the world时间非常短,你会怎么设计垃圾回收机制?
+### 假设一个场景,要求stop the world时间非常短,你会怎么设计垃圾回收机制?
STW时间短即要求应用响应时间快,应用的绝大多数对象都存在年轻代中,并且能够活到GC的对象很少,所以采用复制算法,只需要复制少量的对象就可以完成收集,同时将年轻代大小调大,通过-Xmn设置。由于年轻代分为Eden区和两个Survivor区,大部分新生对象都存在Eden区,因此还可以通过-XX:SurvivorRatio 调大Eden区的比例,比如-XX:SurvivorRatio=4,表示两个Survivor区与一个Eden区的比值为2:4
+### 现在有一个A类,其中有A、B、C方法,C方法中调用了A、B,定义了一个A、B方法的日志切面,请问能打印出日志吗?
-
-##### 现在有一个A类,其中有A、B、C方法,C方法中调用了A、B,定义了一个A、B方法的日志切面,请问能打印出日志吗?
-
-
-
-##### 分级代理问题
+### 分级代理问题
某公司销售一款智能硬件柜机,内含多种可消费的服务。
@@ -27,9 +23,17 @@ STW时间短即要求应用响应时间快,应用的绝大多数对象都存
2. 假设订单成功消息将触发onTransactionSuccess( ... )方法,请给出(...)部分的必要参数列表
3. 写出onTransactionSuccess方法的伪代码,调用#1列出的方法完成分成逻辑
+### 设计短链接问题
+https://blog.csdn.net/xlgen157387/article/details/80026452
+
+
+
+### TCP连接如何保证安全
+
+TCP 连接只要有IP+端口就可以,首先要保证连接的安全性,通过TLS对TCP的传输数据进行加密。
+
+防止报文重放:TCP连接后,由平台生成一个随机秘钥下发给客户端,每次数据传输都对数据进行签名,接收方对签名进行校验,计算规则可以是:data+timeStamp+signKey,接收方首先会校验时间戳有效性(比如30秒内有效),接着校验数据签名,签名不一致表示报文数据可能有篡改。
-##### 设计短链接问题
-https://blog.csdn.net/xlgen157387/article/details/80026452
diff --git a/19.Distribute_MicroService.md b/19.Distribute_MicroService.md
old mode 100755
new mode 100644
index 472a466..98922cc
--- a/19.Distribute_MicroService.md
+++ b/19.Distribute_MicroService.md
@@ -30,7 +30,11 @@ Soft-state:在基于client-server模式的系统中,server端是否有状态
Eventually consistent:数据最终一致性
+### CAP 为什么只能满足两项
+由于分布式系统中存在网络的不稳定因素(网络故障、丢包等),因此在分布式系统中P(分区容错性)是首先要满足的。此时,如果要保证C(一致性),当A更新了数据,必须等待B同步更新数据才能响应客户端,如果中间出现网络问题,就不能响应客户端,这时就无法保证A(可用性);
+
+如果要保证A(可用性),就需要立即响应客户端,但A、B数据可能会不一致,无法保证C(一致性)
### 微服务与 SOA 的区别
@@ -80,7 +84,7 @@ SOA即面向服务架构,关注点是服务,现有的分布式服务化技
1. 2PC两阶段提交
- 分准备阶段、提交阶段,由事务管理协调器发起
+ 分**准备阶段、提交阶段**,由事务管理协调器发起
准备阶段:事务管理器向参与者发起指令,参与者评估自己的状态,如果参与者评估指令可以完成,则会写redo或者undo日志,然后锁定资源,执行操作,但并不提交。如果其中一个参与者返回准备准备失败,则协调者向参与者发起中止指令,参与者取消已经变更的事务,执行undo日志,释放锁定的资源
@@ -140,6 +144,13 @@ SOA即面向服务架构,关注点是服务,现有的分布式服务化技
Paxos 算法运行在运行宕机故障的异步系统中,它不要求可靠的消息传递,也容忍消息丢失,延迟,乱序和重复,它利用大多数机制保证了"2F+1"的容错能力,即"2F+1"个节点的系统最多允许F个节点同时出现故障
+### Seata 支持事务模式
+
+1. AT模式,基于2PC实现,适用高并发、对性能敏感的业务场景
+2. TCC模式,基于TCC实现,侵入业务,需要实现TCC的逻辑
+3. Saga模式,基于Saga实现,适用业务流程长的场景
+4. XA模式,基于XA协议(2PC实现),适用使用XA模式的老应用迁移到Seata平台,以及AT模式未适配的数据库应用
+
### 说说达到最终一致性的方案
1. 查询模式,通过查询了解调用服务的最终处理情况,决定下一步做什么
@@ -158,8 +169,29 @@ SOA即面向服务架构,关注点是服务,现有的分布式服务化技
如果实例服务是分布式部署,需要将同一请求路由到同一个实例,可以通过某个请求参数的hash路由,也可以通过Nginx的hash路由功能
- https://blog.csdn.net/dustin_cds/article/details/79595297
+ https://blog.csdn.net/dustin_cds/article/details/79595297
+
+### 架构设计原则
+
+要保持模块模块大小适中,尽可能减少调用深度,多扇入少扇出,保持高内聚低耦合,单入口、单出口,模块的作用域要在模块内,模块功能是可预测的,另外面向对象设计要遵守如下原则:
+
+- 单一责任原则:一个类只做一种责任类型
+
+比如,一个"用户类"不应同时负责用户信息管理和订单生成,这两项职责应拆分到"用户类"和"订单类"中
+
+- 开放-封闭原则:支持扩展,不支持修改
+
+比如,一个"支付接口"可以通过新增"支付宝实现类","微信支付实现类"来扩展支付方式,而不是修改原有的接口
+
+- 里氏替换原则:子类可以替换父类
+
+比如,一个支付接口,子类无论是"支付宝实现类"还是"微信支付实现类",都能正常实现支付
+
+- 依赖倒置原则:细节依赖抽象
+
+比如,订单服务调用物流服务时,依赖的是物流服务的抽象接口,而非具体的"顺丰物流"、"圆通物流"
+- 接口分离原则:不强迫适用,依赖抽象,不依赖具体
+一个 "多功能设备接口" 不应包含 "打印""扫描""复印" 所有方法,而应拆分为 "打印接口""扫描接口" 等,让仅需打印功能的客户端只依赖 "打印接口"
-###
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/2.Java Concurrent.md b/2.Java Concurrent.md
old mode 100755
new mode 100644
index 9b138ec..d78dcfd
--- a/2.Java Concurrent.md
+++ b/2.Java Concurrent.md
@@ -6,7 +6,7 @@
### 运行中的线程能否强制杀死
-Jdk提供了stop()方法用于强制停止线程,但官方并不建议使用,因为强制停止线程会导致线程使用的资源,比如文件描述符、网络连接处于不正常的状态。建议使用标志位的方式来终止线程,如果线程中有使用无限期的阻塞方式,比如wait()没有设置超时时间,就只能使用interrupt()方法来终止线程
+Jdk提供了stop()方法用于强制停止线程,但官方并不建议使用,因为强制停止线程会导致线程使用的资源,比如文件描述符、网络连接处于不正常的状态。建议使用标志位的方式来终止线程,如果线程中有使用无限期的阻塞方式,比如wait()没有设置超时时间,就只能使用interrupt()方法来终止线程
```java
@SneakyThrows
@@ -39,15 +39,24 @@ class Thread1 extends Thread{
### ThreadLocal 子类及原理, OOM产生原因及防治
- InheritableThreadLocal
-
- 继承了ThreadLocal,并重写childValue、getMap、createMap,对该类的操作实际是对线程ThreadLocalMap的操作
-
+ 继承了ThreadLocal,并重写childValue、getMap、createMap,对该类的操作实际是对线程ThreadLocalMap的操作。
子线程能够读取父线程数据,实际原因是新建子线程的时候,会从父线程copy数据
+
+> 使用场景:子线程能够访问父线程设置的信息
-- OOM原因及防治
+- ThreadLocal原理及OOM原因及防治
ThreadLocal只是一个工具类,具体存放变量的是线程的threadLocals变量,threadLocals是一个ThreadLocalMap类型的变量,内部是一个Entry数组,Entry继承自WeakReference,Entry内部的value用来存放通过ThreadLocal的set方法传递的值,key是ThreadLocal的弱引用,key虽然会被GC回收,但value不能被回收,这时候ThreadLocalMap中会存在key为null,value不为null的entry项,如果时间长了就会存在大量无用对象,造成OOM。虽然set,get也提供了一些对Entry项清理的时机,但不及时,`所以在使用完毕后需要及时调用remove`
-
- https://www.cnblogs.com/micrari/p/6790229.html
+
+> 源码分析:[ThreadLocal源码解读](源码分析/ThreadLocal.md) 源码分析/ThreadLocal.md
+
+### 分布式系统中使用ThreadLocal 要注意的问题
+
+- 跨服务调用,ThreadLocal存储的数据丢失
+
+通过协议头(HTTP Header、RPC元数据)携带ThreadLocal中存储的数据,接收方在将协议头中的数据重新设置到本地ThreadLocal中
+
+- 线程池复用,导致数据污染
+ 无论是否使用线程池,都在数据使用完毕后,调用ThreadLocal.remove(),避免复用污染
### 有哪些并发队列
@@ -56,8 +65,11 @@ LinkedBlockingQueue: 有界阻塞队列,使用单向链表实现,通过Reent
ArrayBlockingQueue: 有界数组方式实现的阻塞队列 , 通过ReentrantLock实现线程安全,阻塞通过Condition实现,出队和入队使用同一把锁
PriorityBlockingQueue: 带优先级的无界阻塞队列,内部使用平衡二叉树堆实现,遍历保证有序需要自定排序
DelayQueue: 无界阻塞延迟队列,队列中的每个元素都有个过期时间,当从队列获取元素时,只有过期元素才会出队列,队列头元素是最快要过期的元素
-SynchronousQueue: 任何一个写需要等待一个读的操作,读操作也必须等待一个写操作,相当于数据交换 https://www.cnblogs.com/dwlsxj/p/Thread.html
-LinkedTransferQueue: 由链表组成的无界阻塞队列,多了tryTransfer 和 transfer方法。transfer方法,能够把生产者元素立刻传输给消费者,如果没有消费者在等待,那就会放入队列的tail节点,并阻塞等待元素被消费了返回,可以使用带超时的方法。tryTransfer方法,会在没有消费者等待接收元素的时候马上返回false
+SynchronousQueue: 任何一个写需要等待一个读的操作,读操作也必须等待一个写操作,相当于数据交换
+
+> [SynchronousQueue原理详解-公平模式](源码分析/SynchronousQueue.md) 源码分析/SynchronousQueue.md
+
+LinkedTransferQueue: 由链表组成的无界阻塞队列,多了tryTransfer 和 transfer方法。transfer方法,能够把生产者元素立刻传输给消费者,如果没有消费者在等待,那就会放入队列的tail节点,并**阻塞**等待元素被消费了返回,可以使用带超时的方法。tryTransfer方法,会在没有消费者等待接收元素的时候**马上返回false**
LinkedBlockingDeque: 由链表组成的双向阻塞队列,可以从队列的两端插入和移除元素
@@ -65,27 +77,18 @@ LinkedBlockingDeque: 由链表组成的双向阻塞队列,可以从队列的
- 构造参数:
corePoolSize: 线程池核心线程个数
-
maximunPoolSize: 线程池最大线程数量
-
keeyAliveTime: 空闲线程存活时间
-
TimeUnit: 存活时间单位
-
workQueue: 用于保存等待执行任务的阻塞队列
-
ThreadFactory: 创建线程的工厂
RejectedExecutionHandler: 队列满,并且线程达到最大线程数量的时候,对新任务的处理策略,AbortPolicy(抛出异常)、CallerRunsPolicy(使用调用者所在线程执行)、DiscardOldestPolicy(调用poll丢弃一个任务,执行当前任务)、DiscardPolicy(默默丢弃、不抛异常)
-
+
- 原理:
线程池主要是解决两个问题:
-
一个是当执行大量异步任务时能够提供较好的性能,能复用线程处理任务;
-
二是能够对线程池进行资源限制和管理。
-
一个任务提交的线程池,首先会判断核心线程池是否已满,未满就会创建worker线程执行任务,已满判断阻塞队列是否已满,阻塞队列未满加入阻塞队列,已满就判断线程池线程数量是否已经达到最大值,没有就新建线程执行任务,达到最大值的话执行拒绝策略。
-
拒绝策略有:直接抛出异常、使用调用者所在线程执行、丢弃一个旧任务,执行当前任务、直接丢弃什么都不做。
- 创建线程池的方式:直接new ThreadPoolExecutor 或者通过Executors工具类创建
@@ -97,7 +100,7 @@ LinkedBlockingDeque: 由链表组成的双向阻塞队列,可以从队列的
3. newCachedThreadPool 创建一个核心线程数为0,最大线程为Inter.MAX_VALUE的线程池,也就是说没有限制,线程池中的线程数量不确定,但如果有空闲线程可以复用,则优先使用,如果没有空闲线程,则创建新线程处理任务,处理完放入线程池
4. newSingleThreadScheduledExecutor 创建只有一个线程的可以定时执行的线程池
5. newScheduledThreadPool 创建一个没有最大线程数限制的可以定时执行线程池
-6. newWorkStealingPool 创建一个含有足够多线程的线程池,能够调用闲置的CPU去处理其他的任务,使用ForkJoinPool实现,jdk8新增
+6. newWorkStealingPool 创建一个含有足够多线程的线程池,能够调用闲置的CPU去处理其他的任务,使用ForkJoinPool实现,jdk8新增(线程数量根据当前系统的可用处理器核心数(逻辑核心),默认值等于系统的逻辑核心数量)
### 线程池的阻塞队列为什么都用LinkedBlockingQueue,而不用ArrayBlockingQueue
@@ -113,7 +116,7 @@ ArrayBlockingQueue 使用数组实现,在声明的时候必须指定长度,
如CPU密集型的任务,基本线程池应该配置多大?IO密集型的任务,基本线程池应该配置多大?用有界队列好还是无界队列好?任务非常多的时候,使用什么阻塞队列能获取最好的吞吐量?
-CPU密集型,为了充分使用CPU,减少上下文切换,线程数配置成CPU个数+1个即可
+CPU密集型,为了充分使用CPU,减少上下文切换,线程数配置成CPU个数+1个即可(线程数略多于核心数可避免因个别线程偶尔阻塞导致的CPU闲置,同时避免过多上下文切换)
IO密集型,由于可能大部分线程在处理IO,IO都比较耗时,因此可以配置成 2*CPU个数的线程,去处理其他任务
@@ -206,83 +209,83 @@ public class CopyOnWriteArrayListTest {
- CountDownLatch:
使用AQS实现,通过AQS的状态变量state来作为计数器值,当多个线程调用countdown方法时实际是原子性递减AQS的状态值,当线程调用await方法后当前线程会被放入AQS阻塞队列等待计数器为0再返回
-
- ```java
- public class CountDownLatchTest {
-
- public static final CountDownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(2);
-
- ExecutorService executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2);
-
- @Test
- public void test1() throws InterruptedException {
- executor.submit(() -> {
- System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " step1");
- countDownLatch.countDown();
- });
- executor.submit(() -> {
- System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " step2");
- countDownLatch.countDown();
- });
-
- countDownLatch.await();
- System.out.println("thread end");
- }
- }
- ```
-
- ```
- pool-1-thread-1 step1
- pool-1-thread-2 step2
- thread end
- ```
-
-
+
+ ```java
+ public class CountDownLatchTest {
+
+ public static final CountDownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(2);
+
+ ExecutorService executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2);
+
+ @Test
+ public void test1() throws InterruptedException {
+ executor.submit(() -> {
+ System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " step1");
+ countDownLatch.countDown();
+ });
+ executor.submit(() -> {
+ System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " step2");
+ countDownLatch.countDown();
+ });
+
+ countDownLatch.await();
+ System.out.println("thread end");
+ }
+ }
+ ```
+
+ ```
+ pool-1-thread-1 step1
+ pool-1-thread-2 step2
+ thread end
+ ```
+
+
- CyclicBarrier:
区别:CountDownLatch计数器是一次性的,变为0后就起不到线程同步的作用了。而CyclicBarrier(撒克里克巴瑞儿)在计数器变为0后重新开始,通过调用await方法,能在所有线程到达屏障点后统一执行某个任务,再执行完后继续执行子线程,通过ReentrantLock实现
-
- ```java
- public class CyclicBarrierTest {
-
- public static final CyclicBarrier cycle = new CyclicBarrier(3);
-
- ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2);
-
- @Test
- public void test1() throws BrokenBarrierException, InterruptedException {
- executorService.submit(() -> {
- System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());
- try {
- cycle.await();
- System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ",执行结束");
- } catch (InterruptedException | BrokenBarrierException e) {
- e.printStackTrace();
- }
- });
-
- executorService.submit(() -> {
- System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());
- try {
- Thread.sleep(3000);
- cycle.await();
- System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ",执行结束");
- } catch (InterruptedException | BrokenBarrierException e) {
- e.printStackTrace();
- }
- });
- cycle.await();
- }
- }
- ```
-
- ```
- pool-1-thread-1
- pool-1-thread-2
- pool-1-thread-2,执行结束
- pool-1-thread-1,执行结束
- ```
-
+
+ ```java
+ public class CyclicBarrierTest {
+
+ public static final CyclicBarrier cycle = new CyclicBarrier(3);
+
+ ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2);
+
+ @Test
+ public void test1() throws BrokenBarrierException, InterruptedException {
+ executorService.submit(() -> {
+ System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());
+ try {
+ cycle.await();
+ System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ",执行结束");
+ } catch (InterruptedException | BrokenBarrierException e) {
+ e.printStackTrace();
+ }
+ });
+
+ executorService.submit(() -> {
+ System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());
+ try {
+ Thread.sleep(3000);
+ cycle.await();
+ System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ",执行结束");
+ } catch (InterruptedException | BrokenBarrierException e) {
+ e.printStackTrace();
+ }
+ });
+ cycle.await();
+ }
+ }
+ ```
+
+ ```
+ pool-1-thread-1
+ pool-1-thread-2
+ pool-1-thread-2,执行结束
+ pool-1-thread-1,执行结束
+ # 等待所有线程都执行完成
+ ```
### Phaser 的实现
@@ -307,7 +310,7 @@ public class PhaserTest {
executor.submit(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " step2");
- phaser.arrive(d);
+ phaser.arrive();
});
//等同await()
@@ -401,39 +404,40 @@ Thread2:1
什么时候使用volatile?
+- 有一个变量,这个变量需要被多线程检查某个条件,此时使用volatile确保每次都从主内存读取
+
- 写入变量值不依赖变量的当前值。因为如果依赖当前值,将是获取-计算-写入三步操作,这三步操作不是原子性的,而volatile不保证原子性
- 读写变量值时没有加锁。因为加锁已经保证了内存可见性,没必要再使用volatile
-
volatile不能保证原子性
-
- ```java
- public class VolatileTest {
-
- public volatile int inc = 0;
-
- public void increase() {
- inc++;
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- final VolatileTest test = new VolatileTest();
-
- for(int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { - new Thread(() -> {
- for(int j = 0; j < 1000; j++) - test.increase(); - }).start(); - } - //保证前面的线程都执行完 - while (Thread.activeCount()> 1)
- Thread.yield();
-
- System.out.println(test.inc);
- }
- }
- //输出:<=10000 - ``` + + ```java + public class VolatileTest { + + public volatile int inc = 0; + + public void increase() { + inc++; + } + + public static void main(String[] args) { + final VolatileTest test = new VolatileTest(); + + for(int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { + new Thread(() -> {
+ for(int j = 0; j < 1000; j++) + test.increase(); + }).start(); + } + //保证前面的线程都执行完 + while (Thread.activeCount()> 1)
+ Thread.yield();
+
+ System.out.println(test.inc);
+ }
+ }
+ //输出:<=10000 + ``` ### 伪共享 @@ -443,8 +447,6 @@ Thread2:1> @Contended注解只用于Java核心类,如果用户类路径下的类要使用这个注解,需要添加JVM参数:-XX:-RestrictContended。默认填充宽度为128,需要自定义宽度设置 -XX:ContendedPaddingWidth参数
-> CPU缓存行详细说明:https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/yosnZr0bDdLrhmpnX8TY5A
-
### 原子操作类
**AtomicBoolean**
@@ -456,19 +458,15 @@ Thread2:1
整型的原子操作类,1.8后提供函数式操作的方法
- int getAndUpdate(IntUnaryOperator updateFunction)
-
使用指定函数计算并更新,返回计算前结果
- int updateAndGet(IntUnaryOperator updateFunction)
-
使用指定函数计算并更新,返回计算后的结果
- int getAndAccumulate(int x,IntBinaryOperator accumulatorFunction)
-
使用指定的函数计算x值和当前值,返回计算前结果
- int accumulateAndGet(int x,IntBinaryOperator accumulatorFunction)
-
使用指定的函数计算x值和当前值,返回结算后的结果
```java
@@ -510,15 +508,12 @@ public void atomicIntegerTest() {
提供了原子性更新整型数组元素的方式
- int getAndUpdate(int i, IntUnaryOperator updateFunction)
-
使用指定函数计算i索引的值,返回计算前结果
- int updateAndGet(int i, IntUnaryOperator updateFunction)
-
使用指定函数计算i索引的值,返回计算后结果
- int getAndAccumulate(int i, int x, IntBinaryOperator accumulatorFunction)
-
使用指定的函数计算x值和i索引的值,返回计算前结果
- int accumulateAndGet(int i, int x, IntBinaryOperator accumulatorFunction)
@@ -683,46 +678,53 @@ public void test1() {
AtomicStampedReference解决ABA问题,通过维护一个版本号
```java
-@SneakyThrows
-@Test
-public void test2() {
- AtomicStampedReference atomicStampedReference = new AtomicStampedReference(10,1);
-
- CountDownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(2);
+ //AtomicStampedReference,通过维护一个版本号
+ @SneakyThrows
+ @Test
+ public void test2() {
+ AtomicStampedReference atomicStampedReference = new AtomicStampedReference(10,1);
- new Thread(() -> {
- System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 第一次版本:" + atomicStampedReference.getStamp());
- atomicStampedReference.compareAndSet(10, 11, atomicStampedReference.getStamp(), atomicStampedReference.getStamp() + 1);
- System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 第二次版本:" + atomicStampedReference.getStamp());
- atomicStampedReference.compareAndSet(11, 10, atomicStampedReference.getStamp(), atomicStampedReference.getStamp() + 1);
- System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 第三次版本:" + atomicStampedReference.getStamp());
- countDownLatch.countDown();
- }).start();
+ CountDownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(2);
- new Thread(() -> {
- System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 第一次版本:" + atomicStampedReference.getStamp());
- try {
- TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);
- boolean isSuccess = atomicStampedReference.compareAndSet(10,12, atomicStampedReference.getStamp(), atomicStampedReference.getStamp() + 1);
- System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 修改是否成功:" + isSuccess + " 当前版本:" + atomicStampedReference.getStamp() + " 当前值:" + atomicStampedReference.getReference());
+ new Thread(() -> {
+ //使用第一次获取的版本,因为不知道有其他线程偷摸改了
+ int stamp = atomicStampedReference.getStamp();
+ System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 第一次版本:" + stamp);
+ try {
+ //等待一下
+ TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);
+ //这个线程打算修改10->12
+ boolean isSuccess = atomicStampedReference.compareAndSet(10,12, stamp, stamp + 1);
+ System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 修改是否成功:" + isSuccess + " 当前版本:" + atomicStampedReference.getStamp() + " 当前值:" + atomicStampedReference.getReference());
+ countDownLatch.countDown();
+ } catch (InterruptedException e) {
+ e.printStackTrace();
+ }
+ }).start();
+
+ new Thread(() -> {
+ //这个线程偷摸的把10->11->10
+ System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 第一次版本:" + atomicStampedReference.getStamp());
+ atomicStampedReference.compareAndSet(10, 11, atomicStampedReference.getStamp(), atomicStampedReference.getStamp() + 1);
+ System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 第二次版本:" + atomicStampedReference.getStamp());
+ atomicStampedReference.compareAndSet(11, 10, atomicStampedReference.getStamp(), atomicStampedReference.getStamp() + 1);
+ System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 第三次版本:" + atomicStampedReference.getStamp());
countDownLatch.countDown();
- } catch (InterruptedException e) {
- e.printStackTrace();
- }
- }).start();
+ }).start();
- countDownLatch.await();
-}
+
+ countDownLatch.await();
+ }
```
```java
//输出
+Thread-1 第一次版本:1
Thread-0 第一次版本:1
-Thread-0 第二次版本:2
-Thread-0 第三次版本:3
-Thread-1 第一次版本:3
-Thread-1 修改是否成功:true 当前版本:4 当前值:12
+Thread-1 第二次版本:2
+Thread-1 第三次版本:3
+Thread-0 修改是否成功:false 当前版本:3 当前值:10
```
AtomicMarkableReference 通过标志位,由于其标志位只有true和false,如果每次更新都变更标志位,在第三次的时候标志位还是跟第一次一样,并没有解决ABA问题
@@ -911,7 +913,7 @@ public void LongAccumulatorTest() {
3. BlockingQueue阻塞队列 put() 和take方法
4. Semaphore 基于计数的信号量
5. PipedInputStream / PipedOutputStream 管道输入输出流
-https://blog.csdn.net/ldx19980108/article/details/81707751
+ https://blog.csdn.net/ldx19980108/article/details/81707751
### 说说Random 与 ThreadLocalRandom
@@ -931,3 +933,71 @@ https://www.jianshu.com/p/89dfe990295c
https://blog.csdn.net/m0_37542889/article/details/92640903
+### Lambda表达式和Stream API 的底层实现原理
+
+- Lambda表达式
+
+Java8引入的函数式编程语法糖,依赖函数式接口(只有一个抽象方法的接口),本质是该接口抽象方法的实现,通过invokedynamic 指令和方法句柄(Method Handle)实现动态绑定,能够减少匿名内部类带来的类加载开销和字节码冗余
+
+- Stream API
+
+底层通过Pipeline(流水线)、Spliterator(拆分器)实现,支持串行和并行处理。
+
+Pipeline(流水线)由数据源(如List)、中间操作(如filter、map)和终端操作(如collect、forEach)组成,中间操作是"惰性的",仅记录操作逻辑,不立即执行,到达终点后才遍历数据源,依次执行中间操作
+
+Spliterator 用于拆分数据源的迭代器(支持并行处理),定义了`trySplit()` 方法(拆分数据为子部分)和 `tryAdvance()` 方法(遍历元素)
+
+并行流:基于ForkJoin框架,通过 Spliterator 将数据源拆分为多个子任务,由多个线程并行处理,最后合并结果
+
+### 用过流没有,流怎么实现
+
+Stream流是Java8中引入的新特性,Stream有几个特点:
+
+不存数据,都是通过管道将源数据元素传递给操作;
+
+对Stream的任何修改都不会修改数据源,都是新产生一个流
+
+流的很多操作如filter、map都是延迟执行的,只有到终点才会将操作顺序执行
+
+对于无限流可以通过"短路"操作访问到有限元素后就返回
+
+流的元素只访问一次,如果需要重新访问,需要重新生成一个新的流
+
+Stream中BaseStream规定了流的基本接口,在Stream中使用Stage来描述一个完整的操作,将具有先后顺序的各个Stage连一起,就构成了整个流水线。
+
+AbstractPipeline是流水线的核心,定义了三个AbstractPipeline类型的变量:sourceStage(源阶段)、previousStage(上游pipeline,上一阶段),nexStage(下一阶段)
+
+ReferencePipeline 继承了AbstractPipeline
+
+Head、StatefulOp、StatelessOp继承了ReferencePipeline,分别表示源,无状态操作,有状态操作
+
+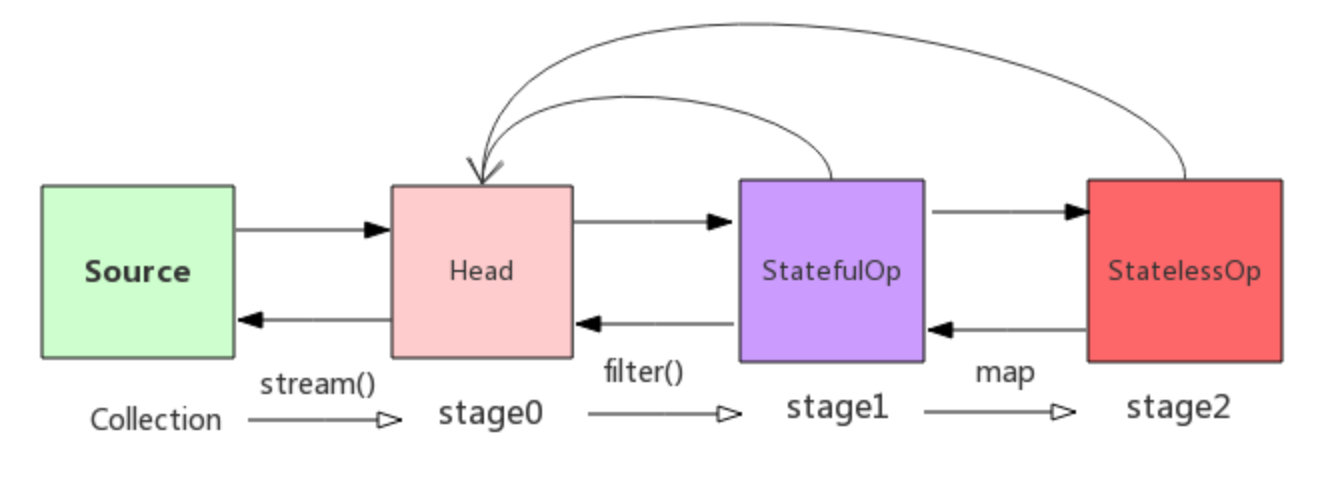
+
+比如Collection.stream()方法得到Head也就是stage0,紧接着调用一系列的中间操作,不断产生新的stage。这些stage对象以双向链表的形式组织在一起,构成整个流水线。
+由于每个Stage都记录了前一个Stage和本次的操作以及回调函数,依靠这种结构就建立起对数据源的所有操作。
+
+### parallelStream 怎么实现的并行处理
+
+parallelStream 底层使用ForkJoinPool 实现并行处理,默认线程为可用的CPU数量。
+
+### 解释一下ForkJoin框架
+
+parallelStream的底层是基于ForkJoinPool的,ForkJoinPool实现了ExecutorService接口
+
+Fork/Join框架主要采用分而治之的理念来处理问题,对于一个比较大的任务,首先将它拆分(fork)为多个小任务task1、task2等。再使用新的线程thread1去处理task1,thread2去处理task2。
+
+如果thread1认为task1还是太大,则继续往下拆分成新的子任务task1.1与task1.2。thread2认为task2任务量不大,则立即进行处理,形成结果result2。
+
+之后将task1.1和task1.2的处理结果合并(join)成result1,最后将result1与result2合并成最后的结果。
+
+img
+
+### CompletableFuture 异步编程实现原理
+
+CompletableFuture是Java8引入的异步编程工具,基于回调机制和事件驱动模型实现异步操作,核心原理是:
+
+1. 异步执行任务:通过线程池(默认使用ForkJoinPool)执行异步任务,任务执行期间主线程无需阻塞等待
+2. 回调触发机制:任务完成后,自动触发注册的回调函数(如thenApply、exceptionally等),回调函数在任务完成后由线程池中的线程执行
+3. 链式编程:内部实现CompletionStage接口,允许将多个异步操作串联或并联,形成流水线式的异步处理流程
+
+传统Future 要get()阻塞等待获取结果,或轮询isDone();无法直接串联多个异步任务;难以合并多个独立异步任务的结果。
diff --git a/20.Java Performance.md b/20.Java Performance.md
old mode 100755
new mode 100644
index 5da6730..4088448
--- a/20.Java Performance.md
+++ b/20.Java Performance.md
@@ -244,6 +244,8 @@ jstat -gcutil 31798
-XX:+UseConcMarkSweepGC: 设置CMS收集器
+-XX:+UseZGC: 使用ZGC
+
**垃圾回收统计信息**
@@ -284,7 +286,7 @@ jstat -gcutil 31798
-XX:ParallelGCThreads=n: 设置并发收集器年轻代收集方式为并行收集时,使用的CPU数。并行收集线程数。
--XX:+CMSInitiatingOccupancyFraction: 设置CMS收集器在老年代空间被使用多少后触发,默认68%
+-XX:+CMSInitiatingOccupancyFraction: 设置CMS收集器在老年代空间被使用多少后触发,默认92%
-XX:+UseCMSCompactAtFullCollection: 设置CMS收集器在完成垃圾收集后是否要进行一次内存碎片的整理
@@ -294,24 +296,40 @@ jstat -gcutil 31798
-XX:+CMSParallelRemarkEnabled: 启用并行重标记
+-XX:+CMSParallelInitialMarkEnabled:在初始标记的时候使用多线程
+
-XX:CMSInitiatingPermOccupancyFraction: 当永久区占用率达到这一百分比时,启动CMS回收(前提是开启-XX:+CMSClassUnloadingEnabled)
--XX:UseCMSInitiatingOccupancyOnly: 表示只在到达阈值的时候,才进行CMS回收
+-XX:+UseCMSInitiatingOccupancyOnly: 表示只在到达阈值的时候(-XX:CMSInitiatingPermOccupancyFraction指定的值),才进行CMS回收,如果不指定,JVM仅在第一次使用设定值,后续会自动调整
+
+-XX:+CMSScavengeBeforeRemark:在CMS GC 前启动一次minor gc,目的在于减少老年代对年轻代的引用,降低CMS GC 标记阶段的开销,一般CMS的GC耗时80%都在标记阶段
**G1回收器设置**
--XX:+UseG1GC: 使用G1回收器
+ -XX:+UseG1GC: 使用G1回收器
-XX:+UnlockExperimentalVMOptions: 允许使用实验性参数
--XX:MaxGCPauseMillis: 设置最大垃圾收集停顿时间
+-XX:MaxGCPauseMillis: 设置最大垃圾收集停顿时间(默认200ms)
-XX:GCPauseIntervalMillis: 设置停顿间隔时间
-XX:+DisableExplicitGC: 禁用显示GC
+-XX:ParallelGCThreads:指定GC工作的线程数量
+
+-XX:G1HeapRegionSize: 指定分区大小(1MB-32MB,必须是2的N次幂),默认将整堆划分为2048个分区
+
+-XX:G1NewSizePercent: 新生代内存初始空间(默认整堆5%,值配置整数,默认就是百分比)
+
+-XX:G1MaxNewSizePercent: 新生代内存最大空间
+
+-XX:TargentSurvivorRatio: Survivor区的填充容量(默认50%),Survivor区域里的一批对象总和超过了Survivor区域的50%,此时会把年龄n(含)以上的对象都放入老年代
+
+-XX:MaxTenuringThreshold:最大年龄阈值(默认15)
+
> 更多垃圾回收器参数,见
@@ -540,7 +558,55 @@ the space 69632K, 4% used [0x227d0000, 0x22aeb958, 0x22aeba00, 0x26bd0000)
+### 如何根据业务场景选择合适的垃圾收集器
+
+从延迟、吞吐量、内存大小来考虑。
+
+- #### SerialGC
+
+ - 适用场景:
+ - 堆内存较小(通常 < 1GB)的应用; + - 单核 CPU 或资源受限的环境(如嵌入式设备、简单客户端应用); + - 对延迟不敏感的场景(如本地工具类程序)。 + + - 不适用:服务端应用、多线程高并发场景。 + +- #### ParallelGC + + - 适用场景: + - 对吞吐量要求高,对延迟不敏感的应用(如后台批处理任务、数据分析、科学计算); + - 堆内存中等(1GB ~ 10GB),且 CPU 核心数较多(充分利用多线程加速 GC); + - 不需要低延迟的服务(如离线数据处理)。 + + - 不适用:对响应时间敏感的服务(如 Web 应用、实时交易系统)。 + +- #### CMS + + - 适用场景: + - 对延迟敏感的服务端应用(如 Web 服务器、电商网站、API 服务),需要快速响应用户请求; + - 堆内存中等(1GB ~ 10GB),且 CPU 资源充足(需预留线程处理并发 GC); + - 无法接受长时间 STW 的场景。 + - 不适用: + - 堆内存过大(>10GB)(并发阶段耗时太长,反而可能增加延迟);
+ - CPU 资源紧张的环境(并发阶段会抢占用户线程 CPU);
+ - JDK 9 及以上(CMS 已被标记为 deprecated,JDK 14 移除)。
+- #### G1
+ - 适用场景:
+ - 堆内存较大(4GB ~ 数百 GB)的服务端应用(如企业级应用、中间件、微服务);
+ - 需要平衡吞吐量和延迟的场景(既不能接受过长停顿,也需要一定的吞吐量);
+ - 替代 CMS 的主流选择(JDK 9 后默认 GC)。
+ - 不适用:
+ - 堆内存极小(<4gb)(region 管理的 overhead 不划算); + - 对延迟要求极高(如微秒级响应)的场景(STW 停顿通常在几十到几百毫秒)。 +- #### ZGC + - 适用场景: + - 对延迟要求极高的场景(如高频交易系统、实时数据分析、大型分布式服务); + - 堆内存超大(数十 GB 到 TB 级),且需要快速响应的应用; + - 希望在大内存下保持低延迟的现代服务(如云原生应用)。 + - 不适用: + - JDK 版本过低(需 JDK 11+,且 JDK 15 后才正式可用); + - 对吞吐量要求极致且可接受长停顿的场景(ZGC 为低延迟牺牲了部分吞吐量优化)。 diff --git a/21. Nginx.md b/21. Nginx.md old mode 100755 new mode 100644 diff --git a/22. ShardingJDBC.md b/22. ShardingJDBC.md old mode 100755 new mode 100644 index c09302b..8996851 --- a/22. ShardingJDBC.md +++ b/22. ShardingJDBC.md @@ -1,4 +1,4 @@ -# 22.Sharding-JDBC +# 22.分库分表 [toc] @@ -10,6 +10,8 @@>
> 数据库分库分表思路:https://www.cnblogs.com/butterfly100/p/9034281.html
+## Sharding-JDBC
+
### 分库分表的方式
- 垂直分库
@@ -248,10 +250,12 @@ mycat:自己上官网,找一个官网最基本的例子,自己写一下,
orderId 模 32 = 库
orderId / 32 模 32 = 表
-259 3 8
-1189 5 5
-352 0 11
-4593 17 15
+orderId 库 表
+
+259 3 8
+1189 5 5
+352 0 11
+4593 17 15
1、设定好几台数据库服务器,每台服务器上几个库,每个库多少个表,推荐是32库 * 32表,对于大部分公司来说,可能几年都够了;
@@ -263,4 +267,6 @@ orderId / 32 模 32 = 表
5、我们这边就是修改一下配置,调整迁移的库所在数据库服务器的地址;
-6、重新发布系统,上线,原先的路由规则变都不用变,直接可以基于2倍的数据库服务器的资源,继续进行线上系统的提供服务。
\ No newline at end of file
+6、重新发布系统,上线,原先的路由规则变都不用变,直接可以基于2倍的数据库服务器的资源,继续进行线上系统的提供服务。
+
+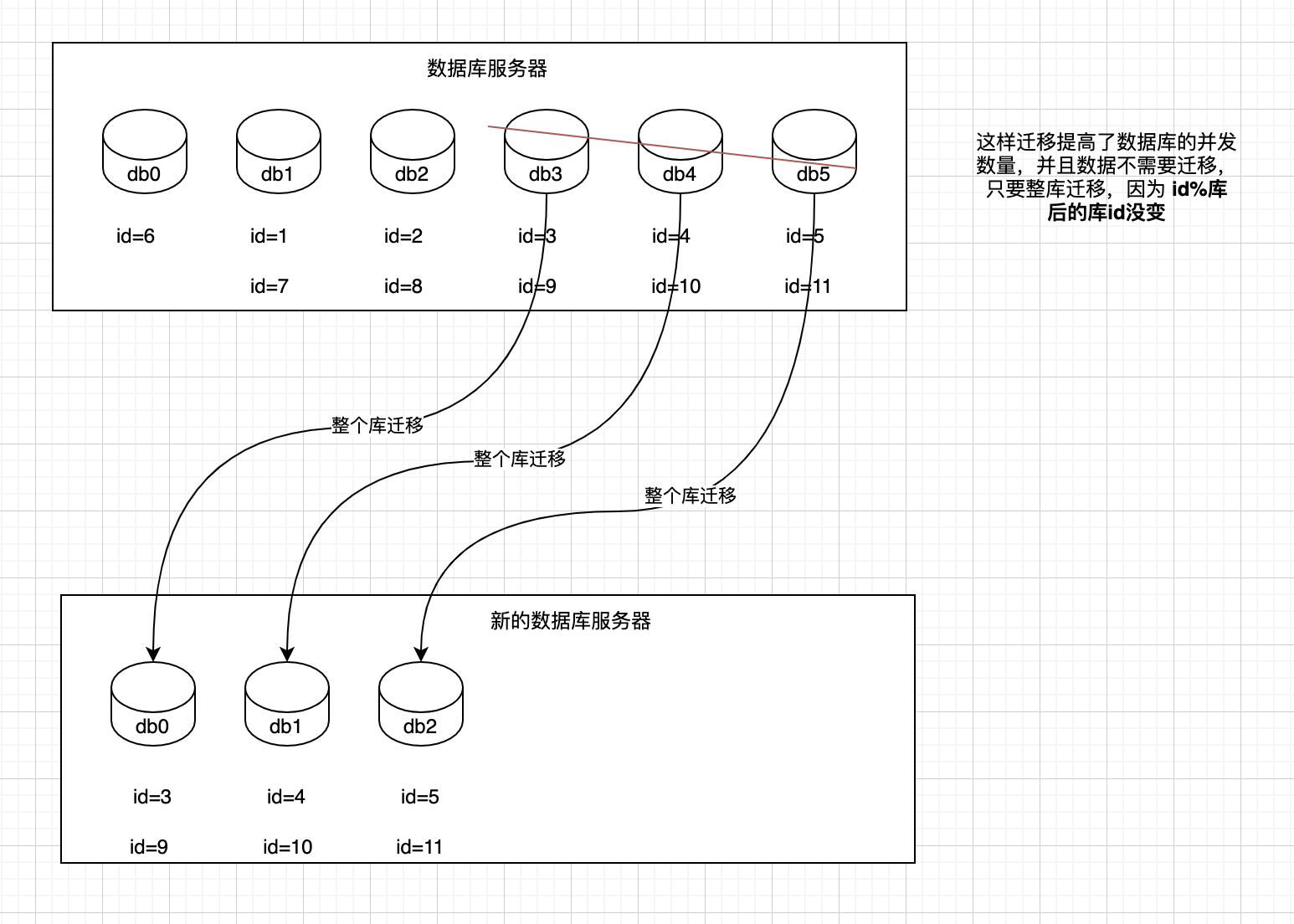
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/23.ES.md b/23.ES.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..45d63e7
--- /dev/null
+++ b/23.ES.md
@@ -0,0 +1,62 @@
+# 23.ES
+
+### ES的分布式架构原理
+
+核心思想是在多台机器上启动多个ES进程实例,组成一个ES集群。ES中存储数据的基本单位是索引,用来存储具有共同特性的文档集合,一个索引差不多就相当于Mysql中的表。为了提高可伸缩性和容错性,ES会将索引划分为多个分片,每个分片都是一个独立的Lucene索引,可以部署在集群中的任何节点上,一个索引包含一个或多个主分片和零个或多个副本分片,主分片负责数据的写入,而副本分片则用于数据的容错和读请求的分流。
+
+### ES 的核心概念
+
+- 索引(Index)
+
+类似数据库中的"表",是文档的逻辑集合。每个索引有一个唯一的名称(如products)
+
+- 文档(Document)
+
+索引中的基本数据单元,以JSON格式存储;每个文档有一个唯一ID和类型
+
+- 分片(Shard)
+
+索引被水平拆分的子集,每个分片是一个独立的Lucene索引;
+
+主分片:数据写入的目标分片,数量在索引创建时固定
+
+副本分片:主分片的拷贝,提供高可用和读负载均衡
+
+- 节点(Node)
+
+一个运行的ES实例,可以是数据节点、主节点或协调节点
+
+### ES写入数据的流程
+
+1. 客户端请求:文档发送到协调节点
+2. 路由与分片选择:协调节点根据文档ID的哈希值选择目标分片
+3. 写入主分片:主分片先写入内存缓冲区,同时记录到事务日志(用于崩溃恢复)
+4. 刷新:默认1秒,内存缓冲区的内容生成一个新的段(Segment)并开放搜索
+5. 刷盘:定期将内存中的段持久化到磁盘
+6. 同步副本:主分片将写入操作同步到所有副本分片
+
+### ES 如何实现全文搜索
+
+- 倒排索引:核心数据结构,记录每个词项出现在哪些文档中
+- 分词:将文本转换为词项的过程
+
+**查询流程**:
+
+1. 对查询字符串分词(使用相同的分析器)。
+2. 在倒排索引中匹配词项,计算相关性得分(如 TF-IDF、BM25)。
+3. 返回排序后的文档。
+
+### ES在数据量很大的情况下如何提高性能
+
+1. **索引设计**:
+ - 合理设置分片数(建议单个分片大小 10-50GB)。
+ - 使用 `routing` 将相关文档存到同一分片,减少跨分片查询。
+2. **查询优化**:
+ - 避免 `wildcard` 查询(性能差),改用 `keyword` 类型 + 前缀搜索。
+ - 使用 `filter` 替代 `query` 条件(不计算得分,结果可缓存)。
+3. **硬件与配置**:
+ - 数据节点使用 SSD,内存分配给文件系统缓存(建议不超过 50% 堆内存)。
+ - 调整 `indices.query.bool.max_clause_count` 解决大量 `terms` 查询问题。
+4. **聚合优化**:
+ - 对高基数字段(如用户 ID)使用 `cardinality` 聚合时,开启 `precision_threshold`。
+
diff --git a/24. AI.md b/24. AI.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..4f136a5
--- /dev/null
+++ b/24. AI.md
@@ -0,0 +1,15 @@
+# 24. AI
+
+### 大模型聊天中有哪些配置,他们的作用
+
+temperature:较高的温度生成的内容随机性更大,较低的温度会使大模型选择最可能的单词
+
+top_p: 模型从累计概率大于或等于"p"的最小集合中随机选择一个
+
+repetition_penalty: 重复惩罚
+
+### 大模型中有哪几种role,他们的区别
+
+1. system : 用于设定模型的行为规范、背景或任务指令,由开发者或系统设定,用户不可见,内容通常是对模型的隐性提示,如角色设定,回答格式等
+2. user:真实用户的输入,即用户向模型提出的问题或指令
+3. assistant:模型自身的回复,在多轮对话中起到记录历史响应,维持上下文连贯性的作用
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/25.Netty.md b/25.Netty.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..be839be
--- /dev/null
+++ b/25.Netty.md
@@ -0,0 +1,173 @@
+# 25.Netty
+
+### TCP 的粘包和拆包
+
+TCP 是以流的方式来处理数据的,一个完整的包可能会被TCP拆分成多个包进行发送,也可能把小的封装成一个大的数据包发送。
+
+### BIO、NIO、AIO的区别
+
+BIO:一个连接一个线程,客户端有连接请求时服务器端就需要启动一个线程进行处理,线程开销大。是面向流的,阻塞流,流是单向的。
+
+NIO: 一个请求一个线程,但客户端发送的连接请求都会注册到多路复用器上,多路复用器轮询到连接有IO请求时才启动一个线程进行处理。面向缓存区,非阻塞,channe是双向的。
+
+AIO:一个有效请求一个线程,客户端的IO请求都是由OS先完成了再通知服务器应用去启动线程进行处理
+
+### NIO 的组成
+
+Buffer:与Channel进行交互,数据从Channel读入缓冲区,从缓冲区写入Channel中
+
+flip方法:反转缓冲区,将position给limit,然后将position置为0,就是读写切换
+
+clear方法:清除此缓冲区,将position置为0,把capacity的值给limit
+
+rewind方法:重置此缓冲区,将position置为0
+
+DirectByteBuffer:可减少一次系统空间到用户空间的拷贝
+
+Channel:与数据源的连接,是双向的,只能与Buffer交互
+
+Selector:允许单个线程管理多个Channel
+
+Pipe:两个线程之间的单向数据连接,数据会被写到sink通道,从source通道读取
+
+
+
+NIO服务端建立过程:
+
+1. ServerSocketChannel.open 创建服务端Channel
+2. bind 绑定服务端端口
+3. 配置非阻塞模式
+4. Selector.open 打开一个selector
+5. 注册关注的事件到selector上
+
+```java
+// 服务端代码
+public class NioServer {
+
+ public static void main(String[] args) {
+ try(ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open()) {
+ serverSocketChannel.socket().bind(new InetSocketAddress(3388));
+
+ Selector selector = Selector.open();
+ serverSocketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
+ serverSocketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
+
+ System.out.println("服务器准备就绪,开始监听,端口3388");
+
+
+ while (true) {
+ int wait = selector.select();
+ if (wait == 0)
+ continue;
+
+ Set keys = selector.selectedKeys();
+ Iterator iterator = keys.iterator();
+ ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
+
+ while (iterator.hasNext()) {
+
+ SelectionKey key = iterator.next();
+
+ if (key.isAcceptable()) {
+ ServerSocketChannel server = (ServerSocketChannel) key.channel();
+ SocketChannel channel = server.accept();
+ channel.configureBlocking(false);
+ channel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
+ } else if(key.isReadable()) {
+ SocketChannel server = (SocketChannel) key.channel();
+ int len = server.read(byteBuffer);
+ if (len> 0) {
+ byteBuffer.flip();
+ String content = new String(byteBuffer.array(), 0, len);
+ System.out.println(content);
+
+ server.configureBlocking(false);
+ server.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_WRITE);
+ }
+ byteBuffer.clear();
+ } else if (key.isWritable()) {
+ SocketChannel server = (SocketChannel) key.channel();
+ server.write(ByteBuffer.wrap("Hello Client!".getBytes()));
+ }
+
+ iterator.remove();
+ }
+
+ }
+
+ } catch (Exception e) {
+ e.printStackTrace();
+ }
+ }
+}
+
+
+//客户端代码
+public class NIOClient {
+
+ public static void main(String[] args) {
+ try(SocketChannel channel = SocketChannel.open()) {
+ channel.connect(new InetSocketAddress(3388));
+
+ //发送数据
+ if (channel.isConnected()) {
+ channel.write(ByteBuffer.wrap("Hello Server!".getBytes()));
+ }
+
+ ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
+ int len = channel.read(buffer);
+ String content = new String(buffer.array(), 0, len);
+ System.out.println(content);
+ }catch (Exception e) {
+
+ }
+
+ }
+}
+```
+
+### Netty 的特点
+
+一个高性能、异步事件驱动的NIO框架。
+
+使用更高效的socket底层,处理了epoll空轮询引起的cpu占用飙升(Netty检测到空轮询的时候,主动重建Selector)
+
+采用decoder/encoder 支持,对TCP粘包/拆包进行自动化处理
+
+可配置IO线程数、TCP参数,TCP 接收和发送缓冲区使用直接内存代替堆内存,通过内存池的方式循环利用 ByteBuf
+
+通过引用计数器及时申请释放不再引用的对象,降低了 GC 频率
+
+使用单线程串行化的方式,高效的 Reactor 线程模型
+
+大量使用了 volitale、使用了 CAS 和原子类、线程安全类的使用、读写锁的使用
+
+### Netty 使用的线程模型
+
+Netty 通过 Reactor 线程模型基于多路复用器接收并处理用户请求,内部实现了两个线程池,boss 线程池和 work 线程池,
+
+其中 boss 线程池的线程负责处理请求的 accept 事件,当接收到 accept 事件的请求时,把对应的 socket 封装到一个,
+
+NioSocketChannel 中,并交给 work线程池,其中 work 线程池负责请求的 read 和 write 事件,由对应的 Handler 处理。
+
+### Netty 的零拷贝实现
+
+- Direct Buffer
+
+ 使用堆外内存进行Socket读写,避免JVM堆内存与内核缓存之间的拷贝
+
+- CompositeByteBuf
+
+ 将多个缓存区"逻辑上"合并为一个缓冲区,避免物理上的数据拷贝
+
+- 文件传输的零拷贝 FileRegion
+
+ 利用操作系统的 `sendfile` 系统调用,直接在文件描述符和套接字之间传输数据,完全跳过用户态
+
+- 缓存区包装 Wrapped Buffers
+
+ 通过包装现有数据(如字节数组、`ByteBuffer`)创建 `ByteBuf`,避免数据贝,`Unpooled.wrappedBuffer(...)` 方法直接引用原始数据,而非复制
+
+- 延迟缓冲区拷贝 Lazy Copy
+
+ 在某些场景下(如缓冲区切片 `slice()`),仅记录原始缓冲区的引用和偏移量,不立即拷贝数据,直到必要时才执行拷贝。
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/3.Java Lock.md b/3.Java Lock.md
old mode 100755
new mode 100644
index a20ef6a..6d7e655
--- a/3.Java Lock.md
+++ b/3.Java Lock.md
@@ -17,7 +17,7 @@
公平锁:根据线程请求锁的顺序来获取锁
非公平锁:抢占式获取锁
-### 什么是死锁
+### 什么是死锁,什么情况下产生死锁
具备以下4个条件就会产生死锁:
@@ -125,9 +125,26 @@ yield:
### 什么是虚假唤醒?如何避免
-https://blog.csdn.net/LuckyBug007/article/details/70053669
+AB线程执行了wait()方法,C线程执行了notifyAll()方法唤醒了它们,AB线程就都开始执行,但其中只有一个线程能执行成功,另外一个线程会得到错误的结果。
-wait(),notify()源码分析:https://www.jianshu.com/p/f4454164c017
+避免方式是将wait()方法包裹在while(条件)中,进行循环判断
+
+```java
+synchronized (someObject) {
+ while (!condition) {
+ someObject.wait();
+ }
+ // 现在 condition 为 true,执行你的操作
+}
+
+// 错误用法
+synchronized (someObject) {
+ if (!condition) { // 仅判断一次
+ lock.wait(); // 若此处发生虚假唤醒,线程会直接执行下面的逻辑
+ }
+ // 执行需要条件满足的操作(可能因条件未满足而出错)
+}
+```
### Synchronized原理
@@ -138,7 +155,8 @@ Synchronized可以修饰普通方法、同步方法块、静态方法;
同步方法块锁是Synchonized配置的对象;
用的锁是存在对象头里的,根据mark word的锁状态来判断锁,如果锁只被同一个线程持有使用的是偏向锁,不同线程互相交替持有锁使用轻量级锁,多线程竞争使用重量级锁。锁会按偏向锁->轻量级锁->重量级锁 升级,称为锁膨胀
- https://github.com/farmerjohngit/myblog/issues/12
+
+> 扩展:https://github.com/farmerjohngit/myblog/issues/12
### synchronized和Lock的区别
@@ -146,7 +164,7 @@ Synchronized可以修饰普通方法、同步方法块、静态方法;
2. synchronized 无法显式的判断是否获取锁的状态,Lock可以判断是否获取到锁
3. synchronized 会自动释放锁,Lock需要在finally中手工释放锁
4. synchronized 不同线程获取锁只有一个线程能获取成功,其他线程会一直阻塞直到获取锁,Lock有阻塞锁,也有非阻塞锁,阻塞锁还有尝试设置,功能更强
-5. synchronized 可重入,不可中断,非公平,Lock锁可重入,可判断,有公平锁,非公平锁
+5. synchronized 可重入,不可中断,非公平,Lock锁可重入,可中断,有公平锁,非公平锁
6. Lock锁适合大量同步代码的同步问题,synchronized锁适合代码少量的同步问题
### synchronized 可重入是怎么实现的
@@ -157,7 +175,7 @@ Synchronized可以修饰普通方法、同步方法块、静态方法;
### ReentrantLock可重入性怎么实现的?
-由于ReentrantLock是通过AQS来实现的,其使用了AQS的state状态值来表示线程获取该锁的可重入次数,默认情况下state为0表示当前锁没有被任何线程持有,当一个线程获取该锁时会尝试使用CAS设置state值为1,如果CAS设置成功则当前线程获取了该锁,然后记录该锁的持有者为当前线程,在该线程没有释放锁的情况下第二次获取该锁后,状态值被设置2,这就是可以重入次数,在释放锁的时候,需要通过CAS将状态值减1,直到状态值为0,表示当前线程释放该锁
+由于ReentrantLock是通过AQS来实现的,其使用了AQS的state状态值来表示线程获取该锁的可重入次数,默认情况下state为0表示当前锁没有被任何线程持有,当一个线程获取该锁时会尝试使用**CAS设置state值为1**,如果CAS设置成功则当前线程获取了该锁,然后**记录该锁的持有者为当前线程**,在该线程没有释放锁的情况下第二次获取该锁后,**状态值被设置2**,这就是可以重入次数,在释放锁的时候,需要通过CAS将状态值减1,直到状态值为0,表示当前线程释放该锁
### 非公平锁和公平锁在ReetrantLock里的实现过程是怎样的
@@ -178,15 +196,15 @@ Synchronized可以修饰普通方法、同步方法块、静态方法;
### AbstractQueuedSynchronizer的作用
-抽象同步队列简称AQS,是实现同步器的基础组件,并发包中的锁都是基于其实现的,关键是先进先出的队列,state状态,并且定义了 ConditionObject ,拥有两种线程模式,独占模式和共享模式
+抽象同步队列简称AQS,是实现同步器的基础组件,并发包中的锁都是基于其实现的,关键是**先进先出的队列,state状态**,并且定义了 ConditionObject ,拥有两种线程模式,**独占模式和共享模式**
- AQS核心思想
如果被请求的共享资源空闲,则将当前请求资源的线程设置为有效的工作线程,并且将共享资源设置为锁定状态。如果被请求的共享资源被占用,那么就需要一套线程阻塞等待以及被唤醒时锁分配的机制,这个机制使用CLH队列实现的,即将暂时获取不到锁的线程加入到队列中
-> CLH(Craig,Landin,and Hagersten)队列是一个虚拟的双向队列(虚拟的双向队列即不存在队列实例,仅存在结点之间的关联关系)。AQS是将每条请求共享资源的线程封装成一个CLH锁队列的一个结点(Node)来实现锁的分配, 并保持了上下节点,当前请求资源的线程
+> CLH(Craig,Landin,and Hagersten)(3个人名)队列是一个虚拟的双向队列(虚拟的双向队列即不存在队列实例,仅存在结点之间的关联关系)。AQS是将每条请求共享资源的线程封装成一个CLH锁队列的一个结点(Node)来实现锁的分配, 并保持了上下节点,当前请求资源的线程
-AQS原理图
+
@@ -197,3 +215,11 @@ StampedLock 提供了三种模式的读写控制,当调用获取锁的系列
悲观读锁readLock: 共享锁,在没有线程独占获取写锁的情况下,多个线程可以同时获取该锁,如果已经有其他线程持有写锁,则其他线程请求读锁会被阻塞
乐观读锁tryOptimisticRead: 在操作数据前并没有通过CAS设置锁的状态,仅通过位运算测试
+### CAS 实现的锁和synchronized 锁的性能差异
+
+| 维度 | CAS(乐观锁) | synchronized(悲观锁,可升级) |
+| ------------ | ------------------------------------ | -------------------------------------------- |
+| **竞争低时** | 无锁,自旋少,性能最优 | 偏向锁 / 轻量级锁,开销接近但略高 |
+| **竞争高时** | 自旋浪费 CPU,性能急剧下降 | 重量级锁阻塞线程,避免 CPU 空转,性能更稳定 |
+| **资源开销** | 自旋消耗 CPU,无上下文切换 | 高竞争时上下文切换开销大,但无自旋浪费 |
+| **适用场景** | 简单操作、低冲突(如原子类、计数器) | 复杂逻辑、高冲突(如多步更新、共享资源访问) |
diff --git a/4.JVM.md b/4.JVM.md
old mode 100755
new mode 100644
index 51baaa0..70ee478
--- a/4.JVM.md
+++ b/4.JVM.md
@@ -6,18 +6,24 @@
### JVM运行时内存区域划分
-image-20190922235827314
+image-20190922235827314
-线程独享区域:程序计数器,本地方法栈,虚拟机栈
-线程共享区域:元空间(<=1.7方法区), 堆 +线程独享区域:程序计数器,本地方法栈,虚拟机栈 + +线程共享区域:元空间(<=1.7方法区), 堆 程序计数器:线程私有,是一块较小的内存空间,可以看做是当前线程执行的字节码指示器,也是唯一的没有定义OOM的区块 -本地方法栈: 用于执行Native 方法时使用 + +本地方法栈: 用于执行Native 方法时使用 虚拟机栈:用于存储局部变量,操作数栈,动态链接,方法出口等信息 + 元空间:存储已被虚拟机加载的类元信息,常量,静态变量,即时编译器编译后的代码等数据依旧存储在方法区中,方法区位于堆中 + 堆:存储对象实例 -示例: + + +**元空间OOM示例:** ```java /** @@ -47,21 +53,9 @@ public class JavaMetaSpaceOOM { } ``` - - -### OOM,及SOE的示例、原因,排查方法 +**虚拟机栈OOM** ```java -//OOM -Xmx20m -Xms20m -XX:+HeapDumpOnOutOfMemoryError -public class OOMTest { - public static void main(String[] args) { - List objList = new ArrayList();
- while(true) {
- objList.add(new Object());
- }
- }
-}
-
//SOE栈异常 -Xss125k
public class SOETest() {
static int count = 0;
@@ -80,9 +74,55 @@ public class SOETest() {
}
```
+**堆OOM**
+
+```java
+//OOM -Xmx20m -Xms20m -XX:+HeapDumpOnOutOfMemoryError
+public class OOMTest {
+ public static void main(String[] args) {
+ List objList = new ArrayList();
+ while(true) {
+ objList.add(new Object());
+ }
+ }
+}
+```
+
+**直接内存OOM**
+
+> 直接内存(Direct Memory)不属于 JVM 内存区域,是通过`sun.misc.Unsafe`分配的本地内存(如 NIO 的`DirectByteBuffer`),但可能因内存不足触发 OOM
+
+```java
+// -XX:MaxDirectMemorySize=512k
+public class DirectMemoryOOM {
+ private static final int BUFFER_SIZE = 1024 * 1024; // 1MB
+ public static void main(String[] args) {
+ List list = new ArrayList();
+ while (true) {
+ ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(BUFFER_SIZE);
+ list.add(buffer);
+ }
+ }
+}
+```
+
+
+
+### OOM,及SOE的示例、原因,排查方法
+
- OOM排查:如果能看到日志,可以从打印的日志中获取到发送异常的代码行,再去代码中查找具体哪块的代码有问题。如果没有记录日志,通过设置的 -XX:+HeapDumpOnOutOfMemoryError 在发生OOM的时候生成.hprof文件,再导入JProfiler能够看到是由于哪个对象造成的OOM,再通过这个对象去代码中寻找
- SOE排查:栈的深度一般为1000-2000深度,超过了深度或者超过了栈大小就会导致SOE,通过打印的日志定位错误代码位置,检测是否有无限递归,发生了死循环等情况,修改代码
+### JMM 内存模型
+
+Jave Memory Model(JMM)是一种抽象的规范,定义了多线程环境下线程与主内存之间的交互规则,目的是解决多线程并发时因共享内存访问导致的数据一致性问题,如原子性、可见性、有序性,核心是happens-before原则
+
+原子性:指一个操作或一系列操作不可分割,实现方式:synchronized关键字、CAS操作
+
+可见性:指当一个线程修改了共享变量的值后,其他线程能立即看到该修改,实现方式:volatile,synchronized、final(初始化后就不可修改)
+
+有序性:指程序执行的指令顺序与代码逻辑顺序一致,避免因编译器或CPU的指令重排序导致的并发问题,实现方式:volatile、synchronized
+
### 如何判断对象可以回收或存活
判断是否可以回收,或者存活主要是看:
@@ -106,60 +146,56 @@ public class SOETest() {
### 常见的JVM性能监测分析工具
- 1. jps
- 能够查看正在运行的虚拟机进程,并显示虚拟机的执行主类及进程ID
-
- 2. jstat [option vmid [interval[s|ms] [count]] ]
- 可以显示本地或者远程虚拟机中的类装载、内存、垃圾收集、JIT编译等运行数据
-
- 3. jinfo
- 实时查看和调整虚拟机的各项参数
-
- 4. jmap
- 生成堆转储快照
-
- 5. jhat
-
- 生成页面分析导出的堆存储快照
+1. jps
+ 能够查看正在运行的虚拟机进程,并显示虚拟机的执行主类及进程ID
- 6. jstack
- 用于生成虚拟机当前时刻的线程快照
+2. jstat [option vmid [interval[s|ms] [count]] ]
+ 可以显示本地或者远程虚拟机中的类装载、内存、垃圾收集、JIT编译等运行数据
- 7. jstatd
+3. jinfo
+ 实时查看和调整虚拟机的各项参数
- 启动RMI服务端程序,代理本地的Java进程,供远程计算机连接调式
+4. jmap
+ 生成堆转储快照
- 8. 查看当前JVM使用的垃圾收集器
+5. jhat
+ 生成页面分析导出的堆存储快照
- java -XX:+PrintFlagFinal -version 或者 java -XX:+PrintCommandLineFlags -version
+6. jstack
+ 用于生成虚拟机当前时刻的线程快照
- 9. jconsole
-
- Java监视和管理控制台,能够监控内存,线程,类等
-
- 10. jvisualvm
-
- 多合一监视工具
+7. jstatd
+ 启动RMI服务端程序,代理本地的Java进程,供远程计算机连接调式
+
+ 8. 查看当前JVM使用的垃圾收集器
+ java -XX:+PrintFlagFinal -version 或者 java -XX:+PrintCommandLineFlags -version
+
+ 9. jconsole
+ Java监视和管理控制台,能够监控内存,线程,类等
+
+ 10. jvisualvm
+ 多合一监视工具
> 更多资料请学习官网:https://docs.oracle.com/en/java/javase/11/tools/index.html
### JVM优化
- 1. 响应时间优先:年轻代设的大些,直到接近系统的最低响应时间限制。年轻代设大,可以减少到达年老代的对象。对于永久代的设置需要参考:永久代并发收集的次数、年轻代和永久代回收时间比例,调整达到一个合适的值
- 2. 吞吐量优先:年轻代设的大些,永久代较小
+1. 响应时间优先:年轻代设的大些,直到接近系统的最低响应时间限制。年轻代设大,可以减少到达年老代的对象。对于永久代的设置需要参考:永久代并发收集的次数、年轻代和永久代回收时间比例,调整达到一个合适的值
+2. 吞吐量优先:年轻代设的大些,永久代较小
### 什么时候会触发FullGC
1. 永久代空间不足
2. 手动调用触发gc
+3. 元空间不足
### 类加载器有几种
- 1. Bootstrap ClassLoader
- 负责加载JDK自带的rt.jar包中的类文件,它是所有类加载器的父加载器,Bootstrap ClassLoader没有任何父类加载器。
- 2. Extension ClassLoader负责加载Java的扩展类库,也就是从jre/lib/ext目录下或者java.ext.dirs系统属性指定的目录下加载类。
- 3. System ClassLoader负责从classpath环境变量中加载类文件,classpath环境变量通常由"-classpath" 或 "-cp" 命令行选项来定义,或是由 jar中 Mainfest文件的classpath属性指定,System ClassLoader是Extension ClassLoader的子加载器
- 4. 自定义加载器
+1. Bootstrap ClassLoader(C++实现)
+ 负责加载JDK自带的rt.jar包中的类文件,它是所有类加载器的父加载器,Bootstrap ClassLoader没有任何父类加载器。
+2. Extension ClassLoader(ExtClassLoader)负责加载Java的扩展类库,也就是从jre/lib/ext目录下或者java.ext.dirs系统属性指定的目录下加载类。
+3. System ClassLoader(AppClassLoader)负责从classpath环境变量中加载类文件,classpath环境变量通常由"-classpath" 或 "-cp" 命令行选项来定义,或是由 jar中 Mainfest文件的classpath属性指定,System ClassLoader是Extension ClassLoader的子加载器
+4. 自定义加载器
### 什么是双亲委派模型?双亲委派模型的破坏
@@ -171,24 +207,24 @@ public class SOETest() {
类的生命周期一个有7个阶段:加载、验证、准备、解析、初始化、使用、卸载
- 加载:
- 加载阶段,虚拟机需要完成以下3件事
+ 加载阶段,虚拟机需要完成以下3件事
1. 通过类的全限定名来获取此类的二进制字节流
2. 将字节流所代表的静态存储结构转化为方法区的运行时数据结构
3. 在内存中生成代表这个类的java.lang.Class对象,作为方法区这个类的各种数据访问入口
-
-
- 验证:分4个验证
- 1. 文件格式验证,验证是否符合Class文件格式的规范,并且能被当前版本的虚拟机处理
-
- 2. 元数据验证,对字节码描述的信息进行语义分析,以保证其描述的信息符合Java语言规范的要求
-
- 3. 字节码验证,通过数据流和控制流分析,确定程序语义是否合法、符合逻辑
-
- 4. 符合引用验证,是对类自身以外的信息进行匹配性校验(常量池中各种符合引用)
+
+ 1. 文件格式验证,验证是否符合Class文件格式的规范,并且能被当前版本的虚拟机处理
+
+ 2. 元数据验证,对字节码描述的信息进行语义分析,以保证其描述的信息符合Java语言规范的要求
+
+ 3. 字节码验证,通过数据流和控制流分析,确定程序语义是否合法、符合逻辑
+
+ 4. 符合引用验证,是对类自身以外的信息进行匹配性校验(常量池中各种符合引用)
+
+
-
- 准备:正式为类变量分配内存并设置初始值的阶段,这里设置初始值是数据类型的默认值
- 解析:虚拟机将常量池中的符号引用替换为直接引用的过程
- 初始化:执行类构造器的过程
@@ -203,52 +239,126 @@ public class SOETest() {
### 编译器会对指令做哪些优化?
编译器优化分编译期和运行期
-- 编译期:
- 1.标注检查,检查变量使用前是否已被声明、变量与赋值之间的数据类型是否能够匹配,对常量进行折叠
- 2.数据及控制流分析,检查诸如程序局部变量在使用前是否有赋值、是否所有的受检异常都被正确处理等问题
- 3.将语法糖还原为基础的语法结构
- 4.生成字节码
-- 运行期:
- 即时编译器JIT会把运行频繁的代码编译成与本地平台相关的机器码,并进行各种层次的优化
- Client Compiler: 会进行局部性的优化,分三阶段:第一阶段,一个平台独立的前端将字节码构造成一种高级中间代码表示HIR,HIR使用静态单分配(SSA)的形式来代表代码值,在字节码上做方法内联,常量传播等基础优化;第二阶段,从HIR中产生低级中间代码,在这之前会做空值检查消除,范围检查消除等。第三阶段,在LIR上分配寄存器,并在LIR上做窥孔优化,最后产生机器码
- Server Compiler: 会执行无用代码消除、循环展开、循环表达式外提、消除公共子表达式、常量传播、基本块重排序、范围检测消除、空值检查消除,另外还能根据解释器或Client Compiler提供的性能监控信息,进行一些不稳定的激进优化,比如守护内联、分支频率预测等
+
+- 编译期:
+ 1.标注检查,检查变量使用前是否已被声明、变量与赋值之间的数据类型是否能够匹配,对常量进行折叠
+ 2.数据及控制流分析,检查诸如程序局部变量在使用前是否有赋值、是否所有的受检异常都被正确处理等问题
+ 3.将语法糖还原为基础的语法结构
+ 4.生成字节码
+
+- 运行期:
+ 即时编译器JIT会把运行频繁的代码编译成与本地平台相关的机器码,并进行各种层次的优化
+ Client Compiler: 会进行局部性的优化,分三阶段:第一阶段,一个平台独立的前端将字节码构造成一种高级中间代码表示HIR,HIR使用静态单分配(SSA)的形式来代表代码值,在字节码上做方法内联,常量传播等基础优化;第二阶段,从HIR中产生低级中间代码,在这之前会做空值检查消除,范围检查消除等。第三阶段,在LIR上分配寄存器,并在LIR上做窥孔优化,最后产生机器码
+ Server Compiler: 会执行无用代码消除、循环展开、循环表达式外提、消除公共子表达式、常量传播、基本块重排序、范围检测消除、空值检查消除,另外还能根据解释器或Client Compiler提供的性能监控信息,进行一些不稳定的激进优化,比如守护内联、分支频率预测等
- 几种经典的优化技术:
1. 公共子表达式消除
- 如果一个表达式E已经计算过,并且从先前的计算到现在E中所有变量的值都没有发生变化,那么E的这次出现就成为公共子表达式
+ 如果一个表达式E已经计算过,并且从先前的计算到现在E中所有变量的值都没有发生变化,那么E的这次出现就成为公共子表达式
+
2. 数组范围检查消除
- 编译期就判断数组是否在合理的范围内,如果在,那就可以在循环中把数组的上下界检查消除。另外还有隐式异常处理,虚拟机会注册一个Segment Fault信号的异常处理器,但如果代码经常为空,消耗时间比判空慢,但虚拟机会根据运行期收集到的信息选择使用判空还是隐式异常处理
-3. 方法内联
- 一可以给"公共子表达式消除"等其他优化技术提供基础。虚方法即多态情况下,如果要确定是否能内联,虚拟机需要向"类型继承关系分析"器查询,如果只有一个版本,那可以进行内联,但还会留一个"逃生门",这种内联称为"守护内联",如果继承关系发生变化,虚拟机会通过"逃生门"退回到解释状态执行,或重新编译。
- 如果是多版本方法,虚拟机会通过"内联缓存",在第一次调用的时候将目标方法版本缓存起来,下次调用的时候检查版本是否一致,如果不一致就会取消内联,查找虚拟方法表进行方法分派
-4. 逃逸分析
- 分析对象动态作用域,对象是否作为调用参数传递到其他方法中(方法逃逸),是否有被其他线程访问(线程逃逸)。如果没有以上情况,虚拟机会做一些高效优化:栈上分配、同步消除(去掉同步措施)、标量替换(将对象成员变量恢复到原始类型)
+ 编译期就判断数组是否在合理的范围内,如果在,那就可以在循环中把数组的上下界检查消除。另外还有隐式异常处理,虚拟机会注册一个Segment Fault信号的异常处理器,但如果代码经常为空,消耗时间比判空慢,但虚拟机会根据运行期收集到的信息选择使用判空还是隐式异常处理
+3. 方法内联
+ 就是把目标方法的代码复制到发起调用的方法之中,避免发生真是的方法调用
+4. 逃逸分析
+ 分析对象动态作用域,对象是否作为调用参数传递到其他方法中(方法逃逸),是否有被其他线程访问(线程逃逸)。**如果没有以上情况,虚拟机会做一些高效优化:栈上分配、同步消除(去掉同步措施)、标量替换(将对象成员变量恢复到原始类型)**
+
+ ```java
+ public void test() {
+ //obj 对象只有在这个方法内部使用,并没有做为参数传递到其他方法中
+ Object obj = new Object();
+ }
+ ```
+
+5. 锁消除
+ JIT检测到方法是在单线程环境中执行时,会将已有的锁消除,提高性能
+
+6. 标量替换
+ 将原本需要分配到堆上的对象拆解成若干个基础数据类型(标量),并将这些基础数据类型作为局部变量存储在栈上。标量通常指的是不可再分解的数据类型,如int、long、float、double以及引用类型(reference)等。这种优化技术特别适用于那些生命周期短、作用域小、且不会逃逸出当前方法或线程的对象
+
+
### Serial、Parallel、CMS、G1收集器特点
-image-20191008191348602
+image-20191008191348602
-img
+img
-image-20191008202251538
+image-20191008202251538
- Serial
-
- 单线程收集器,在进行垃圾收集时,必须暂停所有的工作线程直到结束,该收集器停顿时间长,-XX:+UseSerialGC 使用串行垃圾收集器
+ 单线程收集器,在进行垃圾收集时,必须暂停所有的工作线程直到结束,该收集器停顿时间长,-XX:+UseSerialGC 年轻代使用串行垃圾收集器,-XX:+UseSerialOldGC 老年代使用串行垃圾收集器
- Parallel
+ 采用多线程来扫描并压缩堆,停顿时间短,回收效率高,-XX:+UseParNewGC 使用并发标记扫描垃圾回收器;能够提高应用吞吐率
+
+> JDK8 默认使用:年轻代UseParallelGC,老年代UseParallelOldGC
+
+- CMS 基于"标记-清除"算法,一共分初始标记、并发标记、重新标记、并发清除,并发重置5个阶段;能够降低STW,提高用户体验
+ 在初始标记、重新标记阶段需要STW,并且CMS收集器占用CPU资源较多,无法处理浮动垃圾
+ 并发重置阶段重新初始化CMS数据结构和数据,为下次垃圾回收做准备
+ 在并发标记和并发清理阶段可能会出现垃圾回收还没执行完,垃圾回收又被触发的情况,此时会发生"concurrent mode failure",垃圾收集器进入STW,用serial old 进行回收。
+
+> (-XX:CMSInitiatingOccupancyFraction 调整老年代占用多少触发回收;-XX:+UseCMSCompactAtFullCollection 默认开启,在即将触发FullGC前对内存碎片进行整理;-XX:CMSFullGCsBeforeCompaction设置执行多少次不压缩的FullGC后,来一次带压缩的的碎片整理)
- 采用多线程来扫描并压缩堆,停顿时间短,回收效率高,-XX:+UseParNewGC 使用并发标记扫描垃圾回收器
+- G1 可以跟用户程序并发进行垃圾收集;分代收集,将堆划分成多个大小相等的独立Region区域;空间整合,默认就会进行内存整理;可预测的停顿,G1跟踪各个Region的回收获得的空间大小和回收所需要的经验值,维护一个优先列表;
+
+
-- CMS 基于"标记-清除"算法,一共分初始标记、并发标记、重新标记、并发清除,并发重置5个阶段
+### G1 垃圾收集分类
- 在初始标记、重新标记阶段需要STW,并且CMS收集器占用CPU资源较多,无法处理浮动垃圾
+**YoungGC:**
- 并发重置阶段重新初始化CMS数据结构和数据,为下次垃圾回收做准备
+YoungGC并不是在现有的Eden区放满了就马上触发,G1会计算现有的Eden区回收大概要多久时间,如果回收时间远小于参数-XX:MaxGCPauseMills 设定的值,那么增加年轻代的region,继续给新对象存放,不会马上做Young GC,直到下一次Eden区放满,G1计算回收时间接近参数-XX:MaxGCPauseMills设定的值,就会触发Young GC
- (-XX:CMSInitiatingOccupancyFraction 调整老年代占用多少触发回收;-XX:+UseCMSCompactAtFullCollection 默认开启,在即将触发FullGC前对内存碎片进行整理;-XX:CMSFullGCsBeforeCompaction设置执行多少次不压缩的FullGC后,来一次带压缩的的碎片整理)
+**MixedGC**
-- G1 可以跟用户程序并发进行垃圾收集;分代收集,将堆划分成多个大小相等的独立Region区域;空间整合,默认就会进行内存整理;可预测的停顿,G1跟踪各个Region的回收获得的空间大小和回收所需要的经验值,维护一个优先列表;
+不是FullGC,老年代的堆占有率达到参数(-XX:InitiatingHeapOccupancyPercent)设定的值则触发,回收所有的Young和部分Old(根据期望的GC停顿时间确定old区垃圾收集的优先顺序)以及大对象,正常情况G1的垃圾收集是先做MixedGC,主要使用复制算法,需要把各个region中的存活的对象拷贝到别的region里去,拷贝过程中如果发现没有足够的空region能够承载拷贝对象就会触发一次Full GC
+
+**Full GC**
+
+停止系统程序,然后采用单线程进行标记、清理、和压缩整理,好空闲出来一批Region来供下一次MixedGC使用,这个过程非常耗时。(Shenandoah已经优化成多线程收集,Shenandoah可以认为是G1的升级版本)
+
+
+
+### ZGC
+
+ZGC 是JDK11 中加入的低延迟垃圾收集器,JDK15正式发布,支持16TB级别的堆,停顿时间不超过1ms,没有采用分代算法,清理过程大致分为:并发标记、并发预备重分配、并发重分配、并发重映射。
+
+ZGC 堆空间分页模型(**无分代**):小页面、中页面、大页面
+
+**一次ZGC流程:**
+
+标记阶段:初始标记、并发标记、再标记,初始标记和再标记会STW
+
+转移阶段:并发转移准备、初始转移、并发转移
+
+**ZGC常见触发时机:**
+
+- 基于分配速率的自适应算法(主要):ZAllocationSpikeTolerance控制
+- 基于固定时间间隔:ZCollectionInterval参数控制
+- 主动触发规则:Zproactive控制
+- 启动预热:关键词warmup
+
+> 开启:-XX:+UseZGC
+
+### 什么是逃逸分析技术
+
+是JVM的一种高级优化技术,用于分析对象的动态作用域,从而决定是否可以在栈上分配对象而不是堆上。
+
+逃逸分析的主要优化:
+
+1. 栈上分配
+
+对于未逃逸的对象,直接在栈帧中分配内存。适用于小对象,大对象还是要在堆上分配
+
+优点:对象随方法调用结束自动销毁,减少GC压力;分配速度比堆上分配快。
+
+2. 标量替换
+
+将对象拆解为基本类型变量分配在栈上
+
+3. 同步消除
+对于不会线程逃逸的对象,移除不必要的同步操作
diff --git a/5.Java Reflect_IO.md b/5.Java Reflect_IO.md
old mode 100755
new mode 100644
index ca58eed..6ffb3c7
--- a/5.Java Reflect_IO.md
+++ b/5.Java Reflect_IO.md
@@ -23,7 +23,7 @@ Class clazz = Class.forName("类的全路径");
1.使用Class对象的newInstance(),这种方法需要Class对象对应的类有默认的空构造器
2.调用Constructor对象的newInstance(),先通过Class对象获取构造器对象,再通过构造器对象的newInstance()创建
-
+> 扩展:[【读码JDK】-带你详细了解lang.Class类(一)_java.lang.class类-CSDN博客](https://itsaysay.blog.csdn.net/article/details/125228566)
### 请说明如何通过反射获取和设置对象私有字段的值?
@@ -36,8 +36,6 @@ BIO(Block IO): jkd1.4以前的IO模型,它是一种阻塞IO
NIO(NoN-Block IO):JDK1.4以后才有的IO模型,提高了程序的性能,借鉴比较先进的设计思想,linux多路复用技术,轮询机制
AIO(Asynchronous IO):JDK1.7以后才有的IO模型,相当于NIO2,相当于NIO2,学习Linux epoll模式
-linux epoll介绍:https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/YUMmIjJzhudrKb8WHcJ49Q
-
### Java NIO的原理
1.多路复用技术:建立连接—发送数据—服务端处理—反馈
2.轮询机制(Select模式)
@@ -82,4 +80,12 @@ try(ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open()) {
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
-```
\ No newline at end of file
+```
+
+### 什么是AIO
+
+AIO 是基于Proactor模型的,就是异步非阻塞模型。
+
+每个连接发送过来的请求,都会绑定一个buffer,然后通知操作系统去异步完成读,此时你的程序是会去干别的事儿的,等操作系统完成数据读取之后,就会回调你的接口,给你操作系统异步读完的数据。
+
+然后你对这个数据处理一下,接着将结果往回写。写的时候也给操作系统一个buffer,让操作系统自己获取数据去完成写操作,写完以后再回来通知你。
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/6.Design Pattern.md b/6.Design Pattern.md
old mode 100755
new mode 100644
index 9411b32..0ea0ac3
--- a/6.Design Pattern.md
+++ b/6.Design Pattern.md
@@ -8,7 +8,7 @@
>
> https://www.runoob.com/design-pattern/design-pattern-tutorial.html
-## 23种设计模式
+## 创建型设计模式
### 抽象工厂模式
@@ -32,6 +32,8 @@
[「单例模式示例代码」](#单例模式代码)
+## 结构型设计模式
+
### 适配器模式
是一种结构型设计模式,它能使接口不兼容的对象能够互相合作
@@ -101,6 +103,8 @@
[「代理模式示例代码」](#代理模式示例代码)
+## 行为型设计模式
+
### 责任链模式
是一种行为型设计模式,允许你将请求沿着处理者链进行发送。收到请求后,每个处理者均可对请求进行处理,或将其传递给链上的下一个处理者
@@ -109,6 +113,10 @@
是一种行为设计模式,它可将请求转换为一个包含在请求相关的所有信息的独立对象
+### 解释器模式
+
+给定一种语言,定义它的文法表示,并定义一个解释器,该解释器根据文法表示来解释语言中的句子
+
### 迭代器模式
是一种行为设计模式,让你能在不暴露集合低层表现形式(列表、栈、树等)的情况下遍历集合中的所有元素
diff --git a/7.Data Structure.md b/7.Data Structure.md
old mode 100755
new mode 100644
diff --git a/8.DataBase.md b/8.DataBase.md
old mode 100755
new mode 100644
index 02c7b65..ba25b4b
--- a/8.DataBase.md
+++ b/8.DataBase.md
@@ -4,9 +4,7 @@
### 数据库三大范式、反模式
-1. 强调属性的原子性约束,要求属性具有原子性,不可再分解
-2. 强调记录的唯一性约束,表必须有一个主键,并且没有包含在主键中的列必须完全依赖于主键,而不能只依赖于主键的一部分
-3. 强调属性冗余性的约束,即非主键列必须直接依赖于主键
+
反模式:如果完全按照三大范式来设计表结构,会导致业务涉及表增多,查询数据需要多表联合查询,导致sql复杂,性能变差,不利于维护,也不利于分库分表,比如会在表中冗余存储城市id对应的城市名称
@@ -136,6 +134,10 @@ B+Tree索引:
设置系统当前隔离级别:set global transaction isolation level repeatable read;
+### 什么是回表,如何解决
+
+"回表" 是指:通过非聚簇索引查询时,因索引未包含所需全部列,需用查到的主键到聚簇索引中再次查询完整数据的过程。解决核心是 **避免回表**,即利用 **覆盖索引**,覆盖索引是指 **索引包含查询所需的列**。
+
### 什么是MVCC, MySQL的MVCC原理
MVCC即多版本并发控制,它能在很多情况下避免加锁操作,降低开销,不同的存储引擎实现方式不同,有乐观并发控制和悲观并发控制
@@ -224,3 +226,18 @@ select * from a left join b where 条件 只返回where中匹配的数据
https://www.cnblogs.com/caowenhao/p/8003846.html
+### Mysql 主从同步延迟问题
+
+主从同步延迟产生的问题:插入新数据后,立马查询会查不到数据
+
+1. 主从同步开启**并行复制**
+2. 调整代码,不要插入后,先查询,再更新,如果要更新,插入后直接更新
+3. 拆库,降低库的并发量,在并发量小的时候(500/s),延迟可以忽略不计
+4. 这个查询操作直连主库
+4. 二次查询,从库查不到,从主库查询
+4. 容忍短暂的数据不一致
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/9.Redis.md b/9.Redis.md
old mode 100755
new mode 100644
index 50358ce..dca4777
--- a/9.Redis.md
+++ b/9.Redis.md
@@ -38,7 +38,11 @@ Redis 3.0 版本支持的策略
### Redis 持久化机制
1.RDB持久化:
把当前进程数据生成快照保存到硬盘的过程,触发方式有手动触发和自动触发
+
+redis-cli 进入redis命令行:
+
手动触发命令:save和bgsave命令
+
- save命令:阻塞当前Redis服务,直到RDB过程完成为止,不建议线上环境使用
- bgsave命令:Redis进程执行fork操作创建子进程,RDB持久化过程由子进程负责,完成后自动结束,阻塞只发生在fork阶段,一般时间很短
自动触发:
@@ -106,7 +110,7 @@ AOF文件错误,可以通过redis-check-aof-fix 修复
### Redis 数据类型
> 字符串
-> key是字符串类型,字符串类型的值可以是字符串、数字、二进制(最大不能超过512MB),是动态字符串,内部通过预分配冗余空间的方式来减少内存的频繁分配
+> key是字符串类型,字符串类型的值可以是字符串、数字、二进制(最大不能超过512MB),是动态字符串,内部通过预分配冗余空间的方式来减少内存的频繁分配,内部使用简单动态字符串(SDS)
| 命令 | 解释 | 备注 |
| ----------- | ------------------ | ------------------------------------------------------------ |
@@ -125,7 +129,7 @@ AOF文件错误,可以通过redis-check-aof-fix 修复
| getrange | 获取部分字符串 | key start end |
> 哈希
-> 一个键值对结构, 内部结构同Java的 HashMap, 数组+链表的结构,值只能存储字符串,编码是ziplist或者hashtable。另外在rehash的时候,采用定时任务渐进式迁移内容
+> 一个键值对结构, 内部结构同Java的 HashMap, 数组+链表的结构,值只能存储字符串,编码是ziplist或者hashtable。另外在rehash的时候,采用定时任务渐进式迁移内容,根据哈希表的元素数量和大小自动切换,数量少且键值对都小时用压缩列表,否则切换为哈希表
| 命令 | 解释 | 备注 |
| -------------------- | ------------------------ | ----------------------------------------------- |
@@ -144,7 +148,7 @@ AOF文件错误,可以通过redis-check-aof-fix 修复
| hstrlen | 计算value字符串长度 | key field |
> 列表
-> 用来存储多个有序的字符串,一个列表最多可以存储232 - 1 个元素,列表中的元素可以是重复的,相当于Java中的LinkedList, 是一个链表而不是数组, 底层是采用quicklist结构,在数据量少的时候会使用ziplist压缩列表,数据量多的时候才使用quicklist
+> 用来存储多个有序的字符串,一个列表最多可以存储232 - 1 个元素,列表中的元素可以是重复的,相当于Java中的LinkedList, 是一个链表而不是数组, 底层是采用quicklist结构(3.2+默认),在数据量少的时候会使用ziplist压缩列表,数据量多的时候才使用quicklist
| 命令 | 解释 | 备注 |
| --------------- | -------------------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------ |
@@ -210,7 +214,7 @@ AOF文件错误,可以通过redis-check-aof-fix 修复
> 查询编码:object encoding key
-
+
> 键相关命令
@@ -285,12 +289,12 @@ object encoding key 查询key的内部编码
Pipeline(流水线) 机制能将一组Redis命令进行组装,通过一次RTT传输给Redis,再将这组Redis命令的执行结果按照顺序返回给客户端
原生批量命令与Pipeline对比:
-* 原生批量命令是原子的,Pipeline是非原子的
+* **原生批量命令是原子的,Pipeline是非原子的**
* 原生批量命令是一个命令对应多个key,Pipeline支持多个命令
* 原生批量命令是Redis服务端支持实现的,而Pipeline需要服务端和客户端共同实现
### 事务
-redis 简单事务功能,将一组需要一起执行的命令放到multi和exec两个命令之间。multi命令代表事务开始,exec命令代表事务结束,他们之间的命令是原子顺序执行的。如果要停止事务的执行,用discard命令代替exec命令
+redis 简单事务功能,将一组需要一起执行的命令放到**multi和exec**两个命令之间。multi命令代表事务开始,exec命令代表事务结束,他们之间的命令是**原子顺序**执行的。如果要停止事务的执行,用discard命令代替exec命令
watch 命令 用来确保事务中的key没有被其他客户端修改过,才执行事务,否则不执行(类似乐观锁)
@@ -316,7 +320,7 @@ evalsha 脚本sha1值 key个数 key列表 参数列表
> config set slowlog-max-len
- 获取慢查询日志:
慢查询只记录命令执行时间,不包括命令排队和网络传输时间
- slowlog get [n] n指定条数
+ slowlog get [n] n指定条数
- 日志数据结构
> 3 1) (integer) 3 (id)
@@ -329,7 +333,7 @@ evalsha 脚本sha1值 key个数 key列表 参数列表
> slowlog reset
### Redis键过期删除策略
-键过期,内部保存在过期字典expires中,Redis采用惰性删除和定时任务删除机制;
+键过期,内部保存在过期字典expires中,Redis采用**惰性删除**和**定时任务删除**机制;
惰性删除用于在客户端读取带有超时属性的键时,如果已经超过设置的过期时间,会执行删除并返回空,但这种方式如果键过期,而且一直没有被重新访问,键一直存在
定时任务删除:能够解决惰性删除问题,Redis内部维护一个定时任务,每秒运行10次。根据键的过期比例,使用快慢两种速率模式回收键,缺点是占用CPU时间,在过期键多的时候会影响服务器的响应时间和吞吐量
@@ -342,20 +346,20 @@ AOF写入的时候,如果某个键过期,会向AOF追加一条DEL命令;AO
复制的时候,主服务器发送删除通知,从服务器接到删除通知时才删除过期键
### Redis高可用方案
-1. 主从模式:一主二从
+1. 主从模式:一主二从(达到支持10万+并发)
配置redis.conf , 从节点配置 slaveof 127.0.0.1 6379
确认主从关系: redis-cli -h 127.0.0.1 -p 6379 info replication
-
2. 哨兵模式:
配置 redis-sentinel.conf ,sentinel monitor mymaster 127.0.0.1 6379 1
最后一位是选举master需要的票数
启动哨兵:
redis-sentinel redis-sentinel.conf
或者 redis-server redis-sentinel.conf --sentinel
-
3. redis-cluster:
- 每个节点保存数据和整个集群状态,每个节点都和其他节点连接。采用哈希函数把数据映射到一个固定范围的整数集合中,整数定义为槽。所有键根据哈希函数映射到0~16383整数槽内,公式 slot = CRC16(key) & 16383
-
+ 每个节点保存数据和整个集群状态,每个节点都和其他节点连接。采用哈希函数把数据映射到一个固定范围的整数集合中,整数定义为槽。所有键根据哈希函数映射到0~16383整数槽内,公式 slot = CRC16(key) & 16383
+ 修改redis.conf,开启集群模式:cluster-enabled yes,集群内部配置文件路径:cluster-config-file "nodes-6379.conf"
+ 启动节点
+ 使用meet把节点加入集群中:cluster meet 127.0.0.1 6381
4. Codis
https://juejin.im/post/5c132b076fb9a04a08218eef
@@ -373,19 +377,55 @@ redis-sentinel redis-sentinel.conf
2. 从节点内部通过每秒运行的定时任务维护复制相关逻辑,当定时任务发现存在新的主节点后,会尝试与该节点建立网络连接
3. 连接建立成功后,从节点发送ping请求进行首次通信,目的是检测主从之间网络套接字是否可用,主节点当前是否接受处理命令
4. 如果主节点配置了密码验证,则从节点必须要配置相同的密码才能通过验证,进行复制同步
- 5. 通过验证后,主从可正常通信了,主节点会把数据持续发给从节点,同步方式有全量同步和部分同步,刚建立建立的时候,会进行全量同步,同步结束后,进行部分同步
+ 5. 通过验证后,主从可正常通信了,主节点会把数据持续发给从节点,**同步方式有全量同步和部分同步**,刚建立建立的时候,会进行全量同步,同步结束后,进行部分同步
6. 当主节点与从节点同步完当前的数据后,主节点会把后续新增的命令持续发送给从节点进行同步
- 哨兵模式 最小配置 1主 2从 3哨兵,3个哨兵能监控每个master和salve
+### 什么是脑裂
+
+脑裂指的是在分布式系统中,由于网络分区(network partition)导致集群被分割成多个独立的部分,每个部分都认为自己是唯一存活的,从而导致数据不一致的情况。
+
+Redis 中的脑裂表现为:
+
+1. 主从集群被分割成两部分
+2. 两部分都认为自己是主节点(或包含主节点)
+3. 客户端可能连接到不同的部分,看到不同的数据
+
+导致脑裂的原因:
+
+1. **网络问题**:主节点和从节点/哨兵之间的网络连接中断
+2. **资源问题**:主节点负载过高导致无法及时响应心跳
+3. **配置问题**:哨兵或集群配置不当
+
+### 解决异步复制和脑裂导致的数据丢失
+
+min-slaves-to-write 1
+
+min-slaves-max-lag 10
+
+要求至少有1个slave,数据复制和同步的延迟不能超过10秒
+
+如果说一旦所有的slave,数据复制和同步的延迟都超过了10秒,那么master就不会再接收任何请求了
+
+这两个配置可以减少异步复制和脑裂导致的数据丢失
+
+(1)减少异步复制的数据丢失
+
+有了min-slaves-max-lag 这个配置,就是说一旦slave复制数据和ack延迟太长,就认为master可能宕机后损失数据太多,就拒绝写入,使得同步造成的数据丢失降到可控范围
+
+(2)减少脑裂的数据丢失
+
+如果一个master 出现了脑裂,跟其他slave丢了连接,那么上面的配置可以确保,如果不能继续给指定数量的slave发送数据,而且slave超过10秒没有给自己ack消息,那么就直接拒绝客户端的写请求,这样脑裂后的旧master不会接受client的新数据,也就避免了数据丢失
+
### 缓存问题
- 缓存穿透
- 缓存穿透是指,缓存中不存在该key的数据,于是就是去数据库中查询,数据库也不存在该数据,导致循环查询数据
+ 缓存穿透是指,**缓存中不存在该key的数据**,于是就是去数据库中查询,**数据库也不存在该数据**,导致循环查询数
优化:
- 1. 缓存空对象��
+ 1. 缓存空对象
对于不存在的数据,依旧将空值缓存起来。但这会造成内存空间的浪费,可以针对这类数据加一个过期时间。对于缓存和存储层数据的一致性,可以在过期的时候,请求存储层,或者通过消息系统更新缓存
@@ -401,7 +441,7 @@ redis-sentinel redis-sentinel.conf
- 缓存击穿
- 缓存击穿指,某key突然变成了热点key,大量请求到该key,但key刚好又失效,导致从数据库中去查询数据
+ 缓存击穿指,**某key突然变成了热点key,大量请求到该key,但key刚好又失效,导致从数据库中去查询数据**
优化:
@@ -409,14 +449,23 @@ redis-sentinel redis-sentinel.conf
- 缓存雪崩
- 指缓存由于大量请求,造成缓存挂掉,大量请求直接打到存储层,造成存储层挂机
+ 指缓存由于**大量请求**,同时**缓存又大量失效**,导致大量请求直接打到存储层,造成存储层压力过大或者挂机
优化:
+ 事前
+
1. 使用主从,哨兵,集群模式保证缓存高可用
- 2. 依赖隔离组件为后端限流并降级
3. 提前演练,做好后备方案
+ 事中:
+
+ 使用限流组件,限流并降级
+
+ 事后:
+
+ redis 持久化,重启后恢复数据
+
- 缓存更新方式
同步更新,先写入数据库,写入成功后,再更新缓存。
@@ -448,10 +497,6 @@ PS: Redis锁可能会在业务逻辑还没执行完的时候就已经超时释
ZK锁 通过在服务端新建一个临时有序节点,哪个客户端成功创建了第一个临时有序节点,就代表该客户端获得了锁,后面节点的客户端会处于监听状态,当释放锁的时候,服务端就会删除第一个临时节点,此时第二个临时节点能监听到上一个节点的释放事件,这样第二个节点就变成第一个节点,此时客户端2就代表获得了锁。如果客户端的会话关闭,临时节点会被删除,也就释放了锁
-[《三种分布式锁的优缺点及解决方案》](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s?__biz=MzA4NjA3MTAyMQ==&mid=2649219741&idx=1&sn=e543b333306af62d1ccb8753c3935f61&chksm=87dd011fb0aa8809ade0cb675f6963d606990aab2ac460ff3b27fb8fedb63a7701370518fee6&token=308357506&lang=zh_CN#rd)
-
-
-
### 在某个时间段,redis某个key变成了热点key,此时请求又都打到了一台slave上,请问该怎么办?
由于之前没有做热点Key监控,不能进行对热点key 进行本地缓存,也没有预料到该key会变成热点key,但现在该key变成了热点key, 此时的办法可以新开redis实例,在新的实例上新建该热点key,将后续的请求分散到其他的实例上。
@@ -462,3 +507,89 @@ ZK锁 通过在服务端新建一个临时有序节点,哪个客户端成功
[《阿里云redis热点key问题的发现与解决》](https://blog.csdn.net/zhanglf88/article/details/103079306)
+### Redis 如何排查大key
+
+**使用`--bigkeys`命令**
+
+- 这是Redis自带的一个命令,用于对整个Key空间进行扫描,统计string、list、set、zset、hash等常见数据类型中每种类型里的最大的key。
+- 使用方法:`redis-cli -h -p -a --bigkeys`
+- 注意:这个命令是以scan延迟计算的方式扫描所有key,因此执行过程中不会阻塞Redis,但当实例存在大量的keys时,命令执行的时间会很长。建议在slave上扫描。
+
+**使用`MEMORY USAGE`命令(仅支持Redis 4.0以后的版本)**
+
+- 这个方法可以查看指定key的内存使用情况。
+- 使用方法:`redis-cli -h -p -a MEMORY USAGE `
+- 该命令会返回key的内存使用情况(以字节为单位)。
+
+**使用Rdbtools工具包**
+
+- Rdbtools是一个第三方开源工具,用于解析Redis的快照文件(rdb文件)。
+- 通过这个工具,可以分析rdb文件中的内容,包括各个key的大小。
+
+### Redisson 如何实现分布式锁
+
+Redisson 的分布式锁实现(`RLock`)基于Redis的Lua脚本和发布/订阅机制
+
+```java
+RLock lock = redisson.getLock("myLock");
+lock.lock();
+try {
+ // 业务代码
+} finally {
+ lock.unlock();
+}
+```
+
+**实现原理:**
+
+1. **加锁机制**:
+ - 使用Lua脚本保证原子性:`SET lock_name uuid NX PX 30000`
+ - 如果锁已被占用,通过发布/订阅机制等待锁释放通知
+ - 支持可重入:通过计数器记录重入次数
+2. **看门狗机制**:
+ - 默认加锁时间30秒
+ - 后台线程每10秒检查一次,如果线程还持有锁则延长锁时间
+3. **解锁机制**:
+ - 使用Lua脚本保证原子性操作
+ - 发布锁释放消息通知其他等待客户端
+
+### Redisson 如何实现延迟队列
+
+Redisson 通过 `RDelayedQueue` 实现延迟队列:
+
+```java
+RQueue queue = redisson.getQueue("myQueue");
+RDelayedQueue delayedQueue = redisson.getDelayedQueue(queue);
+// 延迟10秒放入队列
+delayedQueue.offer("msg1", 10, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
+
+// 在其他地方消费
+String msg = queue.poll();
+```
+
+**实现原理**:
+
+1. 使用Redis的ZSET结构存储延迟消息,score为执行时间戳
+2. 后台线程定期检查到期消息
+3. 到期后从ZSET移除并放入目标队列
+
+### Redisson 如何实现限流器
+
+Redisson 提供 `RRateLimiter` 实现分布式限流:
+
+```java
+RRateLimiter limiter = redisson.getRateLimiter("myLimiter");
+// 每秒10个请求
+limiter.trySetRate(RateType.OVERALL, 10, 1, RateIntervalUnit.SECONDS);
+
+if (limiter.tryAcquire()) {
+ // 通过限流
+}
+```
+
+**实现原理**:
+
+1. 使用Redis的Lua脚本保证原子性
+2. 基于令牌桶算法实现
+3. 支持全局(OVERALL)和单客户端(PER_CLIENT)两种模式
+
diff --git "a/Bug345円210円206円344円272円253円/1.Lock Transactional.md" "b/Bug345円210円206円344円272円253円/1.Lock Transactional.md"
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..be68d6f
--- /dev/null
+++ "b/Bug345円210円206円344円272円253円/1.Lock Transactional.md"
@@ -0,0 +1,157 @@
+# 不当使用Redis锁产生的问题
+
+# 前言
+
+春节放假期间,一个项目上的积分接口被刷,而且不止一个人在刷,并且东西也被兑走,放假晚上被人叫起来排查问题,通过这个人的积分明细观察,基本一秒就能获取一次,远远超过了积分规则限定的次数,这肯定是用脚本了,虽然后期联系死活说自己是正常途径获取。由于是业主,我们还是决定自己来承担这个损失,被项目方从合同中扣除奖品费用1万余元。
+
+# 问题原因
+
+先说下接口的逻辑层次结构:
+
+--controller 积分获取接口,用PointController表示
+
+--service 积分获取接口service,用PointService表示
+
+我用伪代码来表示整个调用逻辑:
+
+*PointController*
+
+```java
+@RestController
+public class PointController {
+
+ @Resource
+ private PointService pointService;
+
+ @PostMapping(/addPoint)
+ public Response addPoint() {
+ //分布式锁,使用redis的NX命令
+ RedisDistributedLock lock = new RedisDistributedLock();
+ //创建一个3s过期,100ms休眠的锁
+ if(lock.lock("POINT_KEY", 3000L, 100L)) {
+ try {
+ //调用
+ pointService.addPoint();
+ } catch (Exception ex) {
+ e.printStackTrace;
+ } finally {
+ //解锁
+ lock.unlock("POINT_KEY");
+ }
+ }
+ return Response.ok(getLastPoint());
+ }
+}
+```
+
+1. 创建一个分布式锁对象,该分布式锁使用redis的`NX`命令实现
+2. 随后创建一个3s过期的分布式锁,以便锁住该新增积分的请求
+3. 最后在新增积分执行完后,在finally中释放锁
+4. 最后返回该用户的最终积分
+
+*PointService*
+
+```java
+public class PointService {
+
+ @Transactional(rollbackFor = Exception.class)
+ public void addPoint() {
+ //查询积分规则
+ PointRule pointRule = getPointRule();
+ //查询用户该积分项的积分获取记录总数
+ Integer total = getPointRecords();
+ //判断该用户的积分记录总数是否大于 积分规则限定的次数
+ //大于则不处理,返回
+ if(total - pointRule.getRuleTimes>= 0) {
+ return;
+ }
+
+ //生成积分记录
+ int insert = insertPointRecords();
+ //更新用户总积分
+ if(insert> 0) {
+ updateUserPoint();
+ }
+ }
+}
+```
+
+PointService 中的添加积分逻辑:
+
+1. 首先查询该项目积分规则,查询用户该积分项的积分获取记录总数
+2. 判断该用户的积分记录总数是否大于 积分规则限定的次数,大于则不处理,返回
+3. 生成积分记录
+4. 更新用户总积分
+
+
+
+该添加积分的逻辑整体上看好像没什么问题,也确实在一切正常的情况下运行是不会有问题的。
+
+如果PointService 中的添加积分逻辑在分布式锁有效期3s内执行完,是不会有问题的。
+
+但如果PointService中的添加积分逻辑超过3s...那是不是后续请求又可以获取锁了,这也正是这次事故的原因。
+
+
+
+`因为PointService中的添加积分逻辑超过了3s,并且上一个请求的事务还未提交,后续请求已经获取锁进入PointService,在查询积分记录后,判断还是满足规则,继续执行后续的逻辑,造成用户能够获取多次积分。`
+
+
+
+# 问题处理
+
+原因总结一下:
+
+1. 添加积分逻辑处理时间过长
+2. 分布式锁超时
+
+
+
+第一个问题:逻辑改动过大,需要时间调整,没有采用
+
+第二个问题:换成Redisson,因为redisson在即使超时的情况下也会续锁,避免锁超时
+
+
+
+# 你以为问题真的解决了吗
+
+如果把上面的代码换成Redisson后,代码一般是这样的
+
+*PointController*
+
+```java
+@RestController
+public class PointController {
+
+ @Resource
+ private PointService pointService;
+
+ @PostMapping(/addPoint)
+ public Response addPoint() {
+ RLock redissonClientLock = redissonClient.getLock("addPoint");
+ try {
+ redissonClientLock.lock();
+ //调用
+ pointService.addPoint();
+ } catch (Exception ex) {
+ e.printStackTrace;
+ } finally {
+ //解锁
+ redissonClientLock.unlock();
+ }
+ return Response.ok(getLastPoint());
+ }
+}
+```
+
+你觉得还会有问题吗?事实证明,这段代码确实没问题了。
+
+但是如果你把锁加到pointService 的addPoint方法里面,你觉得会不会有问题?
+
+> 如果这样做,执行到finally中,释放了锁,但实际该方法还没彻底执行完,还没提交事务,此时下一个阻塞的请求获取了锁,还是会造成锁失效的现象,所以应该把锁加在有事务的方法外面。
+
+# 总结
+
+一方面因为忙于做项目,忽略了代码Review,另一方面测试的时候没有对接口进行并发测试,或者根本没有测出来,第三没有监控工具监控长事务,以及频繁请求。
+
+
+
diff --git a/Other Interview.md b/Other Interview.md
old mode 100755
new mode 100644
diff --git a/README.md b/README.md
old mode 100755
new mode 100644
index 9207da6..68cba31
--- a/README.md
+++ b/README.md
@@ -46,7 +46,7 @@ https://github.com/jujunchen/ebook
#### 交流平台
-
+阿提说说:[阿提说说-CSDN博客](https://itsaysay.blog.csdn.net/)
diff --git a/media/._IMG_082BD9A3B24F-1.jpeg b/media/._IMG_082BD9A3B24F-1.jpeg
deleted file mode 100755
index 23a8c5e..0000000
Binary files a/media/._IMG_082BD9A3B24F-1.jpeg and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/media/._dubbo-keep-connection.png b/media/._dubbo-keep-connection.png
deleted file mode 100755
index e0a6d48..0000000
Binary files a/media/._dubbo-keep-connection.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/media/._image-20191114195305300.png b/media/._image-20191114195305300.png
deleted file mode 100755
index 24a4c4e..0000000
Binary files a/media/._image-20191114195305300.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/media/._serialize-deserialize.png b/media/._serialize-deserialize.png
deleted file mode 100755
index 69c1830..0000000
Binary files a/media/._serialize-deserialize.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/media/006y8mN6ly1g8xdtvdrcyj31jy06adjs.jpg b/media/006y8mN6ly1g8xdtvdrcyj31jy06adjs.jpg
old mode 100755
new mode 100644
diff --git a/media/006y8mN6ly1g8xdwn9fq8j31ki0r8nfb.jpg b/media/006y8mN6ly1g8xdwn9fq8j31ki0r8nfb.jpg
old mode 100755
new mode 100644
diff --git a/media/006y8mN6ly1g8xe5miksnj30w201w74f.jpg b/media/006y8mN6ly1g8xe5miksnj30w201w74f.jpg
old mode 100755
new mode 100644
diff --git a/media/006y8mN6ly1g8xetz5v5jj31so04sgmx.jpg b/media/006y8mN6ly1g8xetz5v5jj31so04sgmx.jpg
old mode 100755
new mode 100644
diff --git a/media/006y8mN6ly1g8xf7p2kg1j30h004omxn.jpg b/media/006y8mN6ly1g8xf7p2kg1j30h004omxn.jpg
old mode 100755
new mode 100644
diff --git a/media/006y8mN6ly1g8xfievgsdj31kk03awf9.jpg b/media/006y8mN6ly1g8xfievgsdj31kk03awf9.jpg
old mode 100755
new mode 100644
diff --git a/media/006y8mN6ly1g8xfrevz58j30v602yaah.jpg b/media/006y8mN6ly1g8xfrevz58j30v602yaah.jpg
old mode 100755
new mode 100644
diff --git a/media/01.png b/media/01.png
old mode 100755
new mode 100644
diff --git a/media/252461fbb6d64d3dbc1914b7eadbfb86.jpeg b/media/252461fbb6d64d3dbc1914b7eadbfb86.jpeg
old mode 100755
new mode 100644
diff --git a/media/36465fd7d91b3a4aeb3b28c3777649e6.jpeg b/media/36465fd7d91b3a4aeb3b28c3777649e6.jpeg
old mode 100755
new mode 100644
diff --git a/media/4935fcc0a209fd1d4b70cade94986f59.jpeg b/media/4935fcc0a209fd1d4b70cade94986f59.jpeg
old mode 100755
new mode 100644
diff --git a/media/6650aa32de0def76db0e4c5228619aef.jpeg b/media/6650aa32de0def76db0e4c5228619aef.jpeg
old mode 100755
new mode 100644
diff --git a/media/IMG_082BD9A3B24F-1.jpeg b/media/IMG_082BD9A3B24F-1.jpeg
old mode 100755
new mode 100644
diff --git a/media/distributed-system-request-sequence.png b/media/distributed-system-request-sequence.png
old mode 100755
new mode 100644
diff --git a/media/dubbo-keep-connection.png b/media/dubbo-keep-connection.png
old mode 100755
new mode 100644
diff --git a/media/dubbo-not-keep-connection.png b/media/dubbo-not-keep-connection.png
old mode 100755
new mode 100644
diff --git a/media/dubbo-service-invoke-road.png b/media/dubbo-service-invoke-road.png
old mode 100755
new mode 100644
diff --git a/media/image-20191114193034340-3731511.png b/media/image-20191114193034340-3731511.png
old mode 100755
new mode 100644
diff --git a/media/image-20191114193034340.png b/media/image-20191114193034340.png
old mode 100755
new mode 100644
diff --git a/media/image-20191114194022209.png b/media/image-20191114194022209.png
old mode 100755
new mode 100644
diff --git a/media/image-20191114194055084.png b/media/image-20191114194055084.png
old mode 100755
new mode 100644
diff --git a/media/image-20191114194125306.png b/media/image-20191114194125306.png
old mode 100755
new mode 100644
diff --git a/media/image-20191114194139915.png b/media/image-20191114194139915.png
old mode 100755
new mode 100644
diff --git a/media/image-20191114194157527.png b/media/image-20191114194157527.png
old mode 100755
new mode 100644
diff --git a/media/image-20191114194224919.png b/media/image-20191114194224919.png
old mode 100755
new mode 100644
diff --git a/media/image-20191114194236837.png b/media/image-20191114194236837.png
old mode 100755
new mode 100644
diff --git a/media/image-20191114194247158.png b/media/image-20191114194247158.png
old mode 100755
new mode 100644
diff --git a/media/image-20191114194335314.png b/media/image-20191114194335314.png
old mode 100755
new mode 100644
diff --git a/media/image-20191114194356825.png b/media/image-20191114194356825.png
old mode 100755
new mode 100644
diff --git a/media/image-20191114194415039.png b/media/image-20191114194415039.png
old mode 100755
new mode 100644
diff --git a/media/image-20191114194430674.png b/media/image-20191114194430674.png
old mode 100755
new mode 100644
diff --git a/media/image-20191114194439833.png b/media/image-20191114194439833.png
old mode 100755
new mode 100644
diff --git a/media/image-20191114194449725.png b/media/image-20191114194449725.png
old mode 100755
new mode 100644
diff --git a/media/image-20191114194503521.png b/media/image-20191114194503521.png
old mode 100755
new mode 100644
diff --git a/media/image-20191114194740033.png b/media/image-20191114194740033.png
old mode 100755
new mode 100644
diff --git a/media/image-20191114194815842.png b/media/image-20191114194815842.png
old mode 100755
new mode 100644
diff --git a/media/image-20191114194918523.png b/media/image-20191114194918523.png
old mode 100755
new mode 100644
diff --git a/media/image-20191114194952076.png b/media/image-20191114194952076.png
old mode 100755
new mode 100644
diff --git a/media/image-20191114195007116.png b/media/image-20191114195007116.png
old mode 100755
new mode 100644
diff --git a/media/image-20191114195010955.png b/media/image-20191114195010955.png
old mode 100755
new mode 100644
diff --git a/media/image-20191114195023197.png b/media/image-20191114195023197.png
old mode 100755
new mode 100644
diff --git a/media/image-20191114195045400.png b/media/image-20191114195045400.png
old mode 100755
new mode 100644
diff --git a/media/image-20191114195113356.png b/media/image-20191114195113356.png
old mode 100755
new mode 100644
diff --git a/media/image-20191114195209444.png b/media/image-20191114195209444.png
old mode 100755
new mode 100644
diff --git a/media/image-20191114195228161.png b/media/image-20191114195228161.png
old mode 100755
new mode 100644
diff --git a/media/image-20191114195305300.png b/media/image-20191114195305300.png
old mode 100755
new mode 100644
diff --git a/media/image-20191114195334883.png b/media/image-20191114195334883.png
old mode 100755
new mode 100644
diff --git a/media/image-20191114195346681.png b/media/image-20191114195346681.png
old mode 100755
new mode 100644
diff --git a/media/image-20191114195421280.png b/media/image-20191114195421280.png
old mode 100755
new mode 100644
diff --git a/media/image-20191114195509483.png b/media/image-20191114195509483.png
old mode 100755
new mode 100644
diff --git a/media/image-20191114200036013.png b/media/image-20191114200036013.png
old mode 100755
new mode 100644
diff --git a/media/image-20191114203012441.png b/media/image-20191114203012441.png
old mode 100755
new mode 100644
diff --git a/media/image-20191114203913199.png b/media/image-20191114203913199.png
old mode 100755
new mode 100644
diff --git a/media/image-20191114204200585.png b/media/image-20191114204200585.png
old mode 100755
new mode 100644
diff --git a/media/serialize-deserialize.png b/media/serialize-deserialize.png
old mode 100755
new mode 100644
diff --git "a/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/Interview Exp1.md" "b/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/Interview Exp1.md"
old mode 100755
new mode 100644
index e5e8a66..a5b5169
--- "a/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/Interview Exp1.md"
+++ "b/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/Interview Exp1.md"
@@ -1,5 +1,5 @@
# "四面四杀"面经
-## 前言(经历)123123
+## 前言(经历)
毕业五年了,已经将近两年没有面试了,这次想在自己职业生涯5~8年的阶段在一个大厂的核心部门的某个细分领域沉下心来,总结出自己在复杂领域模型设计的方法论,为未来转型业务架构师打下基础,所以简历投的也不多,只有某里、某团、某滴(简历没过),下步准备再刷刷算法试试某条和拼夕夕,除了某团某个大数据部门方向确实不是很匹配(三面仅仅聊了半个小时,部门的主方向主要是一些某团大数据团队在做的一些事情,而我确实对大数据中间件不是很感兴趣,但在此也要谢谢大数据部门的三轮面试官大佬,他们确实问的问题更偏底层,深度也是这次经历面试最深的,面试收获也是不少),其他技术面试都已经通过,也算是比较顺利的面试经历。
diff --git "a/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/Interview Exp2.md" "b/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/Interview Exp2.md"
old mode 100755
new mode 100644
diff --git "a/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/Interview Exp3.md" "b/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/Interview Exp3.md"
old mode 100755
new mode 100644
diff --git "a/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/Interview Exp4.md" "b/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/Interview Exp4.md"
old mode 100755
new mode 100644
diff --git "a/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/Interview Exp5.md" "b/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/Interview Exp5.md"
old mode 100755
new mode 100644
diff --git "a/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/Interview Exp6.md" "b/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/Interview Exp6.md"
old mode 100755
new mode 100644
diff --git "a/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/Interview Exp7.md" "b/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/Interview Exp7.md"
old mode 100755
new mode 100644
diff --git "a/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/Interview Exp8.md" "b/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/Interview Exp8.md"
old mode 100755
new mode 100644
diff --git "a/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/Interview Exp9.md" "b/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/Interview Exp9.md"
old mode 100755
new mode 100644
diff --git "a/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/._.DS_Store" "b/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/._.DS_Store"
deleted file mode 100755
index 8e82ed9..0000000
Binary files "a/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/._.DS_Store" and /dev/null differ
diff --git "a/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/._image-20191213092233778.png" "b/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/._image-20191213092233778.png"
deleted file mode 100755
index 15c5994..0000000
Binary files "a/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/._image-20191213092233778.png" and /dev/null differ
diff --git "a/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/._image-20191213092446557.png" "b/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/._image-20191213092446557.png"
deleted file mode 100755
index 9a807c8..0000000
Binary files "a/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/._image-20191213092446557.png" and /dev/null differ
diff --git "a/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/006tNbRwgy1g9ux8rjqfwj30g70fhdm4.jpg" "b/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/006tNbRwgy1g9ux8rjqfwj30g70fhdm4.jpg"
old mode 100755
new mode 100644
diff --git "a/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/006tNbRwgy1g9ux8w8661j30hc08u403.jpg" "b/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/006tNbRwgy1g9ux8w8661j30hc08u403.jpg"
old mode 100755
new mode 100644
diff --git "a/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/006tNbRwgy1g9ux90cmw4j30h803iab4.jpg" "b/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/006tNbRwgy1g9ux90cmw4j30h803iab4.jpg"
old mode 100755
new mode 100644
diff --git "a/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/006tNbRwgy1g9ux96vbg7j30i407sgmz.jpg" "b/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/006tNbRwgy1g9ux96vbg7j30i407sgmz.jpg"
old mode 100755
new mode 100644
diff --git "a/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/006tNbRwgy1g9ux9a6cfxj308b049gm0.jpg" "b/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/006tNbRwgy1g9ux9a6cfxj308b049gm0.jpg"
old mode 100755
new mode 100644
diff --git "a/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/006tNbRwgy1g9ux9dyrn5j30ax0a43zm.jpg" "b/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/006tNbRwgy1g9ux9dyrn5j30ax0a43zm.jpg"
old mode 100755
new mode 100644
diff --git "a/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/640-20191213213310547" "b/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/640-20191213213310547"
deleted file mode 100755
index 3e78f41..0000000
Binary files "a/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/640-20191213213310547" and /dev/null differ
diff --git "a/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/640-20191213213310630" "b/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/640-20191213213310630"
deleted file mode 100755
index 393d8dd..0000000
Binary files "a/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/640-20191213213310630" and /dev/null differ
diff --git "a/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/640-20191213213310681" "b/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/640-20191213213310681"
deleted file mode 100755
index 11561ce..0000000
Binary files "a/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/640-20191213213310681" and /dev/null differ
diff --git "a/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/640-20191213213310684" "b/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/640-20191213213310684"
deleted file mode 100755
index cf19ee5..0000000
Binary files "a/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/640-20191213213310684" and /dev/null differ
diff --git "a/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/640-20191213213310692" "b/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/640-20191213213310692"
deleted file mode 100755
index 8c1a170..0000000
Binary files "a/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/640-20191213213310692" and /dev/null differ
diff --git "a/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/640-20191213213310736" "b/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/640-20191213213310736"
deleted file mode 100755
index 3e78f41..0000000
Binary files "a/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/640-20191213213310736" and /dev/null differ
diff --git "a/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/640-20191213213310747" "b/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/640-20191213213310747"
deleted file mode 100755
index 8c1a170..0000000
Binary files "a/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/640-20191213213310747" and /dev/null differ
diff --git "a/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/640-20191213213310749" "b/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/640-20191213213310749"
deleted file mode 100755
index c587984..0000000
Binary files "a/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/640-20191213213310749" and /dev/null differ
diff --git "a/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/640-20191213213310764" "b/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/640-20191213213310764"
deleted file mode 100755
index c587984..0000000
Binary files "a/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/640-20191213213310764" and /dev/null differ
diff --git "a/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/640-20191213213310784" "b/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/640-20191213213310784"
deleted file mode 100755
index c338ed3..0000000
Binary files "a/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/640-20191213213310784" and /dev/null differ
diff --git "a/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/640-20191213213310802" "b/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/640-20191213213310802"
deleted file mode 100755
index 11561ce..0000000
Binary files "a/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/640-20191213213310802" and /dev/null differ
diff --git "a/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/640-20191213213310803" "b/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/640-20191213213310803"
deleted file mode 100755
index 393d8dd..0000000
Binary files "a/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/640-20191213213310803" and /dev/null differ
diff --git "a/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/640-20191213213310828" "b/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/640-20191213213310828"
deleted file mode 100755
index cf19ee5..0000000
Binary files "a/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/640-20191213213310828" and /dev/null differ
diff --git "a/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/640-20191213213310899" "b/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/640-20191213213310899"
deleted file mode 100755
index c338ed3..0000000
Binary files "a/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/640-20191213213310899" and /dev/null differ
diff --git "a/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/640-20191213213322270" "b/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/640-20191213213322270"
deleted file mode 100755
index 8c1a170..0000000
Binary files "a/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/640-20191213213322270" and /dev/null differ
diff --git "a/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/640-20191213213322273" "b/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/640-20191213213322273"
deleted file mode 100755
index 3e78f41..0000000
Binary files "a/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/640-20191213213322273" and /dev/null differ
diff --git "a/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/640-20191213213322276" "b/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/640-20191213213322276"
deleted file mode 100755
index 11561ce..0000000
Binary files "a/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/640-20191213213322276" and /dev/null differ
diff --git "a/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/640-20191213213322278" "b/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/640-20191213213322278"
deleted file mode 100755
index c587984..0000000
Binary files "a/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/640-20191213213322278" and /dev/null differ
diff --git "a/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/640-20191213213322285" "b/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/640-20191213213322285"
deleted file mode 100755
index c338ed3..0000000
Binary files "a/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/640-20191213213322285" and /dev/null differ
diff --git "a/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/640-20191213213322329" "b/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/640-20191213213322329"
deleted file mode 100755
index cf19ee5..0000000
Binary files "a/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/640-20191213213322329" and /dev/null differ
diff --git "a/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/640-20191213213322353" "b/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/640-20191213213322353"
deleted file mode 100755
index 393d8dd..0000000
Binary files "a/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/640-20191213213322353" and /dev/null differ
diff --git "a/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/640-20191213213327997" "b/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/640-20191213213327997"
deleted file mode 100755
index c338ed3..0000000
Binary files "a/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/640-20191213213327997" and /dev/null differ
diff --git "a/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/640-20191213213328002" "b/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/640-20191213213328002"
deleted file mode 100755
index c587984..0000000
Binary files "a/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/640-20191213213328002" and /dev/null differ
diff --git "a/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/640-20191213213328002-6244008." "b/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/640-20191213213328002-6244008."
deleted file mode 100755
index c587984..0000000
Binary files "a/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/640-20191213213328002-6244008." and /dev/null differ
diff --git "a/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/640-20191213213328004" "b/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/640-20191213213328004"
deleted file mode 100755
index 11561ce..0000000
Binary files "a/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/640-20191213213328004" and /dev/null differ
diff --git "a/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/640-20191213213328010" "b/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/640-20191213213328010"
deleted file mode 100755
index cf19ee5..0000000
Binary files "a/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/640-20191213213328010" and /dev/null differ
diff --git "a/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/640-20191213213328034" "b/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/640-20191213213328034"
deleted file mode 100755
index 8c1a170..0000000
Binary files "a/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/640-20191213213328034" and /dev/null differ
diff --git "a/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/640-20191213213328040" "b/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/640-20191213213328040"
deleted file mode 100755
index 393d8dd..0000000
Binary files "a/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/640-20191213213328040" and /dev/null differ
diff --git "a/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/640-20191213213349268" "b/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/640-20191213213349268"
deleted file mode 100755
index c338ed3..0000000
Binary files "a/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/640-20191213213349268" and /dev/null differ
diff --git "a/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/640-20191213213349274" "b/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/640-20191213213349274"
deleted file mode 100755
index cf19ee5..0000000
Binary files "a/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/640-20191213213349274" and /dev/null differ
diff --git "a/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/640-20191213213349278" "b/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/640-20191213213349278"
deleted file mode 100755
index c587984..0000000
Binary files "a/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/640-20191213213349278" and /dev/null differ
diff --git "a/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/640-20191213213349286" "b/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/640-20191213213349286"
deleted file mode 100755
index 11561ce..0000000
Binary files "a/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/640-20191213213349286" and /dev/null differ
diff --git "a/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/640-20191213213349309" "b/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/640-20191213213349309"
deleted file mode 100755
index 393d8dd..0000000
Binary files "a/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/640-20191213213349309" and /dev/null differ
diff --git "a/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/640-20191213213349324" "b/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/640-20191213213349324"
deleted file mode 100755
index 8c1a170..0000000
Binary files "a/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/640-20191213213349324" and /dev/null differ
diff --git "a/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/640-20191213213349350" "b/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/640-20191213213349350"
deleted file mode 100755
index 3e78f41..0000000
Binary files "a/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/640-20191213213349350" and /dev/null differ
diff --git "a/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/640-20191213213358869" "b/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/640-20191213213358869"
deleted file mode 100755
index c338ed3..0000000
Binary files "a/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/640-20191213213358869" and /dev/null differ
diff --git "a/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/640-20191213213358870" "b/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/640-20191213213358870"
deleted file mode 100755
index cf19ee5..0000000
Binary files "a/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/640-20191213213358870" and /dev/null differ
diff --git "a/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/640-20191213213358873" "b/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/640-20191213213358873"
deleted file mode 100755
index c587984..0000000
Binary files "a/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/640-20191213213358873" and /dev/null differ
diff --git "a/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/640-20191213213358875" "b/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/640-20191213213358875"
deleted file mode 100755
index 11561ce..0000000
Binary files "a/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/640-20191213213358875" and /dev/null differ
diff --git "a/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/640-20191213213358889" "b/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/640-20191213213358889"
deleted file mode 100755
index 3e78f41..0000000
Binary files "a/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/640-20191213213358889" and /dev/null differ
diff --git "a/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/640-20191213213358898" "b/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/640-20191213213358898"
deleted file mode 100755
index 8c1a170..0000000
Binary files "a/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/640-20191213213358898" and /dev/null differ
diff --git "a/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/640-20191213213358910" "b/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/640-20191213213358910"
deleted file mode 100755
index 393d8dd..0000000
Binary files "a/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/640-20191213213358910" and /dev/null differ
diff --git "a/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/640-20191213213554931" "b/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/640-20191213213554931"
deleted file mode 100755
index 3e78f41..0000000
Binary files "a/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/640-20191213213554931" and /dev/null differ
diff --git "a/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/640-20191213213602270" "b/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/640-20191213213602270"
deleted file mode 100755
index 3e78f41..0000000
Binary files "a/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/640-20191213213602270" and /dev/null differ
diff --git "a/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/image-20191213092233778.png" "b/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/image-20191213092233778.png"
old mode 100755
new mode 100644
diff --git "a/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/image-20191213092446557.png" "b/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/image-20191213092446557.png"
old mode 100755
new mode 100644
diff --git "a/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/image-20191213093127572.png" "b/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/image-20191213093127572.png"
old mode 100755
new mode 100644
diff --git "a/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/image-20191213093225461.png" "b/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/image-20191213093225461.png"
old mode 100755
new mode 100644
diff --git "a/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/image-20191213093243414.png" "b/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/image-20191213093243414.png"
old mode 100755
new mode 100644
diff --git "a/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/image-20191213093257647.png" "b/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/image-20191213093257647.png"
old mode 100755
new mode 100644
diff --git "a/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/image-20191213213621574.png" "b/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/image-20191213213621574.png"
old mode 100755
new mode 100644
diff --git "a/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/image-20191213213740733.png" "b/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/image-20191213213740733.png"
old mode 100755
new mode 100644
diff --git "a/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/image-20191213213805148.png" "b/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/image-20191213213805148.png"
old mode 100755
new mode 100644
diff --git "a/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/image-20191213213928996.png" "b/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/image-20191213213928996.png"
old mode 100755
new mode 100644
diff --git "a/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/image-20191213214128396.png" "b/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/image-20191213214128396.png"
old mode 100755
new mode 100644
diff --git "a/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/image-20191213214535975.png" "b/345円244円247円345円216円202円351円235円242円347円273円217円/media/image-20191213214535975.png"
old mode 100755
new mode 100644
diff --git "a/345円255円246円344円271円240円350円265円204円346円226円231円/Learning.md" "b/345円255円246円344円271円240円350円265円204円346円226円231円/Learning.md"
old mode 100755
new mode 100644
index 08e9bfc..f0bcd9f
--- "a/345円255円246円344円271円240円350円265円204円346円226円231円/Learning.md"
+++ "b/345円255円246円344円271円240円350円265円204円346円226円231円/Learning.md"
@@ -46,9 +46,6 @@ Java知识库:https://www.yuque.com/lexiangqizhong/java

-## 公众号
-
-image-20191223213731596
diff --git "a/345円255円246円344円271円240円350円265円204円346円226円231円/media/006tNbRwly1ga6z6ig0vej30ck0ju75u.jpg" "b/345円255円246円344円271円240円350円265円204円346円226円231円/media/006tNbRwly1ga6z6ig0vej30ck0ju75u.jpg"
old mode 100755
new mode 100644
diff --git "a/345円255円246円344円271円240円350円265円204円346円226円231円/media/image-20191223212524703.png" "b/345円255円246円344円271円240円350円265円204円346円226円231円/media/image-20191223212524703.png"
old mode 100755
new mode 100644
diff --git "a/345円255円246円344円271円240円350円265円204円346円226円231円/media/image-20191223212734977.png" "b/345円255円246円344円271円240円350円265円204円346円226円231円/media/image-20191223212734977.png"
old mode 100755
new mode 100644
diff --git "a/345円255円246円344円271円240円350円265円204円346円226円231円/media/image-20191223212741417.png" "b/345円255円246円344円271円240円350円265円204円346円226円231円/media/image-20191223212741417.png"
old mode 100755
new mode 100644
diff --git "a/345円255円246円344円271円240円350円265円204円346円226円231円/media/image-20191223212859627.png" "b/345円255円246円344円271円240円350円265円204円346円226円231円/media/image-20191223212859627.png"
old mode 100755
new mode 100644
diff --git "a/345円255円246円344円271円240円350円265円204円346円226円231円/media/image-20191223212918623.png" "b/345円255円246円344円271円240円350円265円204円346円226円231円/media/image-20191223212918623.png"
old mode 100755
new mode 100644
diff --git "a/345円255円246円344円271円240円350円265円204円346円226円231円/media/image-20191223212936257.png" "b/345円255円246円344円271円240円350円265円204円346円226円231円/media/image-20191223212936257.png"
old mode 100755
new mode 100644
diff --git "a/345円255円246円344円271円240円350円265円204円346円226円231円/media/image-20191223212952306.png" "b/345円255円246円344円271円240円350円265円204円346円226円231円/media/image-20191223212952306.png"
old mode 100755
new mode 100644
diff --git "a/345円255円246円344円271円240円350円265円204円346円226円231円/media/image-20191223213011426.png" "b/345円255円246円344円271円240円350円265円204円346円226円231円/media/image-20191223213011426.png"
old mode 100755
new mode 100644
diff --git "a/345円255円246円344円271円240円350円265円204円346円226円231円/media/image-20191223213029704.png" "b/345円255円246円344円271円240円350円265円204円346円226円231円/media/image-20191223213029704.png"
old mode 100755
new mode 100644
diff --git "a/345円255円246円344円271円240円350円265円204円346円226円231円/media/image-20191223213731596.png" "b/345円255円246円344円271円240円350円265円204円346円226円231円/media/image-20191223213731596.png"
old mode 100755
new mode 100644
diff --git "a/346円272円220円347円240円201円345円210円206円346円236円220円/ArrayBlockingQueue.md" "b/346円272円220円347円240円201円345円210円206円346円236円220円/ArrayBlockingQueue.md"
deleted file mode 100755
index 555cf91..0000000
--- "a/346円272円220円347円240円201円345円210円206円346円236円220円/ArrayBlockingQueue.md"
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,643 +0,0 @@
-# ArrayBlockingQueue源码分析
-
-> 源码基于open jdk 11
-
-
-
-ArrayBlockingQueue是通过有界数组方式实现的阻塞队列 , 通过ReentrantLock实现线程安全,阻塞通过Condition实现,出队和入队使用同一把锁。
-
-有两个内部类Itr 和 Itrs,Itrs内部又实现了Node类,像LinkedBlockingQueue和ConcurrentLinkedQueue都有Node类,但两个类有不同,该类的Node类定义在Itrs的内部类中
-
-先来看下该类哪些属性
-
-## 属性
-
-```java
-/** The queued items */
-final Object[] items;
-
-/** items index for next take, poll, peek or remove */
-int takeIndex;
-
-/** items index for next put, offer, or add */
-int putIndex;
-
-/** Number of elements in the queue */
-int count;
-
-/*
- * Concurrency control uses the classic two-condition algorithm
- * found in any textbook.
- */
-
-/** Main lock guarding all access */
-final ReentrantLock lock;
-
-/** Condition for waiting takes */
-private final Condition notEmpty;
-
-/** Condition for waiting puts */
-private final Condition notFull;
-
-/**
- * Shared state for currently active iterators, or null if there
- * are known not to be any. Allows queue operations to update
- * iterator state.
- */
-transient Itrs itrs;
-```
-
-## 内部类
-
-### Itr
-
-```java
-private class Itr implements Iterator {
- /** Index to look for new nextItem; NONE at end */
- private int cursor;
-
- /** Element to be returned by next call to next(); null if none */
- private E nextItem;
-
- /** Index of nextItem; NONE if none, REMOVED if removed elsewhere */
- private int nextIndex;
-
- /** Last element returned; null if none or not detached. */
- private E lastItem;
-
- /** Index of lastItem, NONE if none, REMOVED if removed elsewhere */
- private int lastRet;
-
- /** Previous value of takeIndex, or DETACHED when detached */
- private int prevTakeIndex;
-
- /** Previous value of iters.cycles */
- private int prevCycles;
-
- /** Special index value indicating "not available" or "undefined" */
- private static final int NONE = -1;
-
- /**
- * Special index value indicating "removed elsewhere", that is,
- * removed by some operation other than a call to this.remove().
- */
- private static final int REMOVED = -2;
-
- /** Special value for prevTakeIndex indicating "detached mode" */
- private static final int DETACHED = -3;
-
- Itr() {
- lastRet = NONE;
- final ReentrantLock lock = ArrayBlockingQueue.this.lock;
- lock.lock();
- try {
- if (count == 0) {
- // assert itrs == null;
- cursor = NONE;
- nextIndex = NONE;
- prevTakeIndex = DETACHED;
- } else {
- final int takeIndex = ArrayBlockingQueue.this.takeIndex;
- prevTakeIndex = takeIndex;
- nextItem = itemAt(nextIndex = takeIndex);
- cursor = incCursor(takeIndex);
- if (itrs == null) {
- itrs = new Itrs(this);
- } else {
- itrs.register(this); // in this order
- itrs.doSomeSweeping(false);
- }
- prevCycles = itrs.cycles;
- // assert takeIndex>= 0;
- // assert prevTakeIndex == takeIndex;
- // assert nextIndex>= 0;
- // assert nextItem != null;
- }
- } finally {
- lock.unlock();
- }
- }
-
- boolean isDetached() {
- // assert lock.isHeldByCurrentThread();
- return prevTakeIndex < 0; - } - - private int incCursor(int index) { - // assert lock.isHeldByCurrentThread(); - if (++index == items.length) index = 0; - if (index == putIndex) index = NONE; - return index; - } - - /** - * Returns true if index is invalidated by the given number of - * dequeues, starting from prevTakeIndex. - */ - private boolean invalidated(int index, int prevTakeIndex, - long dequeues, int length) { - if (index < 0) - return false; - int distance = index - prevTakeIndex; - if (distance < 0) - distance += length; - return dequeues> distance;
- }
-
- /**
- * Adjusts indices to incorporate all dequeues since the last
- * operation on this iterator. Call only from iterating thread.
- */
- private void incorporateDequeues() {
- // assert lock.isHeldByCurrentThread();
- // assert itrs != null;
- // assert !isDetached();
- // assert count> 0;
-
- final int cycles = itrs.cycles;
- final int takeIndex = ArrayBlockingQueue.this.takeIndex;
- final int prevCycles = this.prevCycles;
- final int prevTakeIndex = this.prevTakeIndex;
-
- if (cycles != prevCycles || takeIndex != prevTakeIndex) {
- final int len = items.length;
- // how far takeIndex has advanced since the previous
- // operation of this iterator
- long dequeues = (long) (cycles - prevCycles) * len
- + (takeIndex - prevTakeIndex);
-
- // Check indices for invalidation
- if (invalidated(lastRet, prevTakeIndex, dequeues, len))
- lastRet = REMOVED;
- if (invalidated(nextIndex, prevTakeIndex, dequeues, len))
- nextIndex = REMOVED;
- if (invalidated(cursor, prevTakeIndex, dequeues, len))
- cursor = takeIndex;
-
- if (cursor < 0 && nextIndex < 0 && lastRet < 0) - detach(); - else { - this.prevCycles = cycles; - this.prevTakeIndex = takeIndex; - } - } - } - - /** - * Called when itrs should stop tracking this iterator, either - * because there are no more indices to update (cursor < 0 && - * nextIndex < 0 && lastRet < 0) or as a special exception, when - * lastRet>= 0, because hasNext() is about to return false for the
- * first time. Call only from iterating thread.
- */
- private void detach() {
- // Switch to detached mode
- // assert lock.isHeldByCurrentThread();
- // assert cursor == NONE;
- // assert nextIndex < 0; - // assert lastRet < 0 || nextItem == null; - // assert lastRet < 0 ^ lastItem != null; - if (prevTakeIndex>= 0) {
- // assert itrs != null;
- prevTakeIndex = DETACHED;
- // try to unlink from itrs (but not too hard)
- itrs.doSomeSweeping(true);
- }
- }
-
- /**
- * For performance reasons, we would like not to acquire a lock in
- * hasNext in the common case. To allow for this, we only access
- * fields (i.e. nextItem) that are not modified by update operations
- * triggered by queue modifications.
- */
- public boolean hasNext() {
- if (nextItem != null)
- return true;
- noNext();
- return false;
- }
-
- private void noNext() {
- final ReentrantLock lock = ArrayBlockingQueue.this.lock;
- lock.lock();
- try {
- // assert cursor == NONE;
- // assert nextIndex == NONE;
- if (!isDetached()) {
- // assert lastRet>= 0;
- incorporateDequeues(); // might update lastRet
- if (lastRet>= 0) {
- lastItem = itemAt(lastRet);
- // assert lastItem != null;
- detach();
- }
- }
- // assert isDetached();
- // assert lastRet < 0 ^ lastItem != null; - } finally { - lock.unlock(); - } - } - - public E next() { - final E e = nextItem; - if (e == null) - throw new NoSuchElementException(); - final ReentrantLock lock = ArrayBlockingQueue.this.lock; - lock.lock(); - try { - if (!isDetached()) - incorporateDequeues(); - // assert nextIndex != NONE; - // assert lastItem == null; - lastRet = nextIndex; - final int cursor = this.cursor; - if (cursor>= 0) {
- nextItem = itemAt(nextIndex = cursor);
- // assert nextItem != null;
- this.cursor = incCursor(cursor);
- } else {
- nextIndex = NONE;
- nextItem = null;
- if (lastRet == REMOVED) detach();
- }
- } finally {
- lock.unlock();
- }
- return e;
- }
-
- public void forEachRemaining(Consumer action) {
- Objects.requireNonNull(action);
- final ReentrantLock lock = ArrayBlockingQueue.this.lock;
- lock.lock();
- try {
- final E e = nextItem;
- if (e == null) return;
- if (!isDetached())
- incorporateDequeues();
- action.accept(e);
- if (isDetached() || cursor < 0) return; - final Object[] items = ArrayBlockingQueue.this.items; - for (int i = cursor, end = putIndex, - to = (i < end) ? end : items.length; - ; i = 0, to = end) { - for (; i < to; i++) - action.accept(itemAt(items, i)); - if (to == end) break; - } - } finally { - // Calling forEachRemaining is a strong hint that this - // iteration is surely over; supporting remove() after - // forEachRemaining() is more trouble than it's worth - cursor = nextIndex = lastRet = NONE; - nextItem = lastItem = null; - detach(); - lock.unlock(); - } - } - - public void remove() { - final ReentrantLock lock = ArrayBlockingQueue.this.lock; - lock.lock(); - // assert lock.getHoldCount() == 1; - try { - if (!isDetached()) - incorporateDequeues(); // might update lastRet or detach - final int lastRet = this.lastRet; - this.lastRet = NONE; - if (lastRet>= 0) {
- if (!isDetached())
- removeAt(lastRet);
- else {
- final E lastItem = this.lastItem;
- // assert lastItem != null;
- this.lastItem = null;
- if (itemAt(lastRet) == lastItem)
- removeAt(lastRet);
- }
- } else if (lastRet == NONE)
- throw new IllegalStateException();
- // else lastRet == REMOVED and the last returned element was
- // previously asynchronously removed via an operation other
- // than this.remove(), so nothing to do.
-
- if (cursor < 0 && nextIndex < 0) - detach(); - } finally { - lock.unlock(); - // assert lastRet == NONE; - // assert lastItem == null; - } - } - - /** - * Called to notify the iterator that the queue is empty, or that it - * has fallen hopelessly behind, so that it should abandon any - * further iteration, except possibly to return one more element - * from next(), as promised by returning true from hasNext(). - */ - void shutdown() { - // assert lock.isHeldByCurrentThread(); - cursor = NONE; - if (nextIndex>= 0)
- nextIndex = REMOVED;
- if (lastRet>= 0) {
- lastRet = REMOVED;
- lastItem = null;
- }
- prevTakeIndex = DETACHED;
- // Don't set nextItem to null because we must continue to be
- // able to return it on next().
- //
- // Caller will unlink from itrs when convenient.
- }
-
- private int distance(int index, int prevTakeIndex, int length) {
- int distance = index - prevTakeIndex;
- if (distance < 0) - distance += length; - return distance; - } - - /** - * Called whenever an interior remove (not at takeIndex) occurred. - * - * @return true if this iterator should be unlinked from itrs - */ - boolean removedAt(int removedIndex) { - // assert lock.isHeldByCurrentThread(); - if (isDetached()) - return true; - - final int takeIndex = ArrayBlockingQueue.this.takeIndex; - final int prevTakeIndex = this.prevTakeIndex; - final int len = items.length; - // distance from prevTakeIndex to removedIndex - final int removedDistance = - len * (itrs.cycles - this.prevCycles - + ((removedIndex < takeIndex) ? 1 : 0)) - + (removedIndex - prevTakeIndex); - // assert itrs.cycles - this.prevCycles>= 0;
- // assert itrs.cycles - this.prevCycles <= 1; - // assert removedDistance> 0;
- // assert removedIndex != takeIndex;
- int cursor = this.cursor;
- if (cursor>= 0) {
- int x = distance(cursor, prevTakeIndex, len);
- if (x == removedDistance) {
- if (cursor == putIndex)
- this.cursor = cursor = NONE;
- }
- else if (x> removedDistance) {
- // assert cursor != prevTakeIndex;
- this.cursor = cursor = dec(cursor, len);
- }
- }
- int lastRet = this.lastRet;
- if (lastRet>= 0) {
- int x = distance(lastRet, prevTakeIndex, len);
- if (x == removedDistance)
- this.lastRet = lastRet = REMOVED;
- else if (x> removedDistance)
- this.lastRet = lastRet = dec(lastRet, len);
- }
- int nextIndex = this.nextIndex;
- if (nextIndex>= 0) {
- int x = distance(nextIndex, prevTakeIndex, len);
- if (x == removedDistance)
- this.nextIndex = nextIndex = REMOVED;
- else if (x> removedDistance)
- this.nextIndex = nextIndex = dec(nextIndex, len);
- }
- if (cursor < 0 && nextIndex < 0 && lastRet < 0) { - this.prevTakeIndex = DETACHED; - return true; - } - return false; - } - - /** - * Called whenever takeIndex wraps around to zero. - * - * @return true if this iterator should be unlinked from itrs - */ - boolean takeIndexWrapped() { - // assert lock.isHeldByCurrentThread(); - if (isDetached()) - return true; - if (itrs.cycles - prevCycles> 1) {
- // All the elements that existed at the time of the last
- // operation are gone, so abandon further iteration.
- shutdown();
- return true;
- }
- return false;
- }
-
- // /** Uncomment for debugging. */
- // public String toString() {
- // return ("cursor=" + cursor + " " +
- // "nextIndex=" + nextIndex + " " +
- // "lastRet=" + lastRet + " " +
- // "nextItem=" + nextItem + " " +
- // "lastItem=" + lastItem + " " +
- // "prevCycles=" + prevCycles + " " +
- // "prevTakeIndex=" + prevTakeIndex + " " +
- // "size()=" + size() + " " +
- // "remainingCapacity()=" + remainingCapacity());
- // }
-}
-```
-
-### Itrs
-
-```java
-class Itrs {
-
- /**
- * Node in a linked list of weak iterator references.
- */
- private class Node extends WeakReference {
- Node next;
-
- Node(Itr iterator, Node next) {
- super(iterator);
- this.next = next;
- }
- }
-
- /** Incremented whenever takeIndex wraps around to 0 */
- int cycles;
-
- /** Linked list of weak iterator references */
- private Node head;
-
- /** Used to expunge stale iterators */
- private Node sweeper;
-
- private static final int SHORT_SWEEP_PROBES = 4;
- private static final int LONG_SWEEP_PROBES = 16;
-
- Itrs(Itr initial) {
- register(initial);
- }
-
- /**
- * Sweeps itrs, looking for and expunging stale iterators.
- * If at least one was found, tries harder to find more.
- * Called only from iterating thread.
- *
- * @param tryHarder whether to start in try-harder mode, because
- * there is known to be at least one iterator to collect
- */
- void doSomeSweeping(boolean tryHarder) {
- // assert lock.isHeldByCurrentThread();
- // assert head != null;
- int probes = tryHarder ? LONG_SWEEP_PROBES : SHORT_SWEEP_PROBES;
- Node o, p;
- final Node sweeper = this.sweeper;
- boolean passedGo; // to limit search to one full sweep
-
- if (sweeper == null) {
- o = null;
- p = head;
- passedGo = true;
- } else {
- o = sweeper;
- p = o.next;
- passedGo = false;
- }
-
- for (; probes> 0; probes--) {
- if (p == null) {
- if (passedGo)
- break;
- o = null;
- p = head;
- passedGo = true;
- }
- final Itr it = p.get();
- final Node next = p.next;
- if (it == null || it.isDetached()) {
- // found a discarded/exhausted iterator
- probes = LONG_SWEEP_PROBES; // "try harder"
- // unlink p
- p.clear();
- p.next = null;
- if (o == null) {
- head = next;
- if (next == null) {
- // We've run out of iterators to track; retire
- itrs = null;
- return;
- }
- }
- else
- o.next = next;
- } else {
- o = p;
- }
- p = next;
- }
-
- this.sweeper = (p == null) ? null : o;
- }
-
- /**
- * Adds a new iterator to the linked list of tracked iterators.
- */
- void register(Itr itr) {
- // assert lock.isHeldByCurrentThread();
- head = new Node(itr, head);
- }
-
- /**
- * Called whenever takeIndex wraps around to 0.
- *
- * Notifies all iterators, and expunges any that are now stale.
- */
- void takeIndexWrapped() {
- // assert lock.isHeldByCurrentThread();
- cycles++;
- for (Node o = null, p = head; p != null;) {
- final Itr it = p.get();
- final Node next = p.next;
- if (it == null || it.takeIndexWrapped()) {
- // unlink p
- // assert it == null || it.isDetached();
- p.clear();
- p.next = null;
- if (o == null)
- head = next;
- else
- o.next = next;
- } else {
- o = p;
- }
- p = next;
- }
- if (head == null) // no more iterators to track
- itrs = null;
- }
-
- /**
- * Called whenever an interior remove (not at takeIndex) occurred.
- *
- * Notifies all iterators, and expunges any that are now stale.
- */
- void removedAt(int removedIndex) {
- for (Node o = null, p = head; p != null;) {
- final Itr it = p.get();
- final Node next = p.next;
- if (it == null || it.removedAt(removedIndex)) {
- // unlink p
- // assert it == null || it.isDetached();
- p.clear();
- p.next = null;
- if (o == null)
- head = next;
- else
- o.next = next;
- } else {
- o = p;
- }
- p = next;
- }
- if (head == null) // no more iterators to track
- itrs = null;
- }
-
- /**
- * Called whenever the queue becomes empty.
- *
- * Notifies all active iterators that the queue is empty,
- * clears all weak refs, and unlinks the itrs datastructure.
- */
- void queueIsEmpty() {
- // assert lock.isHeldByCurrentThread();
- for (Node p = head; p != null; p = p.next) {
- Itr it = p.get();
- if (it != null) {
- p.clear();
- it.shutdown();
- }
- }
- head = null;
- itrs = null;
- }
-
- /**
- * Called whenever an element has been dequeued (at takeIndex).
- */
- void elementDequeued() {
- // assert lock.isHeldByCurrentThread();
- if (count == 0)
- queueIsEmpty();
- else if (takeIndex == 0)
- takeIndexWrapped();
- }
-}
-```
-
diff --git "a/346円272円220円347円240円201円345円210円206円346円236円220円/AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater.md" "b/346円272円220円347円240円201円345円210円206円346円236円220円/AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater.md"
deleted file mode 100755
index ac2bec9..0000000
--- "a/346円272円220円347円240円201円345円210円206円346円236円220円/AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater.md"
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,466 +0,0 @@
-# AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater源码分析
-
-> 源码基于Java8
-
-这个类是一个基于反射的使用的工具类,可以对指定类的指定的被volatile修饰的int型字段进行原子更新。
-
-
-
-## 创建方法
-
-```java
-//创建并返回一个Updater,
-//要求给定字段在目标对象中必须存在,
-//Class类型的参数用于检查反射类型和泛型之间是否匹配
-//tclass 持有给定字段的目标对象的类类型
-//fieldName 要更新的字段的名字,字符串类型
-//泛型参数U代表了目标类型
-
-//如果目标字段不是volatile描述的整形,会抛出IllegalArgumentException
-//如果目标字段基于访问控制不允许访问,
-//或者目标类型中不含有这个字段
-//或者类型不匹配,可能会出现反射的异常,
-//会在捕获之后抛出RuntimeException
-//此处有个CallerSensitive注解,这个注解具体的内容在对应的地方说
-//对于这个注解此处要明白它在这主要是配合Reflection.getCallerClass()
-//作用是避免自己写Reflection.getCallerClass()的参数
-//增加这个特性主要还是为了修复一个jdk中的利用双重反射的越权漏洞
-@CallerSensitive
-public static AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater newUpdater(Class tclass,
- String fieldName) {
- //这个实现类在下面,是个内部类
- //通过反射Reflection类实现对调用者的反射
- //Reflection属于sun包下的,
- //Oracle曾多次表示sun包不安全,
- //或者说要废弃,
- //所以自己使用的时候要谨慎
- //关于sun包的事情后面单独再说
- return new AtomicIntegerFieldUpdaterImpl
- (tclass, fieldName, Reflection.getCallerClass());
-}
-
-//构造方法protected,
-//用于保证子类可以调用一个无任何作用的构造方法
-protected AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater() {
-}
-
-```
-
-## 抽象方法
-
-这些抽象方法有子类AtomicIntegerFieldUpdaterImpl实现
-
-```java
-
-//如果当前值==预期值,
-//那么就原子的将当前Updater管理的给定的对象的字段设置为给定的更新值
-//这个方法只对compareAndSet和set提供原子保证
-//但是对于字段的其他修改不一定能够提供保证
-//obj 是要进行设置的目标对象
-//expect 是期待的目标对象
-//update 要更新设置的值
-//如果返回true说明设置成功了
-//如果obj不是构造方法里给出的类型的实例,这个方法可能会抛出ClassCastException
-//注: 按照package中对于false的定义,在期待值和当前值不同时,返回false
-public abstract boolean compareAndSet(T obj, int expect, int update);
-
-//方法的基本描述跟上面的一样
-//但是略有不同的地方是
-//这个方法可能会由于错误而失败,
-//并且不提供顺序保证,
-//因此很少用做compareAndSet的替换方法
-//参数以及返回和异常与上一个方法一样
-public abstract boolean weakCompareAndSet(T obj, int expect, int update);
-
-//将这个Updater所管理的给定对象的字段设置为给定的新元素
-//这个操作相对于compareAndSet提供了操作的保证
-public abstract void set(T obj, int newValue);
-
-//可以保证最终会把目标中的被Updater管理的元素更新为给定元素
-public abstract void lazySet(T obj, int newValue);
-
-//读取被当前Updater管理的字段的当前值
-public abstract int get(T obj);
-
-```
-
-## 其他方法
-
-```java
-//原子的被当前Updater管理的目标对象中的字段更新为指定值
-//同时返回原来的元素值
-public int getAndSet(T obj, int newValue) {
- int prev;
- do {
- prev = get(obj);
- } while (!compareAndSet(obj, prev, newValue));
- return prev;
-}
-
-
-//用于将当前Updater管理的目标对象中的字段更新为+1后的值
-//返回原来的值
-public int getAndIncrement(T obj) {
- int prev, next;
- do {
- prev = get(obj);
- next = prev + 1;
- } while (!compareAndSet(obj, prev, next));
- return prev;
-}
-
-//跟上一个方法相似,区别在于这个方法适用于-1
-public int getAndDecrement(T obj) {
- int prev, next;
- do {
- prev = get(obj);
- next = prev - 1;
- } while (!compareAndSet(obj, prev, next));
- return prev;
-}
-
-//用于将当前Updater管理的目标对象中的字段更新为+delta后的值
-//返回原来的值
-public int getAndAdd(T obj, int delta) {
- int prev, next;
- do {
- prev = get(obj);
- next = prev + delta;
- } while (!compareAndSet(obj, prev, next));
- return prev;
-}
-
-//用于将当前Updater管理的目标对象中的字段更新为+1后的值
-//返回新值
-public int incrementAndGet(T obj) {
- int prev, next;
- do {
- prev = get(obj);
- next = prev + 1;
- } while (!compareAndSet(obj, prev, next));
- return next;
-}
-
-//跟上一个方法相似,区别在于这个方法-1
-public int decrementAndGet(T obj) {
- int prev, next;
- do {
- prev = get(obj);
- next = prev - 1;
- } while (!compareAndSet(obj, prev, next));
- return next;
-}
-
-//用于将当前Updater管理的目标对象中的字段更新为+delta后的值
-//返回新值
-public int addAndGet(T obj, int delta) {
- int prev, next;
- do {
- prev = get(obj);
- next = prev + delta;
- } while (!compareAndSet(obj, prev, next));
- return next;
-}
-```
-
-## Java8后增加的方法
-
-```java
-//返回旧元素
-public final int getAndUpdate(T obj, IntUnaryOperator updateFunction) {
- int prev, next;
- do {
- prev = get(obj);
- next = updateFunction.applyAsInt(prev);
- } while (!compareAndSet(obj, prev, next));
- return prev;
-}
-
-//返回新元素
-public final int updateAndGet(T obj, IntUnaryOperator updateFunction) {
- int prev, next;
- do {
- prev = get(obj);
- next = updateFunction.applyAsInt(prev);
- } while (!compareAndSet(obj, prev, next));
- return next;
-}
-
-//执行方法的时候传递的第一个参数是旧元素,第二个参数是x
-//返回旧元素
-public final int getAndAccumulate(T obj, int x,
- IntBinaryOperator accumulatorFunction) {
- int prev, next;
- do {
- prev = get(obj);
- next = accumulatorFunction.applyAsInt(prev, x);
- } while (!compareAndSet(obj, prev, next));
- return prev;
-}
-
-//跟上一个方法相似
-//返回新元素
-public final int accumulateAndGet(T obj, int x,
- IntBinaryOperator accumulatorFunction) {
- int prev, next;
- do {
- prev = get(obj);
- next = accumulatorFunction.applyAsInt(prev, x);
- } while (!compareAndSet(obj, prev, next));
- return next;
-}
-
-```
-
-## AtomicIntegerFieldUpdaterImpl
-
-该类为AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater的内部子类
-
-```java
-private static final class AtomicIntegerFieldUpdaterImpl
- extends AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater {
- //Unsafe实例
- private static final sun.misc.Unsafe U = sun.misc.Unsafe.getUnsafe();
- //偏移量记录
- private final long offset;
- //如果字段受保护,子类构造这个更新器,否则和tclass一样
- //cclass记录的是子类类名
- private final Class cclass;
- //含有目标字段的类的类类型
- //cclass tclass两个字段主要用于校验是否能够进行更新
- private final Class tclass;
-
- //构造方法
- //tclass:含有目标字段的目标类类型
- //caller:调用者的类类型
- AtomicIntegerFieldUpdaterImpl(final Class tclass,
- final String fieldName,
- final Class caller) {
- final Field field;
- final int modifiers;
- try {
- //这里有个AccessController,这个属于Java的Security的一部分
- //包括AccessController,SecurityManager
- //这部分相关内容在对应的部分说
- //在这doPrivileged方法主要是用于越过权限检查
- //在特权块内的代码会越过特权检查,
- //这之后其他的类就可以越过检查执行这段代码
- field = AccessController.doPrivileged(
- //PrivilegedExceptionAction接口中含有一个run方法
- //当做一个doPrivileged调用时,
- //一个PrivilegedAction实现的实例被传递给它。
- //doPrivileged方法在使特权生效后,
- //从PrivilegedAction实现中调用run方法,
- //并返回run方法的返回值以作为doPrivileged的返回值
- //PrivilegedAction和PrivilegedExceptionAction区别在于
- //如果特权块中可能异常,就用PrivilegedExceptionActio
- //否则使用PrivilegedAction
- new PrivilegedExceptionAction() {
- public Field run() throws NoSuchFieldException {
- return tclass.getDeclaredField(fieldName);
- }
- });
- //读取字段修饰符(此处返回的是int类型)
- // PUBLIC: 1
- // PRIVATE: 2
- // PROTECTED: 4
- // STATIC: 8
- // FINAL: 16
- // SYNCHRONIZED: 32
- // VOLATILE: 64
- // TRANSIENT: 128
- // NATIVE: 256
- // INTERFACE: 512
- // ABSTRACT: 1024
- // STRICT: 2048
- //返回值是各项修饰符的加和
- //自己做判断可能有点麻烦
- //可以通过Modifier.toString(int mod)方法来进行解析
- //或者通过Modifier里面的isXXX相关方法判断
- //Modifier.toString方法放到Modifier里面说
- modifiers = field.getModifiers();
- //这个方法也在sun包下面
- //这个方法主要用于校验给定的调用者(第一个参数)
- //第二个参数是目标的类类型
- //第三个参数在静态的情况系可以是null
- //第四个参数是访问修饰
- //判断是否可以访问目标对象中构造方法、字段、普通方法等
- //如果没有访问权限会抛出IllegalAccessException
- sun.reflect.misc.ReflectUtil.ensureMemberAccess(
- caller, tclass, null, modifiers);
- //目标类的类加载器
- ClassLoader cl = tclass.getClassLoader();
- //调用者的类加载器
- ClassLoader ccl = caller.getClassLoader();
- //这个判断条件要求满足目标类和调用者不能使同一个类加载器
- //调用者不能是根加载器
- //目标类加载器是根加载器或者调用者类加载器和目标类加载器的关系不满足isAncestor(没有委托链关系)
- if ((ccl != null) && (ccl != cl) &&
- ((cl == null) || !isAncestor(cl, ccl))) {
- //sun包下面
- //校验目标类的包的可访问性
- sun.reflect.misc.ReflectUtil.checkPackageAccess(tclass);
- }
- } catch (PrivilegedActionException pae) {
- throw new RuntimeException(pae.getException());
- } catch (Exception ex) {
- throw new RuntimeException(ex);
- }
-
- //类型校验
- if (field.getType() != int.class)
- throw new IllegalArgumentException("Must be integer type");
-
- //判断是否有volatile修饰
- if (!Modifier.isVolatile(modifiers))
- throw new IllegalArgumentException("Must be volatile type");
-
- //访问protected字段需要是同包下或者有父子关系的情况
- //这个判断条件指出,如果是
- //在字段为Protected,目标类是调用类的父类,调用类和目标类不是同一个包下时
- //cclass存储调用者的类
- //上面条件任何一个不满足都指向tclass
- //包括不是保护域,没有父子关系,在同一个包下面
- this.cclass = (Modifier.isProtected(modifiers) &&
- tclass.isAssignableFrom(caller) &&
- !isSamePackage(tclass, caller))
- ? caller : tclass;
-
- //记录目标class
- this.tclass = tclass;
- //记录偏移量
- this.offset = U.objectFieldOffset(field);
- }
-
-
- //如果第二个加载器可以再第一个加载器的委托链中找到返回True
- //等价于调用 first.isAncestor(second).
- private static boolean isAncestor(ClassLoader first, ClassLoader second) {
- ClassLoader acl = first;
- do {
- acl = acl.getParent();
- if (second == acl) {
- return true;
- }
- } while (acl != null);
- return false;
- }
-
- //如果两个类具有相同的类加载器和包限定符,则返回true
- private static boolean isSamePackage(Class class1, Class class2) {
- return class1.getClassLoader() == class2.getClassLoader()
- //Objects是一个工具类,具体的放到对应的类讲
- && Objects.equals(getPackageName(class1), getPackageName(class2));
- }
-
- //获取给定类的包名
- private static String getPackageName(Class cls) {
- //这个方法返回虚拟机中Class对象的表示
- //例如String[]类型的表示为: [Ljava.lang.String
- String cn = cls.getName();
- //定位到最后一个点的位置
- int dot = cn.lastIndexOf('.');
- //返回类名的截取
- return (dot != -1) ? cn.substring(0, dot) : "";
- }
-
- //检查目标参数是否为cclass的实例。失败时,抛出异常原因
- private final void accessCheck(T obj) {
- if (!cclass.isInstance(obj))
- throwAccessCheckException(obj);
- }
-
- //如果由于受保护的访问而导致访问检查失败,
- //则引发访问异常,
- //否则将引发ClassCastException。
- //实际上当cclass和tclass如果相等,会抛出ClassCastException
- //也就是说在上面初始化过程中出现了对于受保护字段的访问检查失败
- private final void throwAccessCheckException(T obj) {
- if (cclass == tclass)
- throw new ClassCastException();
- else
- throw new RuntimeException(
- new IllegalAccessException(
- "Class " +
- cclass.getName() +
- " can not access a protected member of class " +
- tclass.getName() +
- " using an instance of " +
- obj.getClass().getName()));
- }
-
- //**************************************************************
-
- //下面终于到了这个类应该做的正经事了
- //由于上面有过叙述,就不进行冗余的叙述了
- //每个方法都是先进行对可访问性的校验
-
- //CAS操作
- public final boolean compareAndSet(T obj, int expect, int update) {
- accessCheck(obj);
- return U.compareAndSwapInt(obj, offset, expect, update);
- }
-
- //弱CAS操作
- public final boolean weakCompareAndSet(T obj, int expect, int update) {
- accessCheck(obj);
- return U.compareAndSwapInt(obj, offset, expect, update);
- }
-
- //set
- public final void set(T obj, int newValue) {
- accessCheck(obj);
- U.putIntVolatile(obj, offset, newValue);
- }
-
- //lazySet
- public final void lazySet(T obj, int newValue) {
- accessCheck(obj);
- U.putOrderedInt(obj, offset, newValue);
- }
-
- //读取
- public final int get(T obj) {
- accessCheck(obj);
- return U.getIntVolatile(obj, offset);
- }
-
- //设置并返回原来的值
- public final int getAndSet(T obj, int newValue) {
- accessCheck(obj);
- return U.getAndSetInt(obj, offset, newValue);
- }
-
- //增加delta后返回原来的元素
- public final int getAndAdd(T obj, int delta) {
- accessCheck(obj);
- return U.getAndAddInt(obj, offset, delta);
- }
-
- //+1然后返回原来的元素,实际调用的是getAndAdd
- public final int getAndIncrement(T obj) {
- return getAndAdd(obj, 1);
- }
-
- //-1然后返回原来的元素,实际调用的是getAndAdd
- public final int getAndDecrement(T obj) {
- return getAndAdd(obj, -1);
- }
-
- //+1然后返回新元素,实际调用的是getAndAdd
- public final int incrementAndGet(T obj) {
- return getAndAdd(obj, 1) + 1;
- }
-
- //-1然后返回新元素,实际调用的是getAndAdd
- public final int decrementAndGet(T obj) {
- return getAndAdd(obj, -1) - 1;
- }
-
- //加delta然后返回新元素,实际调用的是getAndAdd
- public final int addAndGet(T obj, int delta) {
- return getAndAdd(obj, delta) + delta;
- }
-
-}
-```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git "a/346円272円220円347円240円201円345円210円206円346円236円220円/CompletableFuture.md" "b/346円272円220円347円240円201円345円210円206円346円236円220円/CompletableFuture.md"
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..e946189
--- /dev/null
+++ "b/346円272円220円347円240円201円345円210円206円346円236円220円/CompletableFuture.md"
@@ -0,0 +1,27 @@
+# CompletableFuture 源码分析
+
+> 源码基于open jdk 11
+
+CompletableFuture 是 jdk8 引入的类,主要是对Future的补充。
+
+CompletableFuture类的官方API文档解释:
+
+1. CompletableFuture是一个在完成时可以触发相关方法和操作的Future,并且它可以视作为CompletableStage。
+2. 除了直接操作状态和结果的这些方法和相关方法外(CompletableFuture API提供的方法),CompletableFuture还实现了以下的CompletionStage的相关策略:
+ - 非异步方法的完成,可以由当前CompletableFuture的线程提供,也可以由其他调用完方法的线程提供。
+ - 所有没有显示使用Executor的异步方法,会使用ForkJoinPool.commonPool()(那些并行度小于2的任务会创建一个新线程来运行)。为了简化监视、调试和跟踪异步方法,所有异步任务都被标记为CompletableFuture.AsynchronouseCompletionTask。
+ - 所有CompletionStage方法都是独立于其他公共方法实现的,因此一个方法的行为不受子类中其他方法的覆盖影响。
+3. CompletableFuture还实现了Future的以下策略
+ - 不像FutureTask,因CompletableFuture无法直接控制计算任务的完成,所以CompletableFuture的取消会被视为异常完成。调用cancel()方法会和调用completeExceptionally()方法一样,具有同样的效果。isCompletedEceptionally()方法可以判断CompletableFuture是否是异常完成。
+ - 在调用get()和get(long, TimeUnit)方法时以异常的形式完成,则会抛出ExecutionException,大多数情况下都会使用join()和getNow(T),它们会抛出CompletionException。
+
+待回答的几个问题:
+
+1、如何实现并发执行任务?
+
+2、并发执行如何获取任务结果?
+
+
+
+https://blog.csdn.net/CoderBruis/article/details/103181520?utm_medium=distribute.pc_relevant.none-task-blog-BlogCommendFromMachineLearnPai2-2.control&depth_1-utm_source=distribute.pc_relevant.none-task-blog-BlogCommendFromMachineLearnPai2-2.control
+
diff --git "a/346円272円220円347円240円201円345円210円206円346円236円220円/ConcurrentLinkedQueue.md" "b/346円272円220円347円240円201円345円210円206円346円236円220円/ConcurrentLinkedQueue.md"
old mode 100755
new mode 100644
diff --git "a/346円272円220円347円240円201円345円210円206円346円236円220円/Flow_SubmissionPublisher.md" "b/346円272円220円347円240円201円345円210円206円346円236円220円/Flow_SubmissionPublisher.md"
old mode 100755
new mode 100644
diff --git "a/346円272円220円347円240円201円345円210円206円346円236円220円/Helpers.md" "b/346円272円220円347円240円201円345円210円206円346円236円220円/Helpers.md"
old mode 100755
new mode 100644
diff --git "a/346円272円220円347円240円201円345円210円206円346円236円220円/LinkedBlockingQueue.md" "b/346円272円220円347円240円201円345円210円206円346円236円220円/LinkedBlockingQueue.md"
old mode 100755
new mode 100644
diff --git "a/346円272円220円347円240円201円345円210円206円346円236円220円/LinkedHashMap.md" "b/346円272円220円347円240円201円345円210円206円346円236円220円/LinkedHashMap.md"
old mode 100755
new mode 100644
diff --git "a/346円272円220円347円240円201円345円210円206円346円236円220円/LongAdder.md" "b/346円272円220円347円240円201円345円210円206円346円236円220円/LongAdder.md"
old mode 100755
new mode 100644
diff --git "a/346円272円220円347円240円201円345円210円206円346円236円220円/Spring Boot/Spring Boot Reference 2.6.11 .pdf" "b/346円272円220円347円240円201円345円210円206円346円236円220円/Spring Boot/Spring Boot Reference 2.6.11 .pdf"
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..afcd9d4
Binary files /dev/null and "b/346円272円220円347円240円201円345円210円206円346円236円220円/Spring Boot/Spring Boot Reference 2.6.11 .pdf" differ
diff --git "a/346円272円220円347円240円201円345円210円206円346円236円220円/StreamApi.md" "b/346円272円220円347円240円201円345円210円206円346円236円220円/StreamApi.md"
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..705847b
--- /dev/null
+++ "b/346円272円220円347円240円201円345円210円206円346円236円220円/StreamApi.md"
@@ -0,0 +1,3629 @@
+# Stream API源码分析
+
+## 前提
+
+`Stream`是`JDK1.8`中首次引入的,距今已经过去了接近`8`年时间(`JDK1.8`正式版是`2013`年底发布的)。`Stream`的引入一方面极大地简化了某些开发场景,另一方面也可能降低了编码的可读性(确实有不少人说到`Stream`会降低代码的可读性,但是在笔者看来,熟练使用之后反而觉得代码的可读性提高了)。这篇文章会花巨量篇幅,详细分析`Stream`的底层实现原理,参考的源码是`JDK11`的源码,其他版本`JDK`可能不适用于本文中的源码展示和相关例子。
+
+> 这篇文章花费了极多时间和精力梳理和编写,希望能够帮助到本文的读者
+
+## Stream是如何做到向前兼容的
+
+`Stream`是`JDK1.8`引入的,如要需要`JDK1.7`或者以前的代码也能在`JDK1.8`或以上运行,那么`Stream`的引入必定不能在原来已经发布的接口方法进行修改,否则必定会因为兼容性问题导致老版本的接口实现无法在新版本中运行(方法签名出现异常),猜测是基于这个问题引入了接口默认方法,也就是`default`关键字。查看源码可以发现,`ArrayList`的超类`Collection`和`Iterable`分别添加了数个`default`方法:
+
+```java
+// java.util.Collection部分源码
+public interface Collection extends Iterable {
+
+ // 省略其他代码
+
+ @Override
+ default Spliterator spliterator() {
+ return Spliterators.spliterator(this, 0);
+ }
+
+ default Stream stream() {
+ return StreamSupport.stream(spliterator(), false);
+ }
+
+ default Stream parallelStream() {
+ return StreamSupport.stream(spliterator(), true);
+ }
+}
+
+// java.lang.Iterable部分源码
+public interface Iterable {
+
+ // 省略其他代码
+
+ default void forEach(Consumer action) {
+ Objects.requireNonNull(action);
+ for (T t : this) {
+ action.accept(t);
+ }
+ }
+
+ default Spliterator spliterator() {
+ return Spliterators.spliteratorUnknownSize(iterator(), 0);
+ }
+}
+```
+
+从直觉来看,这些新增的方法应该就是`Stream`实现的关键方法(后面会印证这不是直觉,而是查看源码的结果)。接口默认方法在使用上和实例方法一致,在实现上可以直接在接口方法中编写方法体,有点静态方法的意味,但是子类可以覆盖其实现(也就是接口默认方法在本接口中的实现有点像静态方法,可以被子类覆盖,使用上和实例方法一致)。这种实现方式,有可能是一种突破,也有可能是一种妥协,但是无论是妥协还是突破,都实现了向前兼容:
+
+```java
+// JDK1.7中的java.lang.Iterable
+public interface Iterable {
+
+ Iterator iterator();
+}
+
+// JDK1.7中的Iterable实现
+public MyIterable implements Iterable{
+
+ public Iterator iterator(){
+ ....
+ }
+}
+```
+
+如上,`MyIterable`在`JDK1.7`中定义,如果该类在`JDK1.8`中运行,那么调用其实例中的`forEach()`和`spliterator()`方法,相当于直接调用`JDK1.8`中的`Iterable`中的接口默认方法`forEach()`和`spliterator()`。当然受限于`JDK`版本,这里只能确保编译通过,旧功能正常使用,而无法在`JDK1.7`中使用`Stream`相关功能或者使用`default`方法关键字。总结这么多,就是想说明为什么使用`JDK7`开发和编译的代码可以在`JDK8`环境下运行。
+
+## 可拆分迭代器Spliterator
+
+`Stream`实现的基石是`Spliterator`,`Spliterator`是`splitable iterator`的缩写,意为"可拆分迭代器",用于遍历指定数据源(例如数组、集合或者`IO Channel`等)中的元素,在设计上充分考虑了串行和并行的场景。上一节提到了`Collection`存在接口默认方法`spliterator()`,此方法会生成一个`Spliterator`实例,意为着**所有的集合子类都具备创建`Spliterator`实例的能力**。`Stream`的实现在设计上和`Netty`中的`ChannelHandlerContext`十分相似,本质是一个链表,**而`Spliterator`就是这个链表的`Head`节点**(`Spliterator`实例就是一个流实例的头节点,后面分析具体的源码时候再具体展开)。
+
+### Spliterator接口方法
+
+接着看`Spliterator`接口定义的方法:
+
+```java
+public interface Spliterator {
+
+ // 暂时省略其他代码
+
+ boolean tryAdvance(Consumer action);
+
+ default void forEachRemaining(Consumer action) {
+ do { } while (tryAdvance(action));
+ }
+
+ Spliterator trySplit();
+
+ long estimateSize();
+
+ default long getExactSizeIfKnown() {
+ return (characteristics() & SIZED) == 0 ? -1L : estimateSize();
+ }
+
+ int characteristics();
+
+ default boolean hasCharacteristics(int characteristics) {
+ return (characteristics() & characteristics) == characteristics;
+ }
+
+ default Comparator getComparator() {
+ throw new IllegalStateException();
+ }
+
+ // 暂时省略其他代码
+}
+```
+
+**tryAdvance**
+
+- 方法签名:`boolean tryAdvance(Consumer action)`
+- 功能:如果`Spliterator`中存在剩余元素,则对其中的某个元素执行传入的`action`回调,并且返回`true`,否则返回`false`。如果`Spliterator`启用了`ORDERED`特性,会按照顺序(这里的顺序值可以类比为`ArrayList`中容器数组元素的下标,`ArrayList`中添加新元素是天然有序的,下标由零开始递增)处理下一个元素
+- 例子:
+
+```java
+public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
+ List list = new ArrayList();
+ list.add(2);
+ list.add(1);
+ list.add(3);
+ Spliterator spliterator = list.stream().spliterator();
+ final AtomicInteger round = new AtomicInteger(1);
+ final AtomicInteger loop = new AtomicInteger(1);
+ while (spliterator.tryAdvance(num -> System.out.printf("第%d轮回调Action,值:%d\n", round.getAndIncrement(), num))) {
+ System.out.printf("第%d轮循环\n", loop.getAndIncrement());
+ }
+}
+
+// 控制台输出
+第1轮回调Action,值:2
+第1轮循环
+第2轮回调Action,值:1
+第2轮循环
+第3轮回调Action,值:3
+第3轮循环
+```
+
+**forEachRemaining**
+
+- 方法签名:`default void forEachRemaining(Consumer action)`
+- 功能:如果`Spliterator`中存在剩余元素,则对其中的**所有剩余元素**在**当前线程中**执行传入的`action`回调。如果`Spliterator`启用了`ORDERED`特性,会按照顺序处理剩余所有元素。这是一个接口默认方法,方法体比较粗暴,直接是一个死循环包裹着`tryAdvance()`方法,直到`false`退出循环
+- 例子:
+
+```java
+public static void main(String[] args) {
+ List list = new ArrayList();
+ list.add(2);
+ list.add(1);
+ list.add(3);
+ Spliterator spliterator = list.stream().spliterator();
+ final AtomicInteger round = new AtomicInteger(1);
+ spliterator.forEachRemaining(num -> System.out.printf("第%d轮回调Action,值:%d\n", round.getAndIncrement(), num));
+}
+
+// 控制台输出
+第1轮回调Action,值:2
+第2轮回调Action,值:1
+第3轮回调Action,值:3
+```
+
+**trySplit**
+
+- 方法签名:`Spliterator trySplit()`
+- 功能:如果当前的`Spliterator`是可分区(可分割)的,那么此方法将会返回一个全新的`Spliterator`实例,这个全新的`Spliterator`实例里面的元素不会被当前`Spliterator`实例中的元素覆盖(这里是直译了`API`注释,实际要表达的意思是:当前的`Spliterator`实例`X`是可分割的,`trySplit()`方法会分割`X`产生一个全新的`Spliterator`实例`Y`,原来的`X`所包含的元素(范围)也会收缩,类似于`X = [a,b,c,d] => X = [a,b], Y = [c,d]`;如果当前的`Spliterator`实例`X`是不可分割的,此方法会返回`NULL`),**具体的分割算法由实现类决定**
+- 例子:
+
+```java
+public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
+ List list = new ArrayList();
+ list.add(2);
+ list.add(3);
+ list.add(4);
+ list.add(1);
+ Spliterator first = list.stream().spliterator();
+ Spliterator second = first.trySplit();
+ first.forEachRemaining(num -> {
+ System.out.printf("first spliterator item: %d\n", num);
+ });
+ second.forEachRemaining(num -> {
+ System.out.printf("second spliterator item: %d\n", num);
+ });
+}
+
+// 控制台输出
+first spliterator item: 4
+first spliterator item: 1
+second spliterator item: 2
+second spliterator item: 3
+```
+
+**estimateSize**
+
+- 方法签名:`long estimateSize()`
+- 功能:返回`forEachRemaining()`方法需要遍历的元素总量的估计值,如果样本个数是无限、计算成本过高或者未知,会直接返回`Long.MAX_VALUE`
+- 例子:
+
+```java
+public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
+ List list = new ArrayList();
+ list.add(2);
+ list.add(3);
+ list.add(4);
+ list.add(1);
+ Spliterator spliterator = list.stream().spliterator();
+ System.out.println(spliterator.estimateSize());
+}
+
+// 控制台输出
+4
+```
+
+**getExactSizeIfKnown**
+
+- 方法签名:`default long getExactSizeIfKnown()`
+- 功能:如果当前的`Spliterator`具备`SIZED`特性(关于特性,下文再展开分析),那么直接调用`estimateSize()`方法,否则返回`-1`
+- 例子:
+
+```java
+public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
+ List list = new ArrayList();
+ list.add(2);
+ list.add(3);
+ list.add(4);
+ list.add(1);
+ Spliterator spliterator = list.stream().spliterator();
+ System.out.println(spliterator.getExactSizeIfKnown());
+}
+
+// 控制台输出
+4
+```
+
+**int characteristics()**
+
+- 方法签名:`long estimateSize()`
+- 功能:当前的`Spliterator`具备的特性(集合),采用位运算,存储在`32`位整数中(关于特性,下文再展开分析)
+
+**hasCharacteristics**
+
+- 方法签名:`default boolean hasCharacteristics(int characteristics)`
+- 功能:判断当前的`Spliterator`是否具备传入的特性
+
+**getComparator**
+
+- 方法签名:`default Comparator getComparator()`
+- 功能:如果当前的`Spliterator`具备`SORTED`特性,则需要返回一个`Comparator`实例;如果`Spliterator`中的元素是天然有序(例如元素实现了`Comparable`接口),则返回`NULL`;其他情况直接抛出`IllegalStateException`异常
+
+### Spliterator自分割
+
+`Spliterator#trySplit()`可以把一个既有的`Spliterator`实例分割为两个`Spliterator`实例,笔者这里把这种方式称为`Spliterator`自分割,示意图如下:
+
+[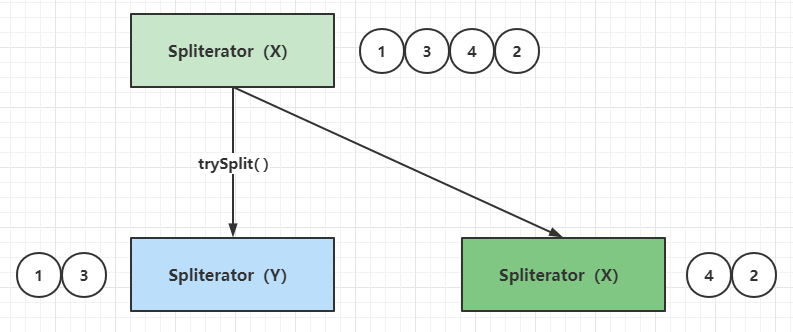](https://throwable-blog-1256189093.cos.ap-guangzhou.myqcloud.com/202110/stream-source-1.png)
+
+这里的分割在实现上可以采用两种方式:
+
+- 物理分割:对于`ArrayList`而言,把底层数组**拷贝**并且进行分割,用上面的例子来说相当于`X = [1,3,4,2] => X = [4,2], Y = [1,3]`,这样实现加上对于`ArrayList`中本身的元素容器数组,相当于多存了一份数据,显然不是十分合理
+- 逻辑分割:对于`ArrayList`而言,由于元素容器数组天然有序,可以采用数组的索引(下标)进行分割,用上面的例子来说相当于`X = 索引表[0,1,2,3] => X = 索引表[2,3], Y = 索引表[0,1]`,这种方式是共享底层容器数组,只对元素索引进行分割,实现上比较简单而且相对合理
+
+参看`ArrayListSpliterator`的源码,可以分析其分割算法实现:
+
+```java
+// ArrayList#spliterator()
+public Spliterator spliterator() {
+ return new ArrayListSpliterator(0, -1, 0);
+}
+
+// ArrayList中内部类ArrayListSpliterator
+final class ArrayListSpliterator implements Spliterator {
+
+ // 当前的处理的元素索引值,其实是剩余元素的下边界值(包含),在tryAdvance()或者trySplit()方法中被修改,一般初始值为0
+ private int index;
+ // 栅栏,其实是元素索引值的上边界值(不包含),一般初始化的时候为-1,使用时具体值为元素索引值上边界加1
+ private int fence;
+ // 预期的修改次数,一般初始化值等于modCount
+ private int expectedModCount;
+
+ ArrayListSpliterator(int origin, int fence, int expectedModCount) {
+ this.index = origin;
+ this.fence = fence;
+ this.expectedModCount = expectedModCount;
+ }
+
+ // 获取元素索引值的上边界值,如果小于0,则把hi和fence都赋值为(ArrayList中的)size,expectedModCount赋值为(ArrayList中的)modCount,返回上边界值
+ // 这里注意if条件中有赋值语句hi = fence,也就是此方法调用过程中临时变量hi总是重新赋值为fence,fence是ArrayListSpliterator实例中的成员属性
+ private int getFence() {
+ int hi;
+ if ((hi = fence) < 0) { + expectedModCount = modCount; + hi = fence = size; + } + return hi; + } + + // Spliterator自分割,这里采用了二分法 + public ArrayListSpliterator trySplit() { + // hi等于当前ArrayListSpliterator实例中的fence变量,相当于获取剩余元素的上边界值 + // lo等于当前ArrayListSpliterator实例中的index变量,相当于获取剩余元素的下边界值 + // mid = (lo + hi)>>> 1,这里的无符号右移动1位运算相当于(lo + hi)/2
+ int hi = getFence(), lo = index, mid = (lo + hi)>>> 1;
+ // 当lo>= mid的时候为不可分割,返回NULL,否则,以index = lo,fence = mid和expectedModCount = expectedModCount创建一个新的ArrayListSpliterator
+ // 这里有个细节之处,在新的ArrayListSpliterator构造参数中,当前的index被重新赋值为index = mid,这一点容易看漏,老程序员都喜欢做这样的赋值简化
+ // lo>= mid返回NULL的时候,不会创建新的ArrayListSpliterator,也不会修改当前ArrayListSpliterator中的参数
+ return (lo>= mid) ? null : new ArrayListSpliterator(lo, index = mid, expectedModCount);
+ }
+
+ // tryAdvance实现
+ public boolean tryAdvance(Consumer action) {
+ if (action == null)
+ throw new NullPointerException();
+ // 获取迭代的上下边界
+ int hi = getFence(), i = index;
+ // 由于前面分析下边界是包含关系,上边界是非包含关系,所以这里要i < hi而不是i <= hi + if (i < hi) { + index = i + 1; + // 这里的elementData来自ArrayList中,也就是前文经常提到的元素数组容器,这里是直接通过元素索引访问容器中的数据 + @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") E e = (E)elementData[i]; + // 对传入的Action进行回调 + action.accept(e); + // 并发修改异常判断 + if (modCount != expectedModCount) + throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); + return true; + } + return false; + } + + // forEachRemaining实现,这里没有采用默认实现,而是完全覆盖实现一个新方法 + public void forEachRemaining(Consumer action) {
+ // 这里会新建所需的中间变量,i为index的中间变量,hi为fence的中间变量,mc为expectedModCount的中间变量
+ int i, hi, mc;
+ Object[] a;
+ if (action == null)
+ throw new NullPointerException();
+ // 判断容器数组存在性
+ if ((a = elementData) != null) {
+ // hi、fence和mc初始化
+ if ((hi = fence) < 0) { + mc = modCount; + hi = size; + } + else + mc = expectedModCount; + // 这里就是先做参数合法性校验,再遍历临时数组容器a中中[i,hi)的剩余元素对传入的Action进行回调 + // 这里注意有一处隐蔽的赋值(index = hi),下界被赋值为上界,意味着每个ArrayListSpliterator实例只能调用一次forEachRemaining()方法 + if ((i = index)>= 0 && (index = hi) <= a.length) { + for (; i < hi; ++i) { + @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") E e = (E) a[i]; + action.accept(e); + } + // 这里校验ArrayList的modCount和mc是否一致,理论上在forEachRemaining()遍历期间,不能对数组容器进行元素的新增或者移除,一旦发生modCount更变会抛出异常 + if (modCount == mc) + return; + } + } + throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); + } + + // 获取剩余元素估计值,就是用剩余元素索引上边界直接减去下边界 + public long estimateSize() { + return getFence() - index; + } + + // 具备ORDERED、SIZED和SUBSIZED特性 + public int characteristics() { + return Spliterator.ORDERED | Spliterator.SIZED | Spliterator.SUBSIZED; + } +} +``` + +在阅读源码的时候务必注意,老一辈的程序员有时候会采用比较**隐蔽**的赋值方式,笔者认为需要展开一下: + +[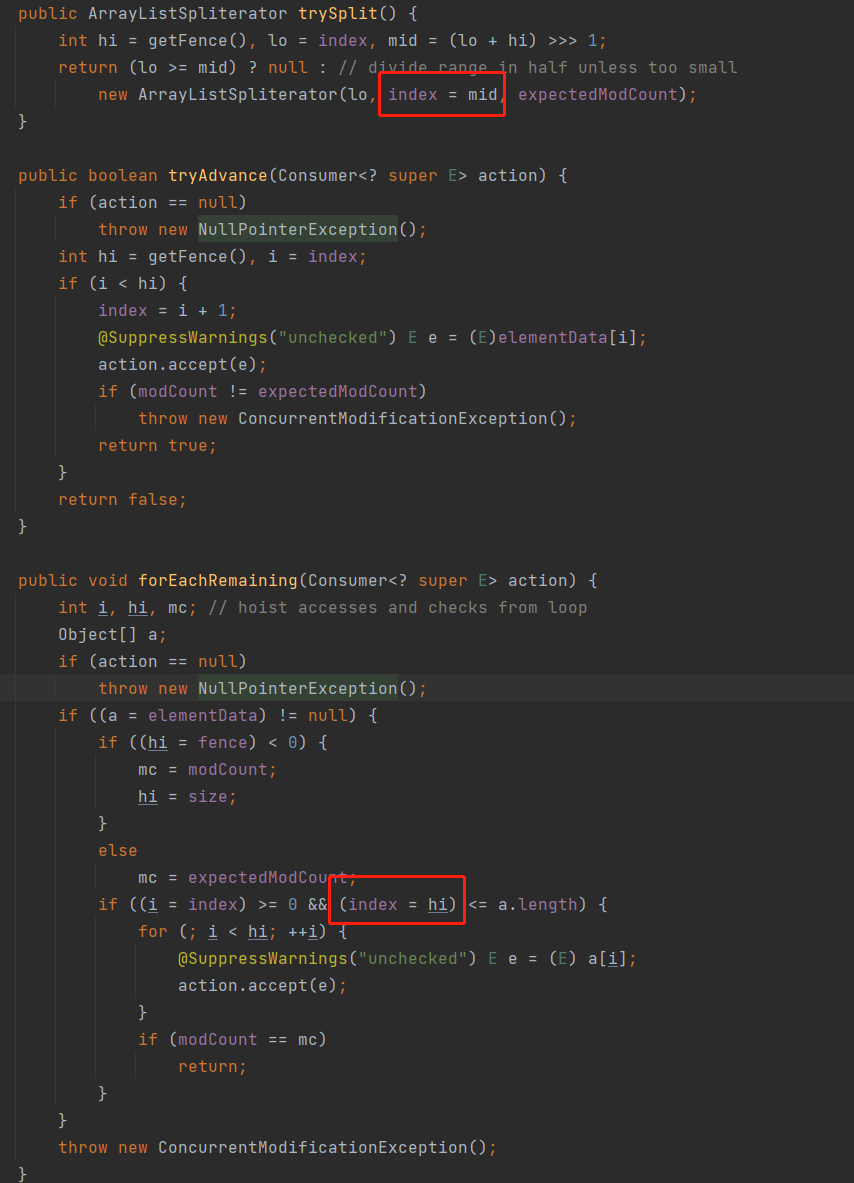](https://throwable-blog-1256189093.cos.ap-guangzhou.myqcloud.com/202110/stream-source-2.png) + +第一处红圈位置在构建新的`ArrayListSpliterator`的时候,当前`ArrayListSpliterator`的`index`属性也被修改了,过程如下图: + +[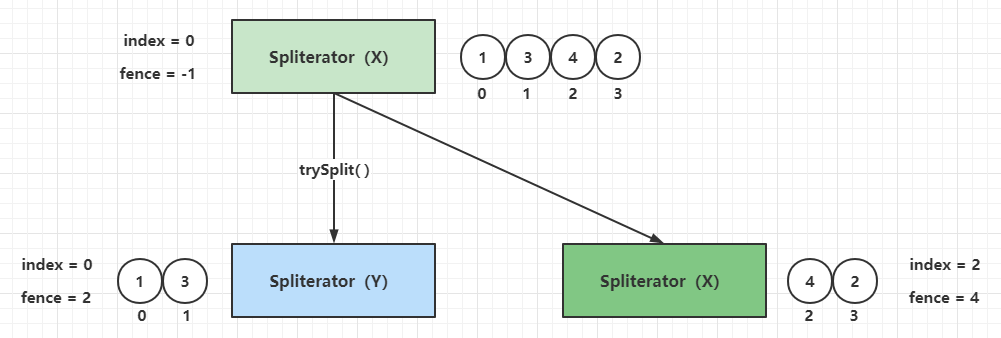](https://throwable-blog-1256189093.cos.ap-guangzhou.myqcloud.com/202110/stream-source-3.png) + +第二处红圈位置,在`forEachRemaining()`方法调用时候做参数校验,并且`if`分支里面把`index`(下边界值)赋值为`hi`(上边界值),**那么一个`ArrayListSpliterator`实例中的`forEachRemaining()`方法的遍历操作必定只会执行一次**。可以这样验证一下: + +```java +public static void main(String[] args) { + List list = new ArrayList();
+ list.add(2);
+ list.add(1);
+ list.add(3);
+ Spliterator spliterator = list.stream().spliterator();
+ final AtomicInteger round = new AtomicInteger(1);
+ spliterator.forEachRemaining(num -> System.out.printf("[第一次遍历forEachRemaining]第%d轮回调Action,值:%d\n", round.getAndIncrement(), num));
+ round.set(1);
+ spliterator.forEachRemaining(num -> System.out.printf("[第二次遍历forEachRemaining]第%d轮回调Action,值:%d\n", round.getAndIncrement(), num));
+}
+
+// 控制台输出
+[第一次遍历forEachRemaining]第1轮回调Action,值:2
+[第一次遍历forEachRemaining]第2轮回调Action,值:1
+[第一次遍历forEachRemaining]第3轮回调Action,值:3
+```
+
+对于`ArrayListSpliterator`的实现可以确认下面几点:
+
+- 一个新的`ArrayListSpliterator`实例中的`forEachRemaining()`方法只能调用一次
+- `ArrayListSpliterator`实例中的`forEachRemaining()`方法遍历元素的边界是`[index, fence)`
+- `ArrayListSpliterator`自分割的时候,分割出来的新`ArrayListSpliterator`负责处理元素下标小的分段(类比`fork`的左分支),而原`ArrayListSpliterator`负责处理元素下标大的分段(类比`fork`的右分支)
+- `ArrayListSpliterator`提供的`estimateSize()`方法得到的分段元素剩余数量是一个准确值
+
+如果把上面的例子继续分割,可以得到下面的过程:
+
+[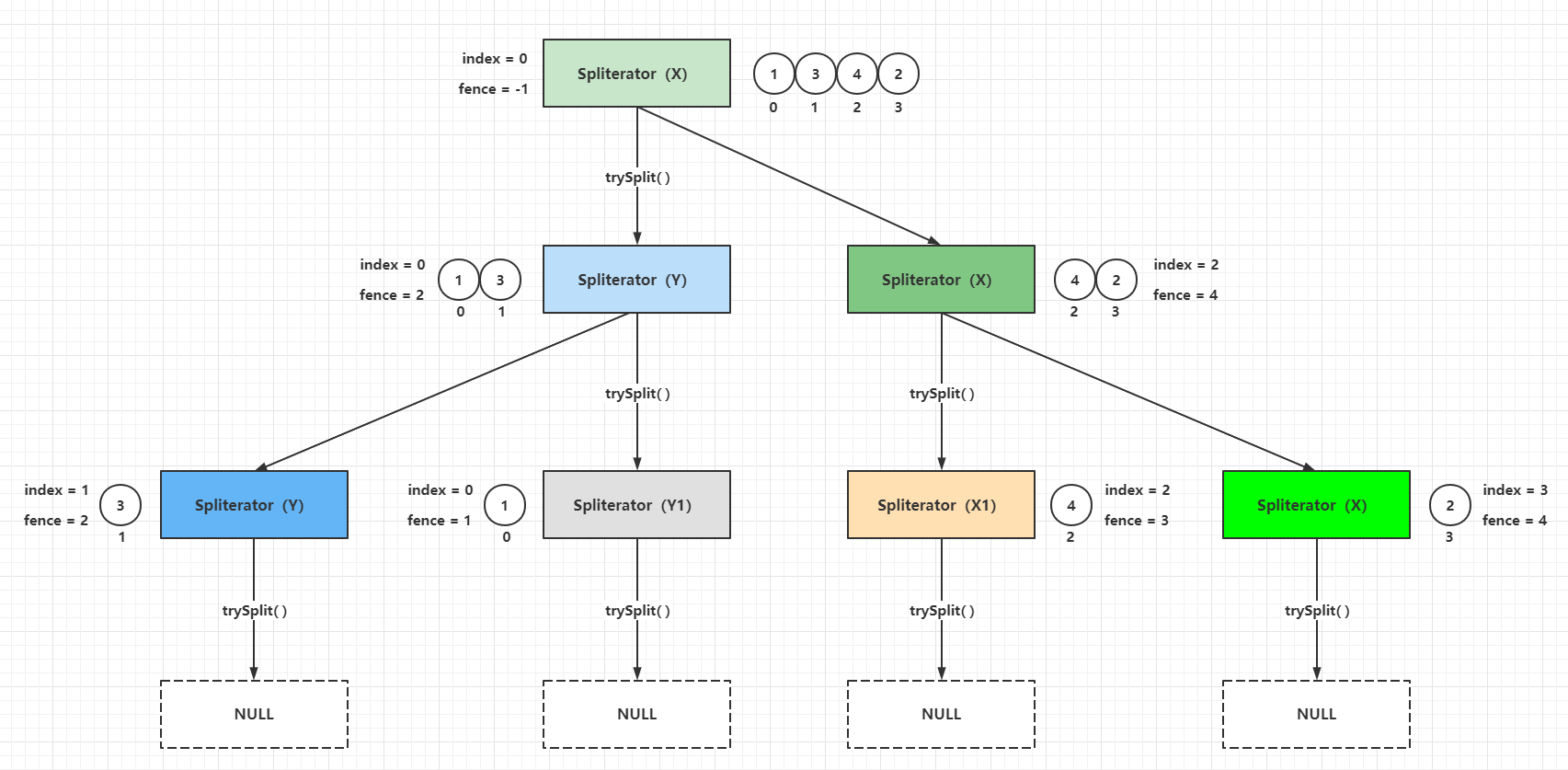](https://throwable-blog-1256189093.cos.ap-guangzhou.myqcloud.com/202110/stream-source-4.png)
+
+**`Spliterator`自分割是并行流实现的基础**,并行流计算过程其实就是`fork-join`的处理过程,`trySplit()`方法的实现决定了`fork`任务的粒度,每个`fork`任务进行计算的时候是并发安全的,这一点由线程封闭(线程栈封闭)保证,每一个`fork`任务计算完成最后的结果再由单个线程进行`join`操作,才能得到正确的结果。下面的例子是求整数`1 ~ 100`的和:
+
+```java
+public class ConcurrentSplitCalculateSum {
+
+ private static class ForkTask extends Thread {
+
+ private int result = 0;
+
+ private final Spliterator spliterator;
+ private final CountDownLatch latch;
+
+ public ForkTask(Spliterator spliterator,
+ CountDownLatch latch) {
+ this.spliterator = spliterator;
+ this.latch = latch;
+ }
+
+ @Override
+ public void run() {
+ long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
+ spliterator.forEachRemaining(num -> result = result + num);
+ long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
+ System.out.printf("线程[%s]完成计算任务,当前段计算结果:%d,耗时:%d ms\n",
+ Thread.currentThread().getName(), result, end - start);
+ latch.countDown();
+ }
+
+ public int result() {
+ return result;
+ }
+ }
+
+ private static int join(List tasks) {
+ int result = 0;
+ for (ForkTask task : tasks) {
+ result = result + task.result();
+ }
+ return result;
+ }
+
+ private static final int THREAD_NUM = 4;
+
+ public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
+ List source = new ArrayList();
+ for (int i = 1; i < 101; i++) { + source.add(i); + } + Spliterator root = source.stream().spliterator();
+ List> spliteratorList = new ArrayList();
+ Spliterator x = root.trySplit();
+ Spliterator y = x.trySplit();
+ Spliterator z = root.trySplit();
+ spliteratorList.add(root);
+ spliteratorList.add(x);
+ spliteratorList.add(y);
+ spliteratorList.add(z);
+ List tasks = new ArrayList();
+ CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(THREAD_NUM);
+ for (int i = 0; i < THREAD_NUM; i++) { + ForkTask task = new ForkTask(spliteratorList.get(i), latch); + task.setName("fork-task-" + (i + 1)); + tasks.add(task); + } + tasks.forEach(Thread::start); + latch.await(); + int result = join(tasks); + System.out.println("最终计算结果为:" + result); + } +} + +// 控制台输出结果 +线程[fork-task-4]完成计算任务,当前段计算结果:1575,耗时:0 ms +线程[fork-task-2]完成计算任务,当前段计算结果:950,耗时:1 ms +线程[fork-task-3]完成计算任务,当前段计算结果:325,耗时:1 ms +线程[fork-task-1]完成计算任务,当前段计算结果:2200,耗时:1 ms +最终计算结果为:5050 +``` + +当然,最终并行流的计算用到了`ForkJoinPool`,并不像这个例子中这么粗暴地进行异步执行。关于并行流的实现下文会详细分析。 + +### Spliterator支持的特性 + +某一个`Spliterator`实例支持的特性由方法`characteristics()`决定,这个方法返回的是一个`32`位数值,实际使用中会展开为`bit`数组,所有的特性分配在不同的位上,而`hasCharacteristics(int characteristics)`就是通过输入的具体特性值通过位运算判断该特性是否存在于`characteristics()`中。下面简化`characteristics`为`byte`分析一下这个技巧: + +```shell +假设:byte characteristics() => 也就是最多8个位用于表示特性集合,如果每个位只表示一种特性,那么可以总共表示8种特性
+特性X:0000 0001
+特性Y:0000 0010
+以此类推
+假设:characteristics = X | Y = 0000 0001 | 0000 0010 = 0000 0011
+那么:characteristics & X = 0000 0011 & 0000 0001 = 0000 0001
+判断characteristics是否包含X:(characteristics & X) == X
+```
+
+上面推断的过程就是`Spliterator`中特性判断方法的处理逻辑:
+
+```java
+// 返回特性集合
+int characteristics();
+
+// 基于位运算判断特性集合中是否存在输入的特性
+default boolean hasCharacteristics(int characteristics) {
+ return (characteristics() & characteristics) == characteristics;
+}
+```
+
+这里可以验证一下:
+
+```java
+public class CharacteristicsCheck {
+
+ public static void main(String[] args) {
+ System.out.printf("是否存在ORDERED特性:%s\n", hasCharacteristics(Spliterator.ORDERED));
+ System.out.printf("是否存在SIZED特性:%s\n", hasCharacteristics(Spliterator.SIZED));
+ System.out.printf("是否存在DISTINCT特性:%s\n", hasCharacteristics(Spliterator.DISTINCT));
+ }
+
+ private static int characteristics() {
+ return Spliterator.ORDERED | Spliterator.SIZED | Spliterator.SORTED;
+ }
+
+ private static boolean hasCharacteristics(int characteristics) {
+ return (characteristics() & characteristics) == characteristics;
+ }
+}
+
+// 控制台输出
+是否存在ORDERED特性:true
+是否存在SIZED特性:true
+是否存在DISTINCT特性:false
+```
+
+目前`Spliterator`支持的特性一共有`8`个,如下:
+
+| 特性 | 十六进制值 | 二进制值 | 功能 |
+| :----------: | :----------: | :-------------------: | :----------------------------------------------------------: |
+| `DISTINCT` | `0x00000001` | `0000 0000 0000 0001` | 去重,例如对于每对要处理的元素`(x,y)`,使用`!x.equals(y)`比较,`Spliterator`中去重实际上基于`Set`处理 |
+| `ORDERED` | `0x00000010` | `0000 0000 0001 0000` | (元素)顺序处理,可以理解为`trySplit()`、`tryAdvance()`和`forEachRemaining()`方法对所有元素处理都保证一个严格的前缀顺序 |
+| `SORTED` | `0x00000004` | `0000 0000 0000 0100` | 排序,元素使用`getComparator()`方法提供的`Comparator`进行排序,如果定义了`SORTED`特性,则必须定义`ORDERED`特性 |
+| `SIZED` | `0x00000040` | `0000 0000 0100 0000` | (元素)预估数量,启用此特性,那么`Spliterator`拆分或者迭代之前,`estimateSize()`返回的是元素的准确数量 |
+| `NONNULL` | `0x00000040` | `0000 0001 0000 0000` | (元素)非`NULL`,数据源保证`Spliterator`需要处理的元素不能为`NULL`,最常用于并发容器中的集合、队列和`Map` |
+| `IMMUTABLE` | `0x00000400` | `0000 0100 0000 0000` | (元素)不可变,数据源不可被修改,也就是处理过程中元素不能被添加、替换和移除(更新属性是允许的) |
+| `CONCURRENT` | `0x00001000` | `0001 0000 0000 0000` | (元素源)的修改是并发安全的,意味着多线程在数据源中添加、替换或者移除元素在不需要额外的同步条件下是并发安全的 |
+| `SUBSIZED` | `0x00004000` | `0100 0000 0000 0000` | (子`Spliterator`元素)预估数量,启用此特性,意味着通过`trySplit()`方法分割出来的所有子`Spliterator`(当前`Spliterator`分割后也属于子`Spliterator`)都启用`SIZED`特性 |
+
+> 细心点观察可以发现:所有特性采用32位的整数存储,使用了隔1位存储的策略,位下标和特性的映射是:(0 => DISTINCT)、(3 => SORTED)、(5 => ORDERED)、(7=> SIZED)、(9 => NONNULL)、(11 => IMMUTABLE)、(13 => CONCURRENT)、(15 => SUBSIZED)
+
+所有特性的功能这里只概括了核心的定义,还有一些小字或者特例描述限于篇幅没有完全加上,这一点可以参考具体的源码中的`API`注释。这些特性最终会转化为`StreamOpFlag`再提供给`Stream`中的操作判断使用,由于`StreamOpFlag`会更加复杂,下文再进行详细分析。
+
+## 流的实现原理以及源码分析
+
+由于流的实现是高度抽象的工程代码,所以在源码阅读上会有点困难。整个体系涉及到大量的接口、类和枚举,如下图:
+
+[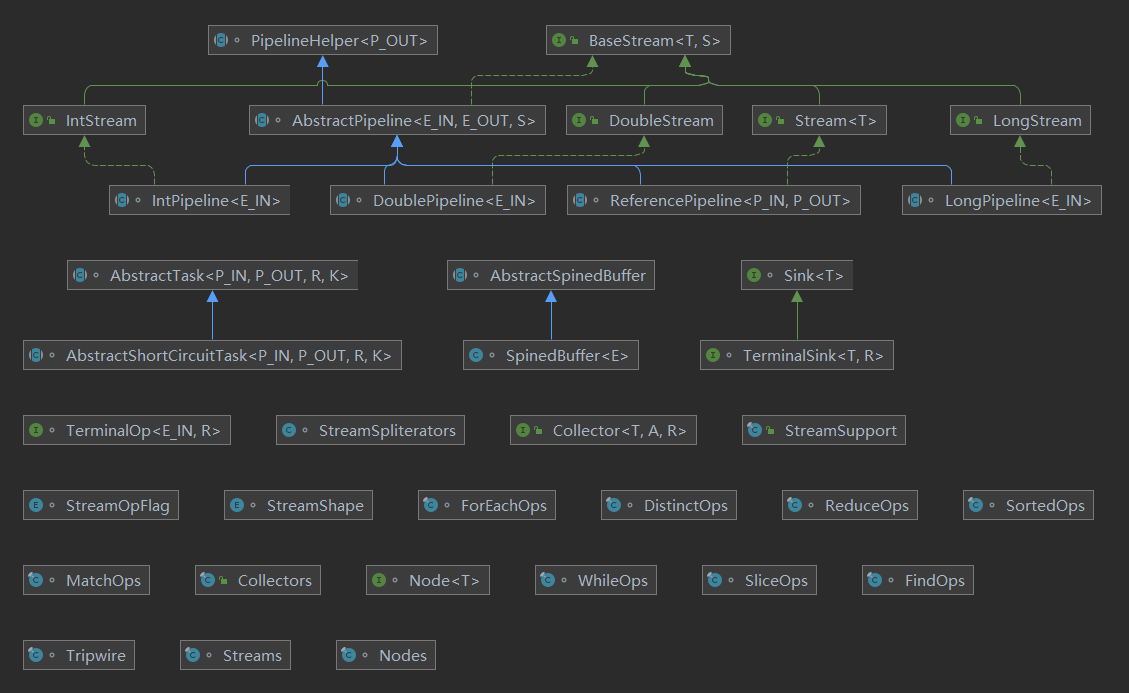](https://throwable-blog-1256189093.cos.ap-guangzhou.myqcloud.com/202110/stream-source-5.png)
+
+图中的顶层类结构图描述的就是流的流水线相关类继承关系,其中`IntStream`、`LongStream`和`DoubleStream`都是特化类型,分别针对于`Integer`、`Long`和`Double`三种类型,其他引用类型构建的`Pipeline`都是`ReferencePipeline`实例,因此笔者认为,`ReferencePipeline`(引用类型流水线)是流的核心数据结构,下面会基于`ReferencePipeline`的实现做深入分析。
+
+### StreamOpFlag源码分析
+
+> 注意,这一小节很烧脑,也有可能是笔者的位操作不怎么熟练,这篇文章大部分时间消耗在这一小节
+
+`StreamOpFlag`是一个枚举,功能是存储`Stream`和操作的标志(`Flags corresponding to characteristics of streams and operations`,下称`Stream`标志),这些标志提供给`Stream`框架用于控制、定制化和优化计算。`Stream`标志可以用于描述与流相关联的若干不同实体的特征,这些实体包括:`Stream`的源、`Stream`的中间操作(`Op`)和`Stream`的终端操作(`Terminal Op`)。但是并非所有的`Stream`标志对所有的`Stream`实体都具备意义,目前这些实体和标志映射关系如下:
+
+| Type(Stream Entity Type) | DISTINCT | SORTED | ORDERED | SIZED | SHORT_CIRCUIT |
+| :----------------------: | :------: | :----: | :-----: | :---: | :-----------: |
+| `SPLITERATOR` | 01 | 01 | 01 | 01 | 00 |
+| `STREAM` | 01 | 01 | 01 | 01 | 00 |
+| `OP` | 11 | 11 | 11 | 10 | 01 |
+| `TERMINAL_OP` | 00 | 00 | 10 | 00 | 01 |
+| `UPSTREAM_TERMINAL_OP` | 00 | 00 | 10 | 00 | 00 |
+
+其中:
+
+- 01:表示设置/注入
+- 10:表示清除
+- 11:表示保留
+- 00:表示初始化值(默认填充值),这是一个关键点,`0`值表示绝对不会是某个类型的标志
+
+`StreamOpFlag`的顶部注释中还有一个表格如下:
+
+| - | DISTINCT | SORTED | ORDERED | SIZED | SHORT_CIRCUIT |
+| :--------------------------------: | :------: | :----: | :-----: | :---: | :-----------: |
+| Stream source(`Stream`的源) | Y | Y | Y | Y | N |
+| Intermediate operation(中间操作) | PCI | PCI | PCI | PC | PI |
+| Terminal operation(终结操作) | N | N | PC | N | PI |
+
+标记 `->` 含义:
+
+- `Y`:允许
+- `N`:非法
+- `P`:保留
+- `C`:清除
+- `I`:注入
+- 组合`PCI`:可以保留、清除或者注入
+- 组合`PC`:可以保留或者清除
+- 组合`PI`:可以保留或者注入
+
+两个表格其实是在描述同一个结论,可以相互对照和理解,但是**最终实现参照于第一个表的定义**。注意一点:这里的`preserved`(`P`)表示保留的意思,如果`Stream`实体某个标志被赋值为`preserved`,意味着该实体可以使用此标志代表的特性。例如此小节第一个表格中的`OP`的`DISTINCT`、`SORTED`和`ORDERED`都赋值为`11`(`preserved`),意味着`OP`类型的实体允许使用去重、自然排序和顺序处理特性。回到源码部分,先看`StreamOpFlag`的核心属性和构造器:
+
+```java
+enum StreamOpFlag {
+
+ // 暂时忽略其他代码
+
+ // 类型枚举,Stream相关实体类型
+ enum Type {
+
+ // SPLITERATOR类型,关联所有和Spliterator相关的特性
+ SPLITERATOR,
+
+ // STREAM类型,关联所有和Stream相关的标志
+ STREAM,
+
+ // STREAM类型,关联所有和Stream中间操作相关的标志
+ OP,
+
+ // TERMINAL_OP类型,关联所有和Stream终结操作相关的标志
+ TERMINAL_OP,
+
+ // UPSTREAM_TERMINAL_OP类型,关联所有在最后一个有状态操作边界上游传播的终止操作标志
+ // 这个类型的意义直译有点拗口,不过实际上在JDK11源码中,这个类型没有被流相关功能引用,暂时可以忽略
+ UPSTREAM_TERMINAL_OP
+ }
+
+ // 设置/注入标志的bit模式,二进制数0001,十进制数1
+ private static final int SET_BITS = 0b01;
+
+ // 清除标志的bit模式,二进制数0010,十进制数2
+ private static final int CLEAR_BITS = 0b10;
+
+ // 保留标志的bit模式,二进制数0011,十进制数3
+ private static final int PRESERVE_BITS = 0b11;
+
+ // 掩码建造器工厂方法,注意这个方法用于实例化MaskBuilder
+ private static MaskBuilder set(Type t) {
+ return new MaskBuilder(new EnumMap(Type.class)).set(t);
+ }
+
+ // 私有静态内部类,掩码建造器,里面的map由上面的set(Type t)方法得知是EnumMap实例
+ private static class MaskBuilder {
+ // Type -> SET_BITS|CLEAR_BITS|PRESERVE_BITS|0
+ final Map map;
+
+ MaskBuilder(Map map) {
+ this.map = map;
+ }
+
+ // 设置类型和对应的掩码
+ MaskBuilder mask(Type t, Integer i) {
+ map.put(t, i);
+ return this;
+ }
+
+ // 对类型添加/inject
+ MaskBuilder set(Type t) {
+ return mask(t, SET_BITS);
+ }
+
+ MaskBuilder clear(Type t) {
+ return mask(t, CLEAR_BITS);
+ }
+
+ MaskBuilder setAndClear(Type t) {
+ return mask(t, PRESERVE_BITS);
+ }
+
+ // 这里的build方法对于类型中的NULL掩码填充为0,然后把map返回
+ Map build() {
+ for (Type t : Type.values()) {
+ map.putIfAbsent(t, 0b00);
+ }
+ return map;
+ }
+ }
+
+ // 类型->掩码映射
+ private final Map maskTable;
+
+ // bit的起始偏移量,控制下面set、clear和preserve的起始偏移量
+ private final int bitPosition;
+
+ // set/inject的bit set(map),其实准确来说应该是一个表示set/inject的bit map
+ private final int set;
+
+ // clear的bit set(map),其实准确来说应该是一个表示clear的bit map
+ private final int clear;
+
+ // preserve的bit set(map),其实准确来说应该是一个表示preserve的bit map
+ private final int preserve;
+
+ private StreamOpFlag(int position, MaskBuilder maskBuilder) {
+ // 这里会基于MaskBuilder初始化内部的EnumMap
+ this.maskTable = maskBuilder.build();
+ // Two bits per flag <= 这里会把入参position放大一倍 + position *= 2; + this.bitPosition = position; + this.set = SET_BITS << position; // 设置/注入标志的bit模式左移2倍position + this.clear = CLEAR_BITS << position; // 清除标志的bit模式左移2倍position + this.preserve = PRESERVE_BITS << position; // 保留标志的bit模式左移2倍position + } + + // 省略中间一些方法 + + // 下面这些静态变量就是直接返回标志对应的set/injec、清除和保留的bit map + /** + * The bit value to set or inject {@link #DISTINCT}. + */ + static final int IS_DISTINCT = DISTINCT.set; + + /** + * The bit value to clear {@link #DISTINCT}. + */ + static final int NOT_DISTINCT = DISTINCT.clear; + + /** + * The bit value to set or inject {@link #SORTED}. + */ + static final int IS_SORTED = SORTED.set; + + /** + * The bit value to clear {@link #SORTED}. + */ + static final int NOT_SORTED = SORTED.clear; + + /** + * The bit value to set or inject {@link #ORDERED}. + */ + static final int IS_ORDERED = ORDERED.set; + + /** + * The bit value to clear {@link #ORDERED}. + */ + static final int NOT_ORDERED = ORDERED.clear; + + /** + * The bit value to set {@link #SIZED}. + */ + static final int IS_SIZED = SIZED.set; + + /** + * The bit value to clear {@link #SIZED}. + */ + static final int NOT_SIZED = SIZED.clear; + + /** + * The bit value to inject {@link #SHORT_CIRCUIT}. + */ + static final int IS_SHORT_CIRCUIT = SHORT_CIRCUIT.set; +} +``` + +又因为`StreamOpFlag`是一个枚举,一个枚举成员是一个独立的标志,而一个标志会对多个`Stream`实体类型产生作用,所以它的一个成员描述的是上面实体和标志映射关系的一个列(竖着看): + +[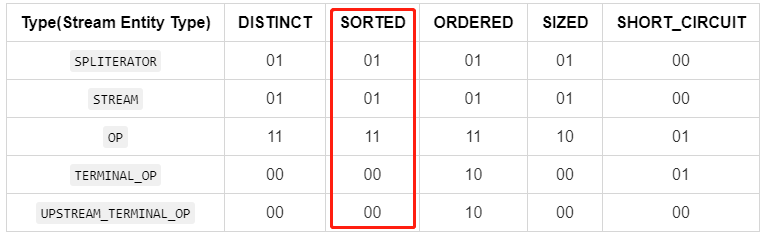](https://throwable-blog-1256189093.cos.ap-guangzhou.myqcloud.com/202110/stream-source-7.png) + +```shell +// 纵向看 +DISTINCT Flag: +maskTable: { + SPLITERATOR: 0000 0001, + STREAM: 0000 0001, + OP: 0000 0011, + TERMINAL_OP: 0000 0000, + UPSTREAM_TERMINAL_OP: 0000 0000 +} +position(input): 0 +bitPosition: 0 +set: 1 => 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0001
+clear: 2 => 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0010
+preserve: 3 => 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0011
+
+SORTED Flag:
+maskTable: {
+ SPLITERATOR: 0000 0001,
+ STREAM: 0000 0001,
+ OP: 0000 0011,
+ TERMINAL_OP: 0000 0000,
+ UPSTREAM_TERMINAL_OP: 0000 0000
+}
+position(input): 1
+bitPosition: 2
+set: 4 => 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0100
+clear: 8 => 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 1000
+preserve: 12 => 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 1100
+
+ORDERED Flag:
+maskTable: {
+ SPLITERATOR: 0000 0001,
+ STREAM: 0000 0001,
+ OP: 0000 0011,
+ TERMINAL_OP: 0000 0010,
+ UPSTREAM_TERMINAL_OP: 0000 0010
+}
+position(input): 2
+bitPosition: 4
+set: 16 => 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0001 0000
+clear: 32 => 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0010 0000
+preserve: 48 => 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0011 0000
+
+SIZED Flag:
+maskTable: {
+ SPLITERATOR: 0000 0001,
+ STREAM: 0000 0001,
+ OP: 0000 0010,
+ TERMINAL_OP: 0000 0000,
+ UPSTREAM_TERMINAL_OP: 0000 0000
+}
+position(input): 3
+bitPosition: 6
+set: 64 => 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0100 0000
+clear: 128 => 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 1000 0000
+preserve: 192 => 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 1100 0000
+
+SHORT_CIRCUIT Flag:
+maskTable: {
+ SPLITERATOR: 0000 0000,
+ STREAM: 0000 0000,
+ OP: 0000 0001,
+ TERMINAL_OP: 0000 0001,
+ UPSTREAM_TERMINAL_OP: 0000 0000
+}
+position(input): 12
+bitPosition: 24
+set: 16777216 => 0000 0001 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000
+clear: 33554432 => 0000 0010 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000
+preserve: 50331648 => 0000 0011 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000
+```
+
+接着就用到按位与(`&`)和按位或(`|`)的操作,假设`A = 0001`、`B = 0010`、`C = 1000`,那么:
+
+- `A|B = A | B = 0001 | 0010 = 0011`(按位或,`1|0=1, 0|1=1,0|0 =0,1|1=1`)
+- `A&B = A & B = 0001 | 0010 = 0000`(按位与,`1|0=0, 0|1=0,0|0 =0,1|1=1`)
+- `MASK = A | B | C = 0001 | 0010 | 1000 = 1011`
+- 那么判断`A|B`是否包含`A`的条件为:`A == (A|B & A)`
+- 那么判断`MASK`是否包含`A`的条件为:`A == MASK & A`
+
+这里把`StreamOpFlag`中的枚举套用进去分析:
+
+```java
+static int DISTINCT_SET = 0b0001;
+static int SORTED_CLEAR = 0b1000;
+
+public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
+ // 支持DISTINCT标志和不支持SORTED标志
+ int flags = DISTINCT_SET | SORTED_CLEAR;
+ System.out.println(Integer.toBinaryString(flags));
+ System.out.printf("支持DISTINCT标志:%s\n", DISTINCT_SET == (DISTINCT_SET & flags));
+ System.out.printf("不支持SORTED标志:%s\n", SORTED_CLEAR == (SORTED_CLEAR & flags));
+}
+
+// 控制台输出
+1001
+支持DISTINCT标志:true
+不支持SORTED标志:true
+```
+
+由于`StreamOpFlag`的修饰符是默认,不能直接使用,可以把它的代码拷贝出来修改包名验证里面的功能:
+
+```java
+public static void main(String[] args) {
+ int flags = StreamOpFlag.DISTINCT.set | StreamOpFlag.SORTED.clear;
+ System.out.println(StreamOpFlag.DISTINCT.set == (StreamOpFlag.DISTINCT.set & flags));
+ System.out.println(StreamOpFlag.SORTED.clear == (StreamOpFlag.SORTED.clear & flags));
+}
+
+// 输出
+
+true
+true
+```
+
+下面这些方法就是基于这些运算特性而定义的:
+
+```java
+enum StreamOpFlag {
+
+ // 暂时忽略其他代码
+
+ // 返回当前StreamOpFlag的set/inject的bit map
+ int set() {
+ return set;
+ }
+
+ // 返回当前StreamOpFlag的清除的bit map
+ int clear() {
+ return clear;
+ }
+
+ // 这里判断当前StreamOpFlag类型->标记映射中Stream类型的标记,如果大于0说明不是初始化状态,那么当前StreamOpFlag就是Stream相关的标志
+ boolean isStreamFlag() {
+ return maskTable.get(Type.STREAM)> 0;
+ }
+
+ // 这里就用到按位与判断输入的flags中是否设置当前StreamOpFlag(StreamOpFlag.set)
+ boolean isKnown(int flags) {
+ return (flags & preserve) == set;
+ }
+
+ // 这里就用到按位与判断输入的flags中是否清除当前StreamOpFlag(StreamOpFlag.clear)
+ boolean isCleared(int flags) {
+ return (flags & preserve) == clear;
+ }
+
+ // 这里就用到按位与判断输入的flags中是否保留当前StreamOpFlag(StreamOpFlag.clear)
+ boolean isPreserved(int flags) {
+ return (flags & preserve) == preserve;
+ }
+
+ // 判断当前的Stream实体类型是否可以设置本标志,要求Stream实体类型的标志位为set或者preserve,按位与要大于0
+ boolean canSet(Type t) {
+ return (maskTable.get(t) & SET_BITS)> 0;
+ }
+
+ // 暂时忽略其他代码
+}
+```
+
+这里有个特殊操作,位运算的时候采用了`(flags & preserve)`,理由是:同一个标志中的同一个`Stream`实体类型只可能存在`set/inject`、`clear`和`preserve`的其中一种,也就是同一个`flags`中不可能同时存在`StreamOpFlag.SORTED.set`和`StreamOpFlag.SORTED.clear`,从语义上已经矛盾,而`set/inject`、`clear`和`preserve`在`bit map`中的大小(为`2`位)和位置已经是固定的,`preserve`在设计的时候为`0b11`刚好`2`位取反,因此可以特化为(这个特化也让判断更加严谨):
+
+```shell
+(flags & set) == set => (flags & preserve) == set
+(flags & clear) == clear => (flags & preserve) == clear
+(flags & preserve) == preserve => (flags & preserve) == preserve
+```
+
+分析这么多,总的来说,就是想通过一个`32`位整数,每`2`位分别表示`3`种状态,那么一个完整的`Flags`(标志集合)一共可以表示`16`种标志(`position=[0,15]`,可以查看`API`注释,`[4,11]`和`[13,15]`的位置是未需实现或者预留的,属于`gap`)。接着分析掩码`Mask`的计算过程例子:
+
+```shell
+// 横向看(位移动运算符优先级高于与或,例如<<的优先级比|高) +SPLITERATOR_CHARACTERISTICS_MASK: +mask(init) = 0 +mask(DISTINCT,SPLITERATOR[DISTINCT]=01,bitPosition=0) = 0000 0000 | 0000 0001 << 0 = 0000 0000 | 0000 0001 = 0000 0001 +mask(SORTED,SPLITERATOR[SORTED]=01,bitPosition=2) = 0000 0001 | 0000 0001 << 2 = 0000 0001 | 0000 0100 = 0000 0101 +mask(ORDERED,SPLITERATOR[ORDERED]=01,bitPosition=4) = 0000 0101 | 0000 0001 << 4 = 0000 0101 | 0001 0000 = 0001 0101 +mask(SIZED,SPLITERATOR[SIZED]=01,bitPosition=6) = 0001 0101 | 0000 0001 << 6 = 0001 0101 | 0100 0000 = 0101 0101 +mask(SHORT_CIRCUIT,SPLITERATOR[SHORT_CIRCUIT]=00,bitPosition=24) = 0101 0101 | 0000 0000 << 24 = 0101 0101 | 0000 0000 = 0101 0101 +mask(final) = 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0101 0101(二进制)、85(十进制) + +STREAM_MASK: +mask(init) = 0 +mask(DISTINCT,SPLITERATOR[DISTINCT]=01,bitPosition=0) = 0000 0000 | 0000 0001 << 0 = 0000 0000 | 0000 0001 = 0000 0001 +mask(SORTED,SPLITERATOR[SORTED]=01,bitPosition=2) = 0000 0001 | 0000 0001 << 2 = 0000 0001 | 0000 0100 = 0000 0101 +mask(ORDERED,SPLITERATOR[ORDERED]=01,bitPosition=4) = 0000 0101 | 0000 0001 << 4 = 0000 0101 | 0001 0000 = 0001 0101 +mask(SIZED,SPLITERATOR[SIZED]=01,bitPosition=6) = 0001 0101 | 0000 0001 << 6 = 0001 0101 | 0100 0000 = 0101 0101 +mask(SHORT_CIRCUIT,SPLITERATOR[SHORT_CIRCUIT]=00,bitPosition=24) = 0101 0101 | 0000 0000 << 24 = 0101 0101 | 0000 0000 = 0101 0101 +mask(final) = 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0101 0101(二进制)、85(十进制) + +OP_MASK: +mask(init) = 0 +mask(DISTINCT,SPLITERATOR[DISTINCT]=11,bitPosition=0) = 0000 0000 | 0000 0011 << 0 = 0000 0000 | 0000 0011 = 0000 0011 +mask(SORTED,SPLITERATOR[SORTED]=11,bitPosition=2) = 0000 0011 | 0000 0011 << 2 = 0000 0011 | 0000 1100 = 0000 1111 +mask(ORDERED,SPLITERATOR[ORDERED]=11,bitPosition=4) = 0000 1111 | 0000 0011 << 4 = 0000 1111 | 0011 0000 = 0011 1111 +mask(SIZED,SPLITERATOR[SIZED]=10,bitPosition=6) = 0011 1111 | 0000 0010 << 6 = 0011 1111 | 1000 0000 = 1011 1111 +mask(SHORT_CIRCUIT,SPLITERATOR[SHORT_CIRCUIT]=01,bitPosition=24) = 1011 1111 | 0000 0001 << 24 = 1011 1111 | 0100 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 = 0100 0000 0000 0000 0000 1011 1111 +mask(final) = 0000 0000 1000 0000 0000 0000 1011 1111(二进制)、16777407(十进制) + +TERMINAL_OP_MASK: +mask(init) = 0 +mask(DISTINCT,SPLITERATOR[DISTINCT]=00,bitPosition=0) = 0000 0000 | 0000 0000 << 0 = 0000 0000 | 0000 0000 = 0000 0000 +mask(SORTED,SPLITERATOR[SORTED]=00,bitPosition=2) = 0000 0000 | 0000 0000 << 2 = 0000 0000 | 0000 0000 = 0000 0000 +mask(ORDERED,SPLITERATOR[ORDERED]=10,bitPosition=4) = 0000 0000 | 0000 0010 << 4 = 0000 0000 | 0010 0000 = 0010 0000 +mask(SIZED,SPLITERATOR[SIZED]=00,bitPosition=6) = 0010 0000 | 0000 0000 << 6 = 0010 0000 | 0000 0000 = 0010 0000 +mask(SHORT_CIRCUIT,SPLITERATOR[SHORT_CIRCUIT]=01,bitPosition=24) = 0010 0000 | 0000 0001 << 24 = 0010 0000 | 0001 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 = 0001 0000 0000 0000 0000 0010 0000 +mask(final) = 0000 0001 0000 0000 0000 0000 0010 0000(二进制)、16777248(十进制) + +UPSTREAM_TERMINAL_OP_MASK: +mask(init) = 0 +mask(DISTINCT,SPLITERATOR[DISTINCT]=00,bitPosition=0) = 0000 0000 | 0000 0000 << 0 = 0000 0000 | 0000 0000 = 0000 0000 +mask(SORTED,SPLITERATOR[SORTED]=00,bitPosition=2) = 0000 0000 | 0000 0000 << 2 = 0000 0000 | 0000 0000 = 0000 0000 +mask(ORDERED,SPLITERATOR[ORDERED]=10,bitPosition=4) = 0000 0000 | 0000 0010 << 4 = 0000 0000 | 0010 0000 = 0010 0000 +mask(SIZED,SPLITERATOR[SIZED]=00,bitPosition=6) = 0010 0000 | 0000 0000 << 6 = 0010 0000 | 0000 0000 = 0010 0000 +mask(SHORT_CIRCUIT,SPLITERATOR[SHORT_CIRCUIT]=00,bitPosition=24) = 0010 0000 | 0000 0000 << 24 = 0010 0000 | 0000 0000 = 0010 0000 +mask(final) = 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0010 0000(二进制)、32(十进制) +``` + +相关的方法和属性如下: + +```java +enum StreamOpFlag { + + // SPLITERATOR类型的标志bit map + static final int SPLITERATOR_CHARACTERISTICS_MASK = createMask(Type.SPLITERATOR); + + // STREAM类型的标志bit map + static final int STREAM_MASK = createMask(Type.STREAM); + + // OP类型的标志bit map + static final int OP_MASK = createMask(Type.OP); + + // TERMINAL_OP类型的标志bit map + static final int TERMINAL_OP_MASK = createMask(Type.TERMINAL_OP); + + // UPSTREAM_TERMINAL_OP类型的标志bit map + static final int UPSTREAM_TERMINAL_OP_MASK = createMask(Type.UPSTREAM_TERMINAL_OP); + + // 基于Stream类型,创建对应类型填充所有标志的bit map + private static int createMask(Type t) { + int mask = 0; + for (StreamOpFlag flag : StreamOpFlag.values()) { + mask |= flag.maskTable.get(t) << flag.bitPosition; + } + return mask; + } + + // 构造一个标志本身的掩码,就是所有标志都采用保留位表示,目前作为flags == 0时候的初始值 + private static final int FLAG_MASK = createFlagMask(); + + // 构造一个包含全部标志中的preserve位的bit map,按照目前来看是暂时是一个固定值,二进制表示为0011 0000 0000 0000 0000 1111 1111 + private static int createFlagMask() { + int mask = 0; + for (StreamOpFlag flag : StreamOpFlag.values()) { + mask |= flag.preserve; + } + return mask; + } + + // 构造一个Stream类型包含全部标志中的set位的bit map,这里直接使用了STREAM_MASK,按照目前来看是暂时是一个固定值,二进制表示为0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0101 0101 + private static final int FLAG_MASK_IS = STREAM_MASK; + + // 构造一个Stream类型包含全部标志中的clear位的bit map,按照目前来看是暂时是一个固定值,二进制表示为0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 1010 1010 + private static final int FLAG_MASK_NOT = STREAM_MASK << 1; + + // 初始化操作的标志bit map,目前来看就是Stream的头节点初始化时候需要合并在flags里面的初始化值,照目前来看是暂时是一个固定值,二进制表示为0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 1111 1111 + static final int INITIAL_OPS_VALUE = FLAG_MASK_IS | FLAG_MASK_NOT; +} +``` + +`SPLITERATOR_CHARACTERISTICS_MASK`等`5`个成员(见上面的`Mask`计算例子)其实就是预先计算好对应的`Stream`实体类型的**所有`StreamOpFlag`标志**的`bit map`,也就是之前那个展示`Stream`的类型和标志的映射图的"横向"展示: + +[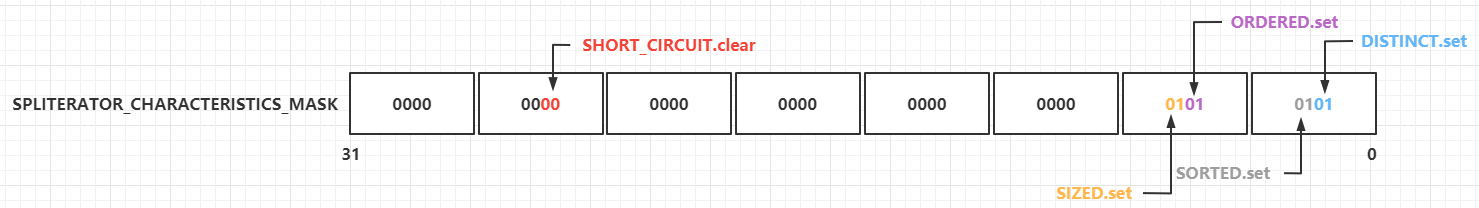](https://throwable-blog-1256189093.cos.ap-guangzhou.myqcloud.com/202110/stream-source-8.png) + +前面的分析已经相对详细,过程非常复杂,但是更复杂的`Mask`应用还在后面的方法。`Mask`的初始化就是提供给标志的合并(`combine`)和转化(从`Spliterator`中的`characteristics`转化为`flags`)操作的,见下面的方法: + +```java +enum StreamOpFlag { + + // 这个方法完全没有注释,只使用在下面的combineOpFlags()方法中 + // 从源码来看 + // 入参flags == 0的时候,那么直接返回0011 0000 0000 0000 0000 1111 1111 + // 入参flags != 0的时候,那么会把当前flags的所有set/inject、clear和preserve所在位在bit map中全部置为0,然后其他位全部置为1 + private static int getMask(int flags) { + return (flags == 0) + ? FLAG_MASK + : ~(flags | ((FLAG_MASK_IS & flags) << 1) | ((FLAG_MASK_NOT & flags)>> 1));
+ }
+
+ // 合并新的flags和前一个flags,这里还是用到老套路先和Mask按位与,再进行一次按位或
+ // 作为Stream的头节点的时候,prevCombOpFlags必须为INITIAL_OPS_VALUE
+ static int combineOpFlags(int newStreamOrOpFlags, int prevCombOpFlags) {
+ // 0x01 or 0x10 nibbles are transformed to 0x11
+ // 0x00 nibbles remain unchanged
+ // Then all the bits are flipped
+ // Then the result is logically or'ed with the operation flags.
+ return (prevCombOpFlags & StreamOpFlag.getMask(newStreamOrOpFlags)) | newStreamOrOpFlags;
+ }
+
+ // 通过合并后的flags,转换出Stream类型的flags
+ static int toStreamFlags(int combOpFlags) {
+ // By flipping the nibbles 0x11 become 0x00 and 0x01 become 0x10
+ // Shift left 1 to restore set flags and mask off anything other than the set flags
+ return ((~combOpFlags)>> 1) & FLAG_MASK_IS & combOpFlags;
+ }
+
+ // Stream的标志转换为Spliterator的characteristics
+ static int toCharacteristics(int streamFlags) {
+ return streamFlags & SPLITERATOR_CHARACTERISTICS_MASK;
+ }
+
+ // Spliterator的characteristics转换为Stream的标志,入参是Spliterator实例
+ static int fromCharacteristics(Spliterator spliterator) {
+ int characteristics = spliterator.characteristics();
+ if ((characteristics & Spliterator.SORTED) != 0 && spliterator.getComparator() != null) {
+ // Do not propagate the SORTED characteristic if it does not correspond
+ // to a natural sort order
+ return characteristics & SPLITERATOR_CHARACTERISTICS_MASK & ~Spliterator.SORTED;
+ }
+ else {
+ return characteristics & SPLITERATOR_CHARACTERISTICS_MASK;
+ }
+ }
+
+ // Spliterator的characteristics转换为Stream的标志,入参是Spliterator的characteristics
+ static int fromCharacteristics(int characteristics) {
+ return characteristics & SPLITERATOR_CHARACTERISTICS_MASK;
+ }
+}
+```
+
+这里的位运算很复杂,只展示简单的计算结果和相关功能:
+
+- `combineOpFlags()`:用于合并新的`flags`和上一个`flags`,因为`Stream`的数据结构是一个`Pipeline`,后继节点需要合并前驱节点的`flags`,例如前驱节点`flags`是`ORDERED.set`,当前新加入`Pipeline`的节点(后继节点)的新`flags`为`SIZED.set`,那么在后继节点中应该合并前驱节点的标志,简单想象为`SIZED.set | ORDERED.set`,如果是头节点,那么初始化头节点时候的`flags`要合并`INITIAL_OPS_VALUE`,这里举个例子:
+
+```java
+int left = ORDERED.set | DISTINCT.set;
+int right = SIZED.clear | SORTED.clear;
+System.out.println("left:" + Integer.toBinaryString(left));
+System.out.println("right:" + Integer.toBinaryString(right));
+System.out.println("right mask:" + Integer.toBinaryString(getMask(right)));
+System.out.println("combine:" + Integer.toBinaryString(combineOpFlags(right, left)));
+
+// 输出结果
+left:1010001
+right:10001000
+right mask:11111111111111111111111100110011
+combine:10011001
+```
+
+- `characteristics`的转化问题:`Spliterator`中的`characteristics`可以通过简单的按位与转换为`flags`的原因是`Spliterator`中的`characteristics`在设计时候本身就是和`StreamOpFlag`匹配的,准确来说就是`bit map`的位分布是匹配的,所以直接与`SPLITERATOR_CHARACTERISTICS_MASK`做按位与即可,见下面的例子:
+
+```shell
+// 这里简单点只展示8 bit
+SPLITERATOR_CHARACTERISTICS_MASK: 0101 0101
+Spliterator.ORDERED: 0001 0000
+StreamOpFlag.ORDERED.set: 0001 0000
+```
+
+至此,已经分析完`StreamOpFlag`的完整实现,`Mask`相关的方法限于篇幅就不打算详细展开,下面会开始分析`Stream`中的"流水线"结构实现,因为习惯问题,下文的"标志"和"特性"两个词语会混用。
+
+## ReferencePipeline源码分析
+
+既然`Stream`具备流的特性,那么就需要一个链式数据结构,让元素能够从`Source`一直往下"流动"和传递到每一个链节点,实现这种场景的常用数据结构就是双向链表(考虑需要回溯,单向链表不太合适),目前比较著名的实现有`AQS`和`Netty`中的`ChannelHandlerContext`。例如`Netty`中的流水线`ChannelPipeline`设计如下:
+
+[](https://throwable-blog-1256189093.cos.ap-guangzhou.myqcloud.com/202110/stream-source-6.png)
+
+对于这个双向链表的数据结构,`Stream`中对应的类就是`AbstractPipeline`,核心实现类在`ReferencePipeline`和`ReferencePipeline`的内部类。
+
+### 主要接口
+
+先简单展示`AbstractPipeline`的核心父类方法定义,主要接父类是`Stream`、`BaseStream`和`PipelineHelper`:
+
+- `Stream`代表一个支持串行和并行聚合操作集合的元素序列,此顶层接口提供了流中间操作、终结操作和一些静态工厂方法的定义(由于方法太多,这里不全部列举),这个接口本质是一个建造器类型接口(对接中间操作来说),可以构成一个多中间操作,单终结操作的链,例如:
+
+```java
+public interface Stream extends BaseStream> {
+
+ // 忽略其他代码
+
+ // 过滤Op
+ Stream filter(Predicate predicate);
+
+ // 映射Op
+ Stream map(Function mapper);
+
+ // 终结操作 - 遍历
+ void forEach(Consumer action);
+
+ // 忽略其他代码
+}
+
+// init
+Stream x = buildStream();
+// chain: head -> filter(Op) -> map(Op) -> forEach(Terminal Op)
+x.filter().map().forEach()
+```
+
+- `BaseStream`:`Stream`的基础接口,定义流的迭代器、流的等效变体(并发处理变体、同步处理变体和不支持顺序处理元素变体)、并发和同步判断以及关闭相关方法
+
+```java
+// T是元素类型,S是BaseStream类型
+// 流的基础接口,这里的流指定的支持同步执行和异步执行的聚合操作的元素序列
+public interface BaseStream> extends AutoCloseable {
+
+ // 返回一个当前Stream实例中所有元素的迭代器
+ // 这是一个终结操作
+ Iterator iterator();
+
+ // 返回一个当前Stream实例中所有元素的可拆分迭代器
+ Spliterator spliterator();
+
+ // 当前的Stream实例是否支持并发
+ boolean isParallel();
+
+ // 返回一个等效的同步处理的Stream实例
+ S sequential();
+
+ // 返回一个等效的并发处理的Stream实例
+ S parallel();
+
+ // 返回一个等效的不支持StreamOpFlag.ORDERED特性的Stream实例
+ // 或者说支持StreamOpFlag.NOT_ORDERED的特性,也就返回的变体Stream在处理元素的时候不需要顺序处理
+ S unordered();
+
+ // 返回一个添加了close处理器的Stream实例,close处理器会在下面的close方法中回调
+ S onClose(Runnable closeHandler);
+
+ // 关闭当前Stream实例,回调关联本Stream的所有close处理器
+ @Override
+ void close();
+}
+```
+
+- `PipelineHelper`:
+
+```java
+abstract class PipelineHelper {
+
+ // 获取流的流水线的数据源的"形状",其实就是数据源元素的类型
+ // 主要有四种类型:REFERENCE(除了int、long和double之外的引用类型)、INT_VALUE、LONG_VALUE和DOUBLE_VALUE
+ abstract StreamShape getSourceShape();
+
+ // 获取合并流和流操作的标志,合并的标志包括流的数据源标志、中间操作标志和终结操作标志
+ // 从实现上看是当前流管道节点合并前面所有节点和自身节点标志的所有标志
+ abstract int getStreamAndOpFlags();
+
+ // 如果当前的流管道节点的合并标志集合支持SIZED,则调用Spliterator.getExactSizeIfKnown()返回数据源中的准确元素数量,否则返回-1
+ abstract long exactOutputSizeIfKnown(Spliterator spliterator);
+
+ // 相当于调用下面的方法组合:copyInto(wrapSink(sink), spliterator)
+ abstract> S wrapAndCopyInto(S sink, Spliterator spliterator);
+
+ // 发送所有来自Spliterator中的元素到Sink中,如果支持SHORT_CIRCUIT标志,则会调用copyIntoWithCancel
+ abstract void copyInto(Sink wrappedSink, Spliterator spliterator);
+
+ // 发送所有来自Spliterator中的元素到Sink中,Sink处理完每个元素后会检查Sink#cancellationRequested()方法的状态去判断是否中断推送元素的操作
+ abstract boolean copyIntoWithCancel(Sink wrappedSink, Spliterator spliterator);
+
+ // 创建接收元素类型为P_IN的Sink实例,实现PipelineHelper中描述的所有中间操作,用这个Sink去包装传入的Sink实例(传入的Sink实例的元素类型为PipelineHelper的输出类型P_OUT)
+ abstract Sink wrapSink(Sink sink);
+
+ // 包装传入的spliterator,从源码来看,在Stream链的头节点调用会直接返回传入的实例,如果在非头节点调用会委托到StreamSpliterators.WrappingSpliterator()方法进行包装
+ // 这个方法在源码中没有API注释
+ abstract Spliterator wrapSpliterator(Spliterator spliterator);
+
+ // 构造一个兼容当前Stream元素"形状"的Node.Builder实例
+ // 从源码来看直接委托到Nodes.builder()方法
+ abstract Node.Builder makeNodeBuilder(long exactSizeIfKnown,
+ IntFunction generator);
+
+ // Stream流水线所有阶段(节点)应用于数据源Spliterator,输出的元素作为结果收集起来转化为Node实例
+ // 此方法应用于toArray()方法的计算,本质上是一个终结操作
+ abstract Node evaluate(Spliterator spliterator,
+ boolean flatten,
+ IntFunction generator);
+}
+```
+
+注意一点(重复`3`次):
+
+- 这里把同步流称为同步处理|执行的流,"并行流"称为并发处理|执行的流,因为并行流有歧义,**实际上只是并发执行,不是并行执行**
+- 这里把同步流称为同步处理|执行的流,"并行流"称为并发处理|执行的流,因为并行流有歧义,**实际上只是并发执行,不是并行执行**
+- 这里把同步流称为同步处理|执行的流,"并行流"称为并发处理|执行的流,因为并行流有歧义,**实际上只是并发执行,不是并行执行**
+
+### Sink和引用类型链
+
+`PipelineHelper`的几个方法中存在`Sink`这个接口,上一节没有分析,这一小节会详细展开。`Stream`在构建的时候虽然是一个双向链表的结构,但是在最终应用终结操作的时候,会把所有操作转化为引用类型链(`ChainedReference`),记得之前也提到过这种类似于多层包装器的编程模式,简化一下模型如下:
+
+```java
+public class WrapperApp {
+
+ interface Wrapper {
+
+ void doAction();
+ }
+
+ public static void main(String[] args) {
+ AtomicInteger counter = new AtomicInteger(0);
+ Wrapper first = () -> System.out.printf("wrapper [depth => %d] invoke\n", counter.incrementAndGet());
+ Wrapper second = () -> {
+ first.doAction();
+ System.out.printf("wrapper [depth => %d] invoke\n", counter.incrementAndGet());
+ };
+ second.doAction();
+ }
+}
+
+// 控制台输出
+wrapper [depth => 1] invoke
+wrapper [depth => 2] invoke
+```
+
+上面的例子有点突兀,两个不同`Sink`的实现可以做到无感知融合,举另一个例子如下:
+
+```java
+public interface Sink extends Consumer {
+
+ default void begin(long size) {
+
+ }
+
+ default void end() {
+
+ }
+
+ abstract class ChainedReference implements Sink {
+
+ protected final Sink downstream;
+
+ public ChainedReference(Sink downstream) {
+ this.downstream = downstream;
+ }
+ }
+}
+
+@SuppressWarnings({"unchecked", "rawtypes"})
+public class ReferenceChain {
+
+ /**
+ * sink chain
+ */
+ private final List>> sinkBuilders = new ArrayList();
+
+ /**
+ * current sink
+ */
+ private final AtomicReference sinkReference = new AtomicReference();
+
+ public ReferenceChain filter(Predicate predicate) {
+ //filter
+ sinkBuilders.add(() -> {
+ Sink prevSink = (Sink) sinkReference.get();
+ Sink.ChainedReference currentSink = new Sink.ChainedReference(prevSink) {
+
+ @Override
+ public void accept(OUT out) {
+ if (predicate.test(out)) {
+ downstream.accept(out);
+ }
+ }
+ };
+ sinkReference.set(currentSink);
+ return currentSink;
+ });
+ return this;
+ }
+
+ public ReferenceChain map(Function function) {
+ // map
+ sinkBuilders.add(() -> {
+ Sink prevSink = (Sink) sinkReference.get();
+ Sink.ChainedReference currentSink = new Sink.ChainedReference(prevSink) {
+
+ @Override
+ public void accept(OUT in) {
+ downstream.accept(function.apply(in));
+ }
+ };
+ sinkReference.set(currentSink);
+ return currentSink;
+ });
+ return this;
+ }
+
+ public void forEachPrint(Collection collection) {
+ forEachPrint(collection, false);
+ }
+
+ public void forEachPrint(Collection collection, boolean reverse) {
+ Spliterator spliterator = collection.spliterator();
+ // 这个是类似于terminal op
+ Sink sink = System.out::println;
+ sinkReference.set(sink);
+ Sink stage = sink;
+ // 反向包装 -> 正向遍历
+ if (reverse) {
+ for (int i = 0; i <= sinkBuilders.size() - 1; i++) { + Supplier> supplier = sinkBuilders.get(i);
+ stage = (Sink) supplier.get();
+ }
+ } else {
+ // 正向包装 -> 反向遍历
+ for (int i = sinkBuilders.size() - 1; i>= 0; i--) {
+ Supplier> supplier = sinkBuilders.get(i);
+ stage = (Sink) supplier.get();
+ }
+ }
+ Sink finalStage = stage;
+ spliterator.forEachRemaining(finalStage);
+ }
+
+ public static void main(String[] args) {
+ List list = new ArrayList();
+ list.add(1);
+ list.add(2);
+ list.add(3);
+ list.add(12);
+ ReferenceChain chain = new ReferenceChain();
+ // filter -> map -> for each
+ chain.filter(item -> item> 10)
+ .map(item -> item * 2)
+ .forEachPrint(list);
+ }
+}
+
+// 输出结果
+24
+```
+
+执行的流程如下:
+
+[](https://throwable-blog-1256189093.cos.ap-guangzhou.myqcloud.com/202110/stream-source-9.png)
+
+多层包装器的编程模式的核心要领就是:
+
+- 绝大部分操作可以转换为`java.util.function.Consumer`的实现,也就是实现`accept(T t)`方法完成对传入的元素进行处理
+- 先处理的`Sink`总是以后处理的`Sink`为入参,在自身处理方法中判断和回调传入的`Sink`的处理方法回调,也就是构建引用链的时候,需要从后往前构建,这种方式的实现逻辑可以参考`AbstractPipeline#wrapSink()`,例如:
+
+```java
+// 目标顺序:filter -> map
+Sink mapSink = new Sink(inputSink){
+
+ private Function mapper;
+
+ public void accept(E ele) {
+ inputSink.accept(mapper.apply(ele))
+ }
+
+}
+Sink filterSink = new Sink(mapSink){
+
+ private Predicate predicate;
+
+ public void accept(E ele) {
+ if(predicate.test(ele)){
+ mapSink.accept(ele);
+ }
+ }
+}
+```
+
+- 由上一点得知,一般来说,最后的终结操作会应用在引用链的第一个`Sink`上
+
+上面的代码并非笔者虚构出来,可见`java.util.stream.Sink`的源码:
+
+```java
+// 继承自Consumer,主要是继承函数式接口方法void accept(T t)
+interface Sink extends Consumer {
+
+ // 重置当前Sink的状态(为了接收一个新的数据集),传入的size是推送到downstream的准确数据量,无法评估数据量则传入-1
+ default void begin(long size) {}
+
+ //
+ default void end() {}
+
+ // 返回true的时候表示当前的Sink不会接收数据
+ default boolean cancellationRequested() {
+ return false;
+ }
+
+ // 特化方法,接受一个int类型的值
+ default void accept(int value) {
+ throw new IllegalStateException("called wrong accept method");
+ }
+
+ // 特化方法,接受一个long类型的值
+ default void accept(long value) {
+ throw new IllegalStateException("called wrong accept method");
+ }
+
+ // 特化方法,接受一个double类型的值
+ default void accept(double value) {
+ throw new IllegalStateException("called wrong accept method");
+ }
+
+ // 引用类型链,准确来说是Sink链
+ abstract static class ChainedReference implements Sink {
+
+ // 下一个Sink
+ protected final Sink downstream;
+
+ public ChainedReference(Sink downstream) {
+ this.downstream = Objects.requireNonNull(downstream);
+ }
+
+ @Override
+ public void begin(long size) {
+ downstream.begin(size);
+ }
+
+ @Override
+ public void end() {
+ downstream.end();
+ }
+
+ @Override
+ public boolean cancellationRequested() {
+ return downstream.cancellationRequested();
+ }
+ }
+ // 暂时忽略Int、Long、Double的特化类型场景
+}
+```
+
+如果用过`RxJava`或者`Project-Reactor`,`Sink`更像是`Subscriber`,多个`Subscriber`组成了`ChainedReference`(`Sink Chain`,可以理解为一个复合的`Subscriber`),而`Terminal Op`则类似于`Publisher`,只有在`Subscriber`订阅`Publisher`的时候才会进行数据的处理,这里是应用了`Reactive`编程模式。
+
+### AbstractPipeline和ReferencePipeline的实现
+
+`AbstractPipeline`和`ReferencePipeline`都是抽象类,`AbstractPipeline`用于构建`Pipeline`的数据结构,提供一些`Shape`相关的抽象方法给`ReferencePipeline`实现,而`ReferencePipeline`就是`Stream`中`Pipeline`的基础类型,从源码上看,`Stream`链式(管道式)结构的头节点和操作节点都是`ReferencePipeline`的子类。先看`AbstractPipeline`的成员变量和构造函数:
+
+```java
+abstract class AbstractPipeline>
+ extends PipelineHelper implements BaseStream {
+
+ // 流管道链式结构的头节点(只有当前的AbstractPipeline引用是头节点,此变量才会被赋值,非头节点为NULL)
+ @SuppressWarnings("rawtypes")
+ private final AbstractPipeline sourceStage;
+
+ // 流管道链式结构的upstream,也就是上一个节点,如果是头节点此引用为NULL
+ @SuppressWarnings("rawtypes")
+ private final AbstractPipeline previousStage;
+
+ // 合并数据源的标志和操作标志的掩码
+ protected final int sourceOrOpFlags;
+
+ // 流管道链式结构的下一个节点,如果是头节点此引用为NULL
+ @SuppressWarnings("rawtypes")
+ private AbstractPipeline nextStage;
+
+ // 流的深度
+ // 串行执行的流中,表示当前流管道实例中中间操作节点的个数(除去头节点和终结操作)
+ // 并发执行的流中,表示当前流管道实例中中间操作节点和前一个有状态操作节点之间的节点个数
+ private int depth;
+
+ // 合并了所有数据源的标志、操作标志和当前的节点(AbstractPipeline)实例的标志,也就是当前的节点可以基于此属性得知所有支持的标志
+ private int combinedFlags;
+
+ // 数据源的Spliterator实例
+ private Spliterator sourceSpliterator;
+
+ // 数据源的Spliterator实例封装的Supplier实例
+ private Supplier> sourceSupplier;
+
+ // 标记当前的流节点是否被连接或者消费掉,不能重复连接或者重复消费
+ private boolean linkedOrConsumed;
+
+ // 标记当前的流管道链式结构中是否存在有状态的操作节点,这个属性只会在头节点中有效
+ private boolean sourceAnyStateful;
+
+ // 数据源关闭动作,这个属性只会在头节点中有效,由sourceStage持有
+ private Runnable sourceCloseAction;
+
+ // 标记当前流是否并发执行
+ private boolean parallel;
+
+ // 流管道结构头节点的父构造方法,使用数据源的Spliterator实例封装的Supplier实例
+ AbstractPipeline(Supplier> source,
+ int sourceFlags, boolean parallel) {
+ // 头节点的前驱节点置为NULL
+ this.previousStage = null;
+ this.sourceSupplier = source;
+ this.sourceStage = this;
+ // 合并传入的源标志和流标志的掩码
+ this.sourceOrOpFlags = sourceFlags & StreamOpFlag.STREAM_MASK;
+ // The following is an optimization of:
+ // StreamOpFlag.combineOpFlags(sourceOrOpFlags, StreamOpFlag.INITIAL_OPS_VALUE);
+ // 初始化合并标志集合为sourceOrOpFlags和所有流操作标志的初始化值
+ this.combinedFlags = (~(sourceOrOpFlags << 1)) & StreamOpFlag.INITIAL_OPS_VALUE; + // 深度设置为0 + this.depth = 0; + this.parallel = parallel; + } + + // 流管道结构头节点的父构造方法,使用数据源的Spliterator实例 + AbstractPipeline(Spliterator source,
+ int sourceFlags, boolean parallel) {
+ // 头节点的前驱节点置为NULL
+ this.previousStage = null;
+ this.sourceSpliterator = source;
+ this.sourceStage = this;
+ // 合并传入的源标志和流标志的掩码
+ this.sourceOrOpFlags = sourceFlags & StreamOpFlag.STREAM_MASK;
+ // The following is an optimization of:
+ // StreamOpFlag.combineOpFlags(sourceOrOpFlags, StreamOpFlag.INITIAL_OPS_VALUE);
+ // 初始化合并标志集合为sourceOrOpFlags和所有流操作标志的初始化值
+ this.combinedFlags = (~(sourceOrOpFlags << 1)) & StreamOpFlag.INITIAL_OPS_VALUE; + this.depth = 0; + this.parallel = parallel; + } + + // 流管道结构中间操作节点的父构造方法 + AbstractPipeline(AbstractPipeline previousStage, int opFlags) {
+ if (previousStage.linkedOrConsumed)
+ throw new IllegalStateException(MSG_STREAM_LINKED);
+ previousStage.linkedOrConsumed = true;
+ // 设置前驱节点的后继节点引用为当前的AbstractPipeline实例
+ previousStage.nextStage = this;
+ // 设置前驱节点引用为传入的前驱节点实例
+ this.previousStage = previousStage;
+ // 合并传入的中间操作标志和流操作标志的掩码
+ this.sourceOrOpFlags = opFlags & StreamOpFlag.OP_MASK;
+ // 合并标志集合为传入的标志和前驱节点的标志集合
+ this.combinedFlags = StreamOpFlag.combineOpFlags(opFlags, previousStage.combinedFlags);
+ // 赋值sourceStage为前驱节点的sourceStage
+ this.sourceStage = previousStage.sourceStage;
+ if (opIsStateful())
+ // 标记当前的流存在有状态操作
+ sourceStage.sourceAnyStateful = true;
+ // 深度设置为前驱节点深度加1
+ this.depth = previousStage.depth + 1;
+ }
+
+ // 省略其他方法
+}
+```
+
+至此,可以看出流管道的数据结构:
+
+[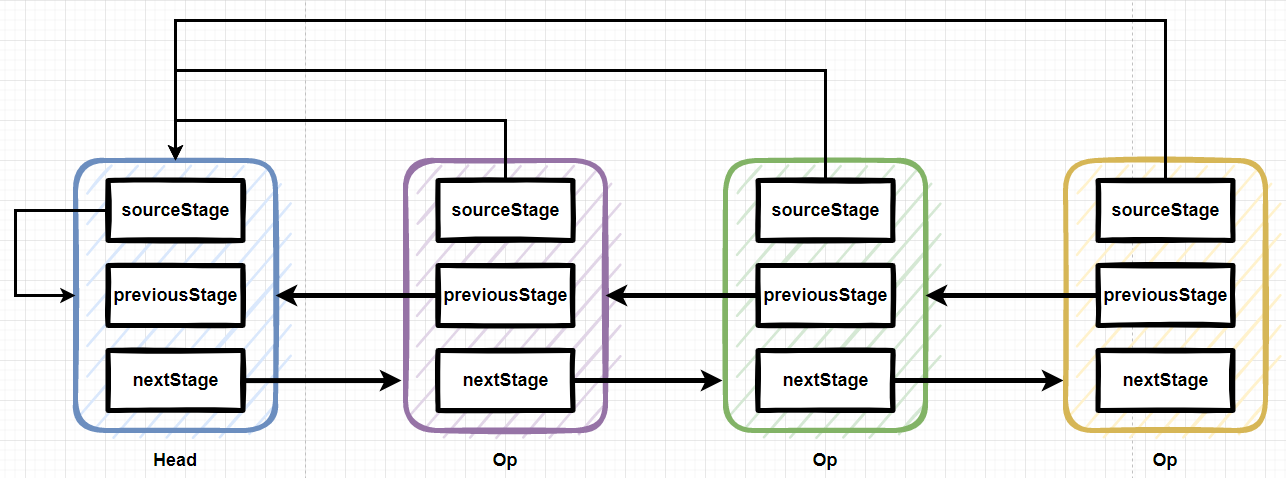](https://throwable-blog-1256189093.cos.ap-guangzhou.myqcloud.com/202110/stream-source-10.png)
+
+`Terminal Op`不参与管道链式结构的构建。接着看`AbstractPipeline`中的终结求值方法(`Terminal evaluation methods`):
+
+```java
+abstract class AbstractPipeline>
+ extends PipelineHelper implements BaseStream {
+
+ // 省略其他方法
+
+ // 基于终结操作进行求值,这个是Stream执行的常用核心方法,常用于collect()这类终结操作
+ final R evaluate(TerminalOp terminalOp) {
+ assert getOutputShape() == terminalOp.inputShape();
+ // 判断linkedOrConsumed,以防多次终结求值,也就是每个终结操作只能执行一次
+ if (linkedOrConsumed)
+ throw new IllegalStateException(MSG_STREAM_LINKED);
+ linkedOrConsumed = true;
+
+ // 如果当前流支持并发执行,则委托到TerminalOp.evaluateParallel(),如果当前流只支持同步执行,则委托到TerminalOp.evaluateSequential()
+ // 这里注意传入到TerminalOp中的方法参数分别是this(PipelineHelper类型)和数据源Spliterator
+ return isParallel()
+ ? terminalOp.evaluateParallel(this, sourceSpliterator(terminalOp.getOpFlags()))
+ : terminalOp.evaluateSequential(this, sourceSpliterator(terminalOp.getOpFlags()));
+ }
+
+ // 基于当前的流实例转换为最终的Node实例,传入的IntFunction用于创建数组实例
+ // 此终结方法一般用于toArray()这类终结操作
+ @SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
+ final Node evaluateToArrayNode(IntFunction generator) {
+ if (linkedOrConsumed)
+ throw new IllegalStateException(MSG_STREAM_LINKED);
+ linkedOrConsumed = true;
+
+ // If the last intermediate operation is stateful then
+ // evaluate directly to avoid an extra collection step
+ // 当前流支持并发执行,并且最后一个中间操作是有状态,则委托到opEvaluateParallel(),否则委托到evaluate(),这两个都是AbstractPipeline中的方法
+ if (isParallel() && previousStage != null && opIsStateful()) {
+ // Set the depth of this, last, pipeline stage to zero to slice the
+ // pipeline such that this operation will not be included in the
+ // upstream slice and upstream operations will not be included
+ // in this slice
+ depth = 0;
+ return opEvaluateParallel(previousStage, previousStage.sourceSpliterator(0), generator);
+ }
+ else {
+ return evaluate(sourceSpliterator(0), true, generator);
+ }
+ }
+
+ // 这个方法比较简单,就是获取当前流的数据源所在的Spliterator,并且确保流已经消费,一般用于forEach()这类终结操作
+ final Spliterator sourceStageSpliterator() {
+ if (this != sourceStage)
+ throw new IllegalStateException();
+
+ if (linkedOrConsumed)
+ throw new IllegalStateException(MSG_STREAM_LINKED);
+ linkedOrConsumed = true;
+
+ if (sourceStage.sourceSpliterator != null) {
+ @SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
+ Spliterator s = sourceStage.sourceSpliterator;
+ sourceStage.sourceSpliterator = null;
+ return s;
+ }
+ else if (sourceStage.sourceSupplier != null) {
+ @SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
+ Spliterator s = (Spliterator) sourceStage.sourceSupplier.get();
+ sourceStage.sourceSupplier = null;
+ return s;
+ }
+ else {
+ throw new IllegalStateException(MSG_CONSUMED);
+ }
+ }
+ // 省略其他方法
+}
+```
+
+`AbstractPipeline`中实现了`BaseStream`的方法:
+
+```java
+abstract class AbstractPipeline>
+ extends PipelineHelper implements BaseStream {
+
+ // 省略其他方法
+
+ // 设置头节点的parallel属性为false,返回自身实例,表示当前的流是同步执行的
+ @Override
+ @SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
+ public final S sequential() {
+ sourceStage.parallel = false;
+ return (S) this;
+ }
+
+ // 设置头节点的parallel属性为true,返回自身实例,表示当前的流是并发执行的
+ @Override
+ @SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
+ public final S parallel() {
+ sourceStage.parallel = true;
+ return (S) this;
+ }
+
+ // 流关闭操作,设置linkedOrConsumed为true,数据源的Spliterator相关引用置为NULL,置空并且回调sourceCloseAction钩子实例
+ @Override
+ public void close() {
+ linkedOrConsumed = true;
+ sourceSupplier = null;
+ sourceSpliterator = null;
+ if (sourceStage.sourceCloseAction != null) {
+ Runnable closeAction = sourceStage.sourceCloseAction;
+ sourceStage.sourceCloseAction = null;
+ closeAction.run();
+ }
+ }
+
+ // 返回一个添加了close处理器的Stream实例,close处理器会在下面的close方法中回调
+ // 如果本来持有的引用sourceStage.sourceCloseAction非空,会使用传入的closeHandler与sourceStage.sourceCloseAction进行合并
+ @Override
+ @SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
+ public S onClose(Runnable closeHandler) {
+ if (linkedOrConsumed)
+ throw new IllegalStateException(MSG_STREAM_LINKED);
+ Objects.requireNonNull(closeHandler);
+ Runnable existingHandler = sourceStage.sourceCloseAction;
+ sourceStage.sourceCloseAction =
+ (existingHandler == null)
+ ? closeHandler
+ : Streams.composeWithExceptions(existingHandler, closeHandler);
+ return (S) this;
+ }
+
+ // Primitive specialization use co-variant overrides, hence is not final
+ // 返回当前流实例中所有元素的Spliterator实例
+ @Override
+ @SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
+ public Spliterator spliterator() {
+ if (linkedOrConsumed)
+ throw new IllegalStateException(MSG_STREAM_LINKED);
+ // 标记当前节点被链接或者消费
+ linkedOrConsumed = true;
+ // 如果当前节点为头节点,那么返回sourceStage.sourceSpliterator或者延时加载的sourceStage.sourceSupplier(延时加载封装由lazySpliterator实现)
+ if (this == sourceStage) {
+ if (sourceStage.sourceSpliterator != null) {
+ @SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
+ Spliterator s = (Spliterator) sourceStage.sourceSpliterator;
+ sourceStage.sourceSpliterator = null;
+ return s;
+ }
+ else if (sourceStage.sourceSupplier != null) {
+ @SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
+ Supplier> s = (Supplier>) sourceStage.sourceSupplier;
+ sourceStage.sourceSupplier = null;
+ return lazySpliterator(s);
+ }
+ else {
+ throw new IllegalStateException(MSG_CONSUMED);
+ }
+ }
+ else {
+ // 如果当前节点不是头节点,重新对sourceSpliterator进行包装,包装后的实例为WrappingSpliterator
+ return wrap(this, () -> sourceSpliterator(0), isParallel());
+ }
+ }
+
+ // 当前流实例是否并发执行,从头节点的parallel属性进行判断
+ @Override
+ public final boolean isParallel() {
+ return sourceStage.parallel;
+ }
+
+ // 从当前combinedFlags中获取数据源标志和所有流中间操作标志的集合
+ final int getStreamFlags() {
+ return StreamOpFlag.toStreamFlags(combinedFlags);
+ }
+
+ /**
+ * Get the source spliterator for this pipeline stage. For a sequential or
+ * stateless parallel pipeline, this is the source spliterator. For a
+ * stateful parallel pipeline, this is a spliterator describing the results
+ * of all computations up to and including the most recent stateful
+ * operation.
+ */
+ @SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
+ private Spliterator sourceSpliterator(int terminalFlags) {
+ // 从sourceStage.sourceSpliterator或者sourceStage.sourceSupplier中获取当前流实例中的Spliterator实例,确保必定存在,否则抛出IllegalStateException
+ Spliterator spliterator = null;
+ if (sourceStage.sourceSpliterator != null) {
+ spliterator = sourceStage.sourceSpliterator;
+ sourceStage.sourceSpliterator = null;
+ }
+ else if (sourceStage.sourceSupplier != null) {
+ spliterator = (Spliterator) sourceStage.sourceSupplier.get();
+ sourceStage.sourceSupplier = null;
+ }
+ else {
+ throw new IllegalStateException(MSG_CONSUMED);
+ }
+
+ // 下面这段逻辑是对于并发执行并且存在有状态操作的节点,那么需要重新计算节点的深度和节点的合并标志集合
+ // 这里只提一下计算过程,从头节点的后继节点开始遍历到当前节点,如果被遍历的节点时有状态的,那么对depth、combinedFlags和spliterator会进行重新计算
+ // depth一旦出现有状态节点就会重置为0,然后从1重新开始增加
+ // combinedFlags会重新合并sourceOrOpFlags、SHORT_CIRCUIT(如果sourceOrOpFlags支持)和Spliterator.SIZED
+ // spliterator简单来看就是从并发执行的toArray()=>Array数组=>Spliterator实例
+ if (isParallel() && sourceStage.sourceAnyStateful) {
+ // Adapt the source spliterator, evaluating each stateful op
+ // in the pipeline up to and including this pipeline stage.
+ // The depth and flags of each pipeline stage are adjusted accordingly.
+ int depth = 1;
+ for (@SuppressWarnings("rawtypes") AbstractPipeline u = sourceStage, p = sourceStage.nextStage, e = this;
+ u != e;
+ u = p, p = p.nextStage) {
+
+ int thisOpFlags = p.sourceOrOpFlags;
+ if (p.opIsStateful()) {
+ depth = 0;
+
+ if (StreamOpFlag.SHORT_CIRCUIT.isKnown(thisOpFlags)) {
+ // Clear the short circuit flag for next pipeline stage
+ // This stage encapsulates short-circuiting, the next
+ // stage may not have any short-circuit operations, and
+ // if so spliterator.forEachRemaining should be used
+ // for traversal
+ thisOpFlags = thisOpFlags & ~StreamOpFlag.IS_SHORT_CIRCUIT;
+ }
+
+ spliterator = p.opEvaluateParallelLazy(u, spliterator);
+
+ // Inject or clear SIZED on the source pipeline stage
+ // based on the stage's spliterator
+ thisOpFlags = spliterator.hasCharacteristics(Spliterator.SIZED)
+ ? (thisOpFlags & ~StreamOpFlag.NOT_SIZED) | StreamOpFlag.IS_SIZED
+ : (thisOpFlags & ~StreamOpFlag.IS_SIZED) | StreamOpFlag.NOT_SIZED;
+ }
+ p.depth = depth++;
+ p.combinedFlags = StreamOpFlag.combineOpFlags(thisOpFlags, u.combinedFlags);
+ }
+ }
+ // 如果传入的terminalFlags标志不为0,则当前节点的combinedFlags会合并terminalFlags
+ if (terminalFlags != 0) {
+ // Apply flags from the terminal operation to last pipeline stage
+ combinedFlags = StreamOpFlag.combineOpFlags(terminalFlags, combinedFlags);
+ }
+
+ return spliterator;
+ }
+
+ // 省略其他方法
+}
+```
+
+`AbstractPipeline`中实现了`PipelineHelper`的方法:
+
+```java
+abstract class AbstractPipeline>
+ extends PipelineHelper implements BaseStream {
+
+ // 省略其他方法
+
+ // 获取数据源元素的类型,这里的类型包括引用、int、double和float
+ // 其实实现上就是获取depth<=0的第一个节点的输出类型 + @Override + final StreamShape getSourceShape() { + @SuppressWarnings("rawtypes") + AbstractPipeline p = AbstractPipeline.this; + while (p.depth> 0) {
+ p = p.previousStage;
+ }
+ return p.getOutputShape();
+ }
+
+ // 基于当前节点的标志集合判断和返回流中待处理的元素数量,无法获取则返回-1
+ @Override
+ final long exactOutputSizeIfKnown(Spliterator spliterator) {
+ return StreamOpFlag.SIZED.isKnown(getStreamAndOpFlags()) ? spliterator.getExactSizeIfKnown() : -1;
+ }
+
+ // 通过流管道链式结构构建元素引用链,再遍历元素引用链
+ @Override
+ final > S wrapAndCopyInto(S sink, Spliterator spliterator) {
+ copyInto(wrapSink(Objects.requireNonNull(sink)), spliterator);
+ return sink;
+ }
+
+ // 遍历元素引用链
+ @Override
+ final void copyInto(Sink wrappedSink, Spliterator spliterator) {
+ Objects.requireNonNull(wrappedSink);
+ // 当前节点不支持SHORT_CIRCUIT(短路)特性,则直接遍历元素引用链,不支持短路跳出
+ if (!StreamOpFlag.SHORT_CIRCUIT.isKnown(getStreamAndOpFlags())) {
+ wrappedSink.begin(spliterator.getExactSizeIfKnown());
+ spliterator.forEachRemaining(wrappedSink);
+ wrappedSink.end();
+ }
+ else {
+ // 支持短路(中途取消)遍历元素引用链
+ copyIntoWithCancel(wrappedSink, spliterator);
+ }
+ }
+
+ // 支持短路(中途取消)遍历元素引用链
+ @Override
+ @SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
+ final boolean copyIntoWithCancel(Sink wrappedSink, Spliterator spliterator) {
+ @SuppressWarnings({"rawtypes","unchecked"})
+ AbstractPipeline p = AbstractPipeline.this;
+ // 基于当前节点,获取流管道链式结构中第最后一个depth=0的前驱节点
+ while (p.depth> 0) {
+ p = p.previousStage;
+ }
+ wrappedSink.begin(spliterator.getExactSizeIfKnown());
+ // 委托到forEachWithCancel()进行遍历
+ boolean cancelled = p.forEachWithCancel(spliterator, wrappedSink);
+ wrappedSink.end();
+ return cancelled;
+ }
+
+ // 返回当前节点的标志集合
+ @Override
+ final int getStreamAndOpFlags() {
+ return combinedFlags;
+ }
+
+ // 当前节点标志集合中是否支持ORDERED
+ final boolean isOrdered() {
+ return StreamOpFlag.ORDERED.isKnown(combinedFlags);
+ }
+
+ // 构建元素引用链,生成一个多重包装的Sink(WrapSink),这里的逻辑可以看前面的分析章节
+ @Override
+ @SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
+ final Sink wrapSink(Sink sink) {
+ Objects.requireNonNull(sink);
+ // 这里遍历的时候,总是从当前节点向前驱节点遍历,也就是传入的sink实例总是包裹在最里面一层执行
+ for ( @SuppressWarnings("rawtypes") AbstractPipeline p=AbstractPipeline.this; p.depth> 0; p=p.previousStage) {
+ sink = p.opWrapSink(p.previousStage.combinedFlags, sink);
+ }
+ return (Sink) sink;
+ }
+
+ // 包装数据源的Spliterator,如果depth=0,则直接返回sourceSpliterator,否则返回的是延迟加载的WrappingSpliterator
+ @Override
+ @SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
+ final Spliterator wrapSpliterator(Spliterator sourceSpliterator) {
+ if (depth == 0) {
+ return (Spliterator) sourceSpliterator;
+ }
+ else {
+ return wrap(this, () -> sourceSpliterator, isParallel());
+ }
+ }
+
+ // 计算Node实例,这个方法用于toArray()方法系列,是一个终结操作,下面会另开章节详细分析
+ @Override
+ @SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
+ final Node evaluate(Spliterator spliterator,
+ boolean flatten,
+ IntFunction generator) {
+ if (isParallel()) {
+ // @@@ Optimize if op of this pipeline stage is a stateful op
+ return evaluateToNode(this, spliterator, flatten, generator);
+ }
+ else {
+ Node.Builder nb = makeNodeBuilder(
+ exactOutputSizeIfKnown(spliterator), generator);
+ return wrapAndCopyInto(nb, spliterator).build();
+ }
+ }
+
+ // 省略其他方法
+}
+```
+
+`AbstractPipeline`中剩余的待如`XXYYZZPipeline`等子类实现的抽象方法:
+
+```java
+abstract class AbstractPipeline>
+ extends PipelineHelper implements BaseStream {
+
+ // 省略其他方法
+
+ // 获取当前流的输出"形状",REFERENCE、INT_VALUE、LONG_VALUE或者DOUBLE_VALUE
+ abstract StreamShape getOutputShape();
+
+ // 收集当前流的所有输出元素,转化为一个适配当前流输出"形状"的Node实例
+ abstract Node evaluateToNode(PipelineHelper helper,
+ Spliterator spliterator,
+ boolean flattenTree,
+ IntFunction generator);
+
+ // 包装Spliterator为WrappingSpliterator实例
+ abstract Spliterator wrap(PipelineHelper ph,
+ Supplier> supplier,
+ boolean isParallel);
+
+ // 包装Spliterator为DelegatingSpliterator实例
+ abstract Spliterator wrap(PipelineHelper ph,
+ Supplier> supplier,
+ boolean isParallel);
+ // 基于Sink遍历Spliterator中的元素,支持取消操作,简单理解就是支持cancel的tryAdvance方法
+ abstract boolean forEachWithCancel(Spliterator spliterator, Sink sink);
+
+ // 返回Node的建造器实例,用于toArray方法系列
+ abstract Node.Builder makeNodeBuilder(long exactSizeIfKnown,
+ IntFunction generator);
+
+ // 判断当前的操作(节点)是否有状态,如果是有状态的操作,必须覆盖opEvaluateParallel方法
+ abstract boolean opIsStateful();
+
+ // 当前操作生成的结果会作为传入的Sink实例的入参,这是一个包装Sink的过程,通俗理解就是之前提到的元素引用链添加一个新的链节点,这个方法算是流执行的一个核心方法
+ abstract Sink opWrapSink(int flags, Sink sink);
+
+ // 并发执行的操作节点求值
+ Node opEvaluateParallel(PipelineHelper helper,
+ Spliterator spliterator,
+ IntFunction generator) {
+ throw new UnsupportedOperationException("Parallel evaluation is not supported");
+ }
+
+ // 并发执行的操作节点惰性求值
+ @SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
+ Spliterator opEvaluateParallelLazy(PipelineHelper helper,
+ Spliterator spliterator) {
+ return opEvaluateParallel(helper, spliterator, i -> (E_OUT[]) new Object[i]).spliterator();
+ }
+
+ // 省略其他方法
+}
+```
+
+这里提到的抽象方法`opWrapSink()`其实就是元素引用链的添加链节点的方法,它的实现逻辑见子类,这里只考虑非特化子类`ReferencePipeline`的部分源码:
+
+```java
+abstract class ReferencePipeline
+ extends AbstractPipeline>
+ implements Stream {
+
+ // 构造函数,用于头节点,传入基于Supplier封装的Spliterator实例作为数据源,数据源的标志集合和是否支持并发执行的判断标记
+ ReferencePipeline(Supplier> source,
+ int sourceFlags, boolean parallel) {
+ super(source, sourceFlags, parallel);
+ }
+
+ // 构造函数,用于头节点,传入Spliterator实例作为数据源,数据源的标志集合和是否支持并发执行的判断标记
+ ReferencePipeline(Spliterator source,
+ int sourceFlags, boolean parallel) {
+ super(source, sourceFlags, parallel);
+ }
+
+ // 构造函数,用于中间节点,传入上一个流管道节点的实例(前驱节点)和当前操作节点支持的标志集合
+ ReferencePipeline(AbstractPipeline upstream, int opFlags) {
+ super(upstream, opFlags);
+ }
+
+ // 这里流的输出"形状"固定为REFERENCE
+ @Override
+ final StreamShape getOutputShape() {
+ return StreamShape.REFERENCE;
+ }
+
+ // 转换当前流实例为Node实例,应用于toArray方法,后面详细分析终结操作的时候再展开
+ @Override
+ final Node evaluateToNode(PipelineHelper